
There's an unsavoury reason for the weird patterns on train and bus seats
Whether it's on a bus or a train, you've probably noticed how the seats have a distinctly bold and garish pattern - but why is this the case? Well, it's not for aesthetic design reasons but rather it's down to the fact that the patterns are able to effectively cover up stains. Just think about how many people get on public transportation for their daily commute to work, the millions of people who will plonk themselves on those seats throughout the year as well as those using the nighttime service. There are bound to be drinks and food spilt on the seat, and so in response to this inevitability it's better to have busy patterns rather than plain ones - otherwise we would perhaps think twice about sitting. But nowadays, the various patterns on different modes of public transportation are seen as iconic designs for that particular area of the world. For example, last year Premier League football team Arsenal released shirts with a design inspired by the bold pattern which appears on Piccadilly line trains. Meanwhile, there are a number of factors to think about when designing the seat pattern such as how it looks in both daylight and artificial light. @plutosdestiny Bus seats are made of a special fabric with unusual patterns because it helps them mask stains, wear and tear and look fresh without the need for much maintenance. The weird, mind-bending patterns are designed to make the seats appear clean and unworn, even though they conceal a lot of dirt within those wild patterns. [Credit - KubulMKM - YT] The fabric is also an integral consideration, the material used for the seats is moquette and it is different to the sofa you sit on at home. “Coming from the French word for carpet, moquette has been seen and sat upon by millions of commuters on buses, trains, trams and trolleybuses for over 100 years,” the London Transport Museum explained. “It is produced on looms using the Jacquard weaving technique, with a pile usually made up of 85% wool mixed with 15% nylon.” But what makes it the ideal material for this purpose? “Moquette was chosen for public transport for two reasons," it continued. "First, because it is hard-wearing and durable. Second, because its colour and patterns disguise signs of dirt, wear and tear. On top of this moquette had the advantage of being easy and cheap to mass-produce.” Something to contemplate next time you're sitting on the bus or tube. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-10 18:24

Deutsche Bank Seeks Expert Help in Probing Nature-Linked Risks, Investments
Deutsche Bank AG said it set up a panel to help it assess nature-related risks and identify new
2023-10-10 17:24

Daimler Truck premieres new eActros 600 in step towards all-electric shift
BERLIN Mercedes-Benz Trucks, the European division of commercial vehicle maker Daimler Truck, premiered its battery-electric long-haul truck eActros
2023-10-10 16:29

Chinese EV startup WM Motor files for bankruptcy
BEIJING (Reuters) -Chinese electric vehicle startup WM Motor has filed for bankruptcy, marking the demise of a promising standout among
2023-10-10 14:22

DWS Executive Warns of ‘Nightmare’ Result as ESG Rules Revamped
As Europe embarks on a wholesale review of the world’s biggest ESG investing rulebook, an executive at Deutsche
2023-10-10 13:27
South Korean firms get indefinite waiver on US chip gear supplies to China
Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will be allowed to supply US chip equipment to their China factories indefinitely without separate US approvals, South Korea's presidential office and the companies said on Monday.
2023-10-10 11:50
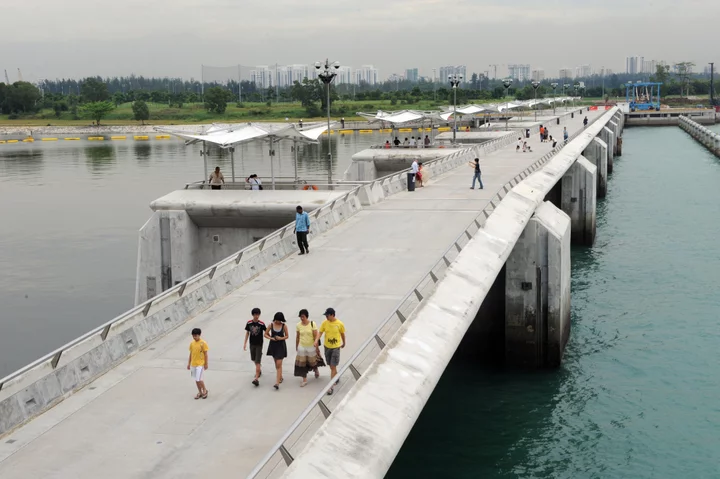

Singapore Is Fighting Rising Seas to Save $50 Billion in Real Estate
(Bloomberg Markets) -- During a half-century of independence, Singapore has fought to expand its territory, inch by hard-won inch. On
2023-10-10 08:56

Unity Says Goodbye To Company CEO After Backlash Over Game Install Fees
Unity is parting ways with the company’s controversial CEO following weeks of backlash from the
2023-10-10 08:50

Xbox Game Pass Might Get Call of Duty, Diablo IV Next Year
Microsoft’s imminent acquisition of Activision Blizzard means the newest Call of Duty and Diablo games
2023-10-10 05:46

One Bond Market Is Defying the Global Selloff With Record Returns
As bond markets everywhere get battered by a cocktail of higher interest rates, deficit angst and hawkish central
2023-10-10 03:59
23andMe says hacker appears to have stolen people’s genetic information
A hacker has stolen the personal genetic information of 23andMe users, the company has said. 23andMe allows people to send in a sample of their DNA and have it tested, with the results sent into them. Customers can find out what their genetic information might tell them about their health, for instance, as well as their relatives and where they might have lived. But some of that same information was accessed by hackers and appears to have been made available online, the company said. It made the statement after the hackers appeared to be attempting to sell the information online. 23andMe did not say whether some or all of that data – which included the names of celebrities – was actually legitimate. But it did say that information had been “compiled from individual 23andMe.com accounts without the account users’ authorization”. Its investigation was still continuing, the company said, and it is unclear the scale of the problem. The data appears to have been taken by a hacker who used recycled login credentials from other websites that had since been hacked, the company said. That is a common technique for breaking into profiles, and cyber security experts suggest using different passwords on different websites and changing them regularly to avoid it. Once the hackers were able to get into those accounts, they used a feature on 23andMe that allowed them to gather yet more information. 23andMe offers a tool called “DNA Relatives”, which lets users connect with people with similar genetic information to help assemble their family tree – meaning that hackers were able to gather information about other people whose accounts had not actually been compromised. The company said that it had no indication that its own systems had been attacked, or that it was the source of the credentials used. But it advised people to change their password and set up multi-factor authentication to ensure that their accounts were secure. Read More Earth hit by a huge solar storm that would devastate civilisation, trees show Keir Starmer deepfake shows alarming AI fears are already here New discovery is ‘holy grail’ breakthrough in search for aliens, scientist say
2023-10-10 01:48

Earth was hit by largest ever solar storm that would devastate civilisation today, tree rings show
Earth was once hit by an extreme solar storm that would devastate human civilisation if it happened today, tree rings show. Scientists were able to piece together the solar storm from ancient tree rings that were found in the French alps, and showed evidence of a dramatic spike in radiocarbon levels some 14,300 years ago. That spike was the result of a massive solar storm, the biggest ever found by scientists. If a similar event happened today, it could knock the power grid offline for months and destroy the infrastructure we rely on for communications, scientists have warned. The researchers behind the new study have urged that the extreme nature of the newly discovered event should be a warning for the future. “Extreme solar storms could have huge impacts on Earth. Such super storms could permanently damage the transformers in our electricity grids, resulting in huge and widespread blackouts lasting months,” said Tim Heaton, professor of applied statistics in the School of Mathematics at the University of Leeds. “They could also result in permanent damage to the satellites that we all rely on for navigation and telecommunication, leaving them unusable. They would also create severe radiation risks to astronauts.” Further work is needed to ensure that the world is protected from similar events happening again, scientists said. And more research is required to actually understand how and why they might happen. Scientists have found nine extreme solar storms, or Miayake Events, that happened in the last 15,000 years. The most recent of them happened in the years 993 AD and 774 AD, but the newly found one was twice as powerful as those. Researchers do not know exactly what happened during those Miyake Events, and studying them is difficult because they can only be understood indirectly. That makes it difficult for scientists to know how and when they might happen again, or if it is even possible to predict them. “Direct instrumental measurements of solar activity only began in the 17th century with the counting of sunspots,” said Edouard Bard, professor of climate and ocean evolution at the Collège de France and CEREGE. “Nowadays, we also obtain detailed records using ground-based observatories, space probes, and satellites. “However, all these short-term instrumental records are insufficient for a complete understanding of the Sun. Radiocarbon measured in tree-rings, used alongside beryllium in polar ice cores, provide the best way to understand the Sun’s behaviour further back into the past.”  The largest solar storm that scientists were able to actually observe and study happened in 1859, and is known as the Carrington Event. It caused vast disruption to society, destroying telegraph machines and creating a bright aurora so bright that birds behaved as if the Sun was rising. The Miayake Events like the newly found storm would have been vastly more powerful, however. They were discovered by slicing ancient trees that are becoming fossils into tiny rings, and then analysing the radiocarbon that was present in them. Their work is published in a new article, ‘A radiocarbon spike at 14,300 cal yr BP in subfossil trees provides the impulse response function of the global carbon cycle during the Late Glacial’, in the journal The Royal Society’s Philosophical Transactions A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences.
2023-10-10 01:16
