
BAE Systems unveils NavGuide™ GPS receiver
SAN DIEGO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 13, 2023--
2023-06-14 01:55

Benin media guide
An overview of the media in Benin, including links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-07-24 20:25
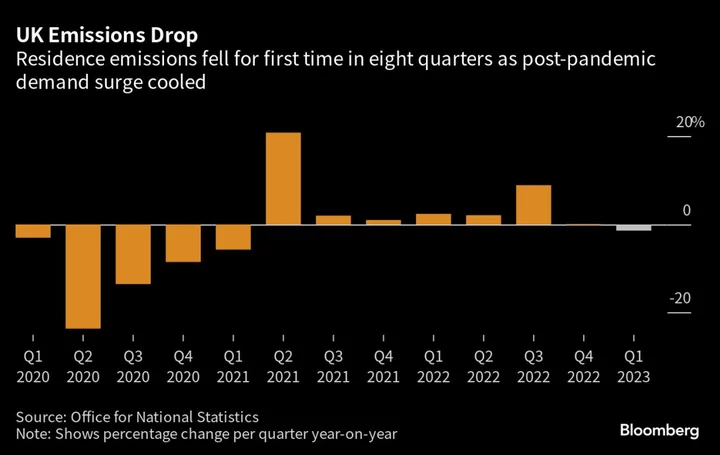
UK CO2 Emissions Drop For The First Time in Two Years, ONS Says
UK greenhouse gas emissions dropped in the first quarter for the first time in two years, as the
2023-07-25 18:47

Leapsome Unveils New Startup Program to Empower Early-Stage Businesses with Intelligent People Enablement Tools
NEW YORK & BERLIN--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 20, 2023--
2023-07-20 20:15
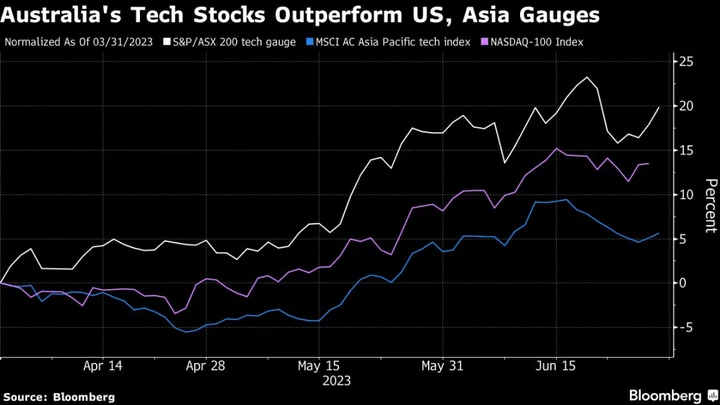
Australia Tech Firms Outperform Peers in Best Quarter Since 2020
A gauge of Australia’s technology shares has advanced 20% so far in the second quarter, outperforming peers in
2023-06-30 05:18

Sonic the Hedgehog’s US Workers Vote to Join Union
The US home of Sonic the Hedgehog is now a union shop. Workers at Sega of America say
2023-07-11 04:48

Google sets its Pixel 8 announcement event for Oct. 4
Google Pixel fans, mark your calendars and start setting aside cash now. On Wednesday, Google
2023-08-31 04:19
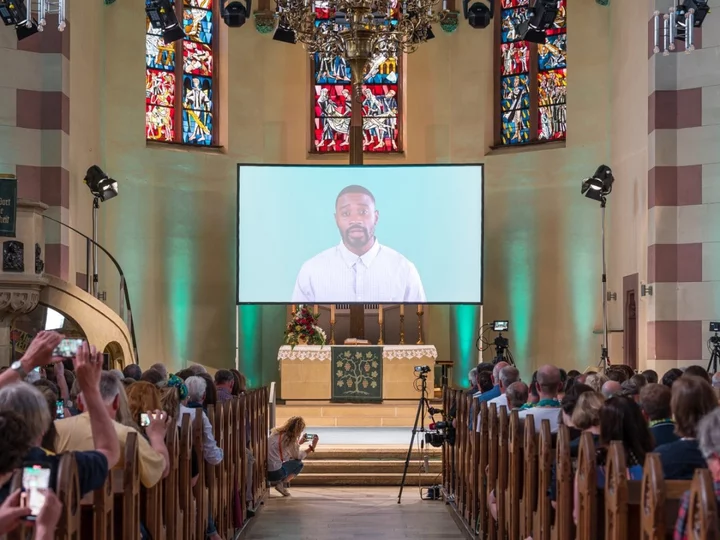

Hundreds attend ‘soulless’ AI-generated church service
Hundreds of people have attended an AI-generated church service in Germany, involving virtual avatars delivering sermons written by ChatGPT. The 40-minute service at Saint Paul’s church in Fürth received mixed reactions from the Protestant congregation, the Associated Press reported, with the avatars occasionally causing unintentional laughter. Some church members even refused to speak along when the digital avatar read out the Lord’s Prayer. “There was no heart and no soul,” said Heiderose Schmidt, a 54-year-old IT worker who attended the service. “The avatars showed no emotions at all, had no body language and were talking so fast and monotonously that it was very hard for me to concentrate on what they said. But maybe it is different for the younger generation who grew up with all of this.” Lutheran pastor Marc Jansen was more impressed by the artificial intelligence, saying he had “imagined it to be worse” than it was. “I was positively surprised how well it worked,” he said. “Also, the language of the AI worked well, even though it was still a bit bumpy at times.” The AI began the service by stating: “Dear friends, it is an honour for me to stand here and preach to you as the first artificial intelligence at this year’s convention of Protestants in Germany.” It went on to talk about leaving the past behind and never losing trust in Jesus, while also urging the congregation to overcome their fear of death. More than 300 people attended the service, which was organised by 29-year-old theologian Jonas Simmerlein from the University of Vienna. Mr Simmerlein instructed ChatGPT to include psalms, prayers and a blessing, saying the experiment was designed to show how religious leaders could use AI to help them with their work. “Artificial intelligence will increasingly take over our lives, in all its facets. And that’s why it’s useful to learn to deal with it,” he said, adding that AI will not be able to replace the role pastors serve in interacting with the local community. “The pastor is in the congregation, she lives with them, she buries the people, she knows them from the beginning. Artificial intelligence cannot do that. It does not know the congregation.” Read More What is superintelligence? How AI could wipe out humanity – and why the boss of ChatGPT is doomsday prepping 10 ways AI will change the world – from curing cancer to wiping out humanity Major Google Bard update allows it to not just write code, but execute it Instagram is working on an AI chatbot with multiple personalities The glaring omission from Apple’s AR headset launch
2023-06-13 20:58
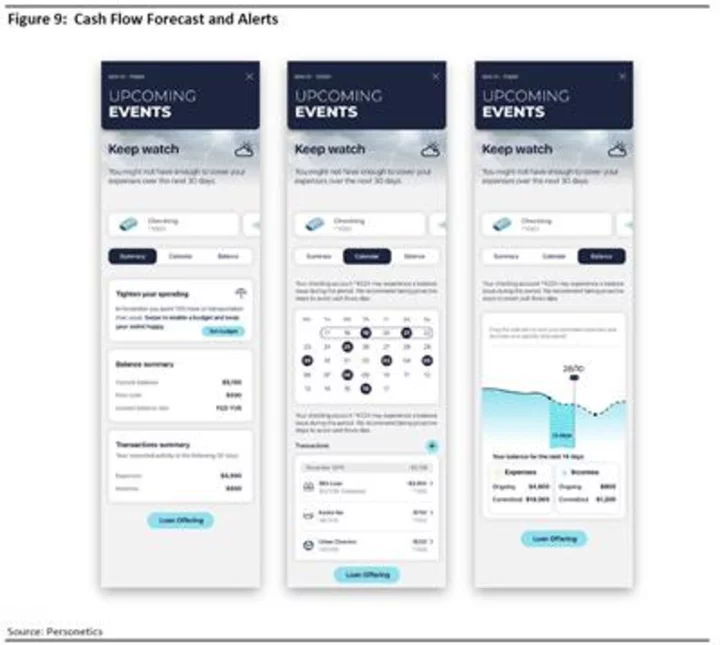
Celent Report Finds Personetics Is the Top Banking Solution for Small Business Banking in North America
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 24, 2023--
2023-05-24 19:22

How to unblock Jerkmate for free
TL;DR: ExpressVPN is a high-speed service that can reliably unblock porn sites like Pornhub, XVideos,
2023-07-29 12:27
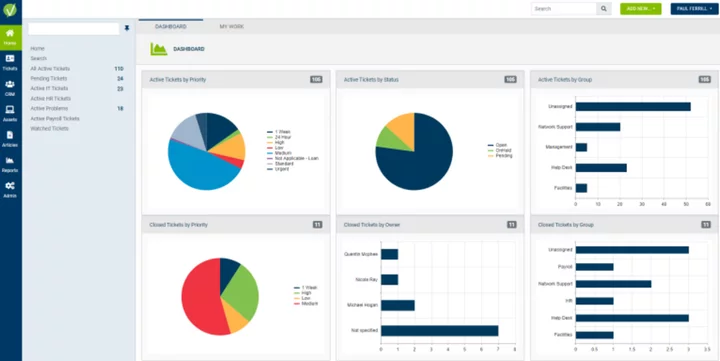
The Best Help Desk Software for 2023
Help desk software automates the process of managing, tracking, and resolving customer issues, making it
2023-09-15 01:57
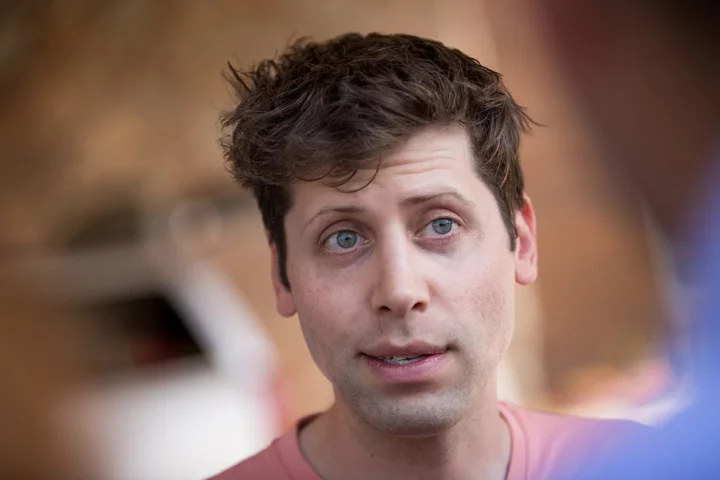

AI’s Threat to Humanity? Altman’s OpenAI Exit Still Unexplained.
Sam Altman looks set to return triumphantly to OpenAI but questions still linger around why he was fired from the artificial-intelligence start-up in the first place.
2023-11-23 23:26
You Might Like...
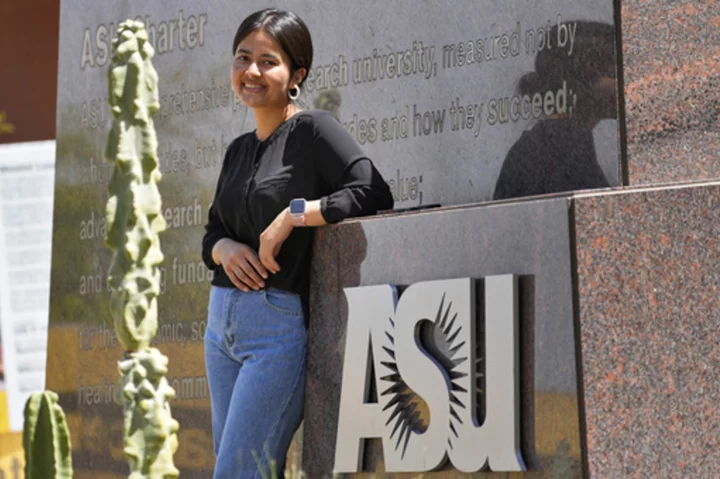

Scholarships have helped displaced Afghan students find homes on university campuses across the US

Most of Florida work group behind controversial new guidelines on African American history did not agree, report says

ForSight Robotics Expands Leadership Team with Appointment of CFO

Verizon executive kicks off week two of US v Google antitrust trial
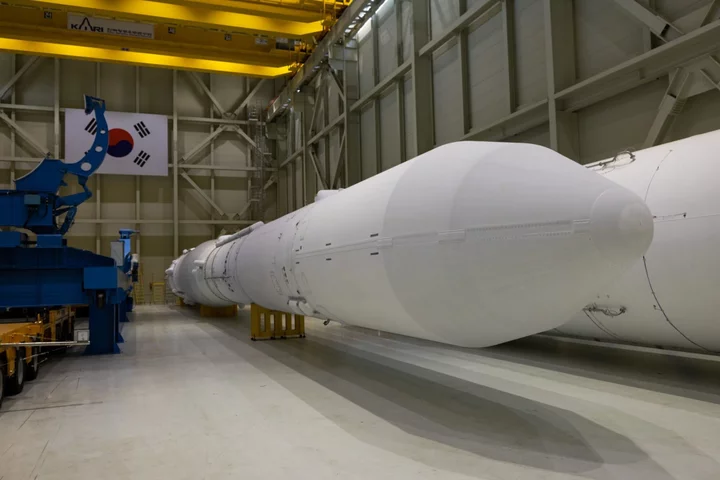

Korea Space Race Heats Up as North and South Plan Launches

Kenya says TikTok agrees content moderation deal

Comcast Introduces NOW TV: A $20 Entertainment Option With 60+ Streaming and Fast Channels, Plus Peacock Premium

A scientist has discovered when Earth's first continent was formed
