
Legislation needed to protect data from AI ‘ghostbots’, say researchers
Lack of data protection laws in the UK could see an increasing problem of AI “ghostbots” made from people’s digital footprints, new research from Queen’s University Belfast has suggested. “Ghostbot” is a term used to describe what happens when artificial intelligence is used to create digital reincarnations of the dead. The technology used to create this includes chatbots, deepfakes or holographs that can replicate the voice, face and even personality of a dead person using data from social media. 'Ghostbots' lie at the intersection of many different areas of law, such as privacy and property, and yet there remains a lack of protection for the deceased’s personality, privacy, or dignity after death Dr Marisa McVey, Queen’s University Belfast As the concept of digital reincarnation moves into the mainstream, celebrities are beginning to showcase the capabilities of such technology, for example, a hologram of the late Robert Kardashian created using deepfake technology was gifted to Kim Kardashian by Kanye West in 2020, which used her father’s likeness and spoke in his voice. A research study titled Governing Ghostbots from Queen’s University Belfast, Aston Law School and Newcastle University Law School, has suggested that greater societal awareness of “ghostbots” and a “do not bot me” clause in wills and other contracts could prevent people from being digitally reincarnated without permission. The research looked at potential legal avenues to protect privacy (including post-mortem privacy), property, personal data, and reputation. Dr Marisa McVey from the School of Law at Queen’s University Belfast said there was a lack of protection for people’s privacy or dignity after death. Currently, in the absence of specific legislation in the UK and further afield, it’s unclear who might have the power to bring back our digital persona after we die Dr Marisa McVey, Queen’s University Belfast “’Ghostbots’ lie at the intersection of many different areas of law, such as privacy and property, and yet there remains a lack of protection for the deceased’s personality, privacy, or dignity after death,” she said. “Furthermore, in the UK, privacy and data protection laws do not extend to heirs after death,” she said. “While it is not thought that ‘ghostbots’ could cause physical harm, the likelihood is that they could cause emotional distress and economic harm, particularly impacting upon the deceased’s loved ones and heirs. “Currently, in the absence of specific legislation in the UK and further afield, it’s unclear who might have the power to bring back our digital persona after we die.” In the US and EU there is increasing momentum to legislate on who has ownership over a person’s digital identity, for example the EU AI Act which requires greater transparency for deepfakes and chatbots. In the absence of legislation in the UK, one way to protect our post-mortem selves might be through the drafting of a legally binding ‘do not bot me’ clause that could be inserted into wills and other contracts while people are still alive Dr Marisa McVey, Queen’s University Belfast Dr McVey has suggested that in addition to more formal legislation, an increased understanding of the phenomenon of “ghostbots” could help people to protect their data. “In the absence of legislation in the UK, one way to protect our post-mortem selves might be through the drafting of a legally binding ‘do not bot me’ clause that could be inserted into wills and other contracts while people are still alive,” she said. “This, combined with a global searchable database of such requests, may prove a useful solution to some of the concerns raised by ‘ghostbots’. “We also suggest that in addition to legal protections, greater societal awareness of the phenomenon of ‘ghostbots’, education on digital legacies and cohesive protection across different jurisdictions is crucial to ensure that this does not happen without our permission.” The research was a part of the Leverhulme Trust-funded project Modern Technologies, Privacy Law And The Dead. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Banking app feature allows economic abuse survivors to mute malicious messages Augmented reality headset Vision Pro is ‘most advanced device ever’ – Apple Revealed: The delivery apps charging you double for your food shop
2023-06-07 00:23
SEC sues Coinbase for allegedly acting as an unregistered crypto broker
The US Securities and Exchange Commission, Wall Street's top regulator, sued Coinbase, America's largest crypto exchange, on Tuesday. The SEC is cracking down on some of the biggest names in cryptocurrency over alleged security violations.
2023-06-07 00:21
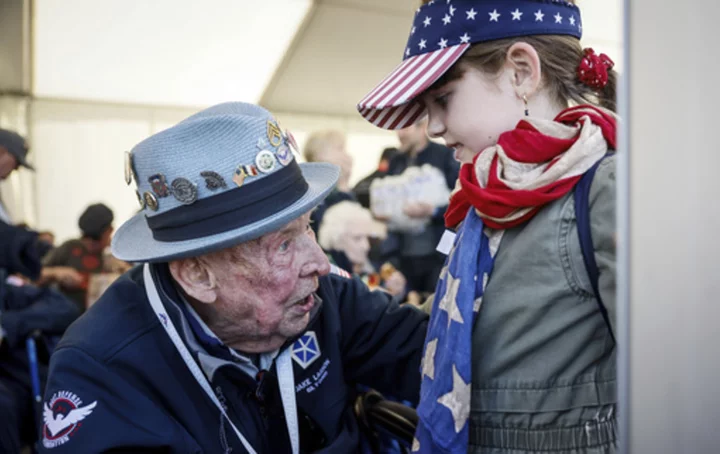

Papa Jake survived D-Day on Omaha Beach, now he's a TikTok star
World War II veteran Jake Larson survived D-Day on Omaha Beach
2023-06-06 23:59

UKG Transforms Multi-country Payroll with Agreement to Acquire Immedis from CluneTech
LOWELL, Mass. & WESTON, Fla.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 23:58
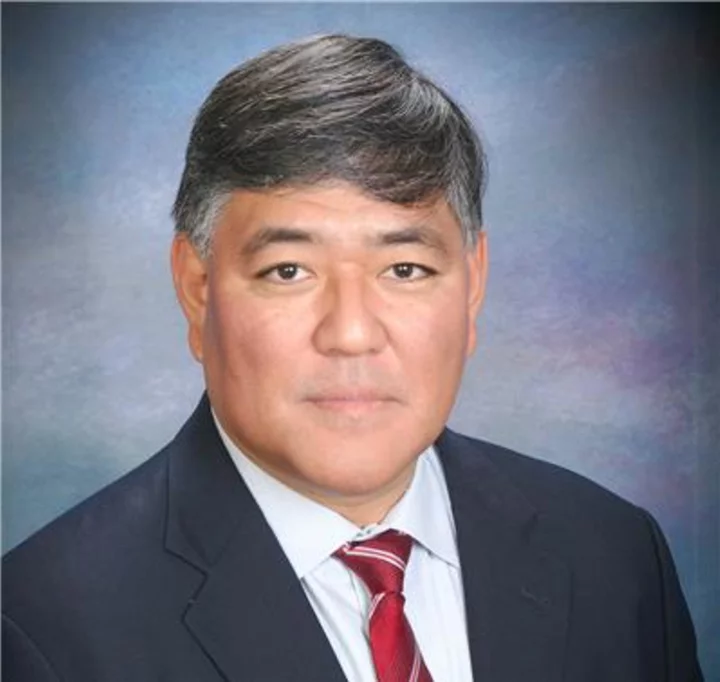

Dr.Evidence® Appoints Ken Kobayashi, MD, FACP to its Medical Strategy Advisory Board
SANTA MONICA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 23:57
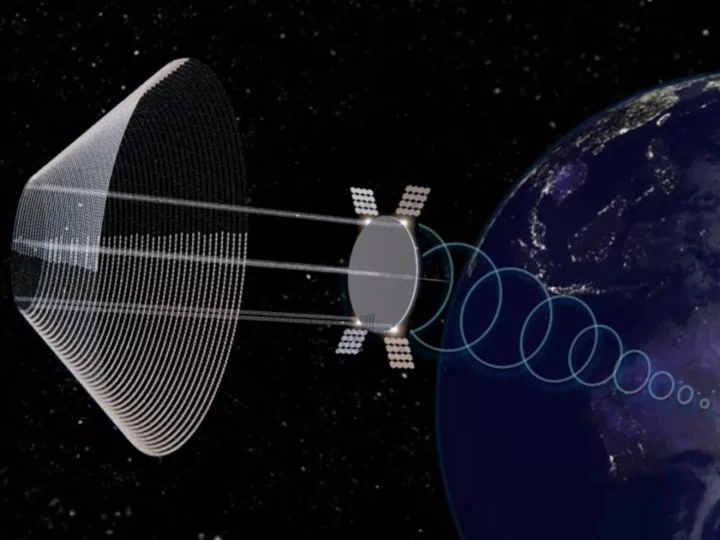
Solar panel breakthrough paves way for ‘utility-scale’ space farms
Scientists have discovered how to double the efficiency of an ultra-lightweight solar cell, which they claim could be used to harvest the Sun’s energy in space at a never-before-seen scale. The next-generation solar panels, built by a team from the University of Pennsylvania, use layers that are over a thousand times thinner than a human hair, yet capable of absorbing a comparable amount of sunlight to commercially available solar cells. The extreme thinness earned them the label two-dimensional, or 2D TMDC, as they are only a few atoms thick. The ability to produce more electricity per weight compared to traditional silicon solar cells makes them highly suitable for sending into space to harvest the Sun’s energy, according to the researchers. “High specific power is actually one of the greatest goals of any space-based light harvesting or energy harvesting technology,” said Deep Jariwala from the University of Pennsylvania. “This is not just important for satellites or space stations, but also if you want real utility-scale solar power in space. The number of [silicon] solar cells you would have to ship up is so large that no space vehicles currently can take those kinds of materials up there in an economically viable way.” By modelling the innovative solar cell computationally, Professor Jariwala and his team were able to come up with a design that has double the efficiency compared to what had previously been demonstrated. A paper detailing the research, titled ‘How good can 2D excitonic solar cells be?’, was published in the scientific journal Device on Tuesday. The researchers now hope to figure out how to achieve large-scale production for the design. “I think people are slowly coming to the realisation that 2D TMDCs are excellent photovoltaic materials, though not for terrestrial applications, but for applications that are mobile, more flexible, like space-based applications,” said Professor Jariwala. “The weight of 2D TMDC solar cells is 100 times less than silicon or gallium arsenide solar cells, so suddenly these cells become a very appealing technology.” The concept of space-based solar arrays was first theorised more than 50 years ago, with scientists noting that the Sun’s energy could be converted into microwaves and beamed down to ground-based receiving stations that convert them into electricity. It has several advantages over terrestrial setups, as they would not be limited by cloud cover or the Sun’s typical cycle. Research has accelerated in recent years following several major breakthroughs and developments with solar energy harvesting and orbital rocket launches, including the emergence of private space companies like SpaceX that have significantly reduced the cost of delivering payloads into space. Last month, Japanese space agency JAXA announced that it was aiming to set up the first satellite transmitters for a commercial-scale solar farm in space by 2025. The European Space Agency is also planning to establish a development program for this untapped renewable energy resource through its Solaris programme. Read More Japan aims to beam solar power from space by 2025 Electric car drives for 100 hours non-stop on futuristic road Scientists smash world record for solar power window material Apple don’t want you to buy a headset - they’re selling a vision of the future Apple lets people get brand new iPhone update early – but there’s a very big warning
2023-06-06 23:50

Diablo® IV Launches, Immediately Sets New Record as Blizzard Entertainment’s Fastest-Selling Game of All Time
IRVINE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 23:28
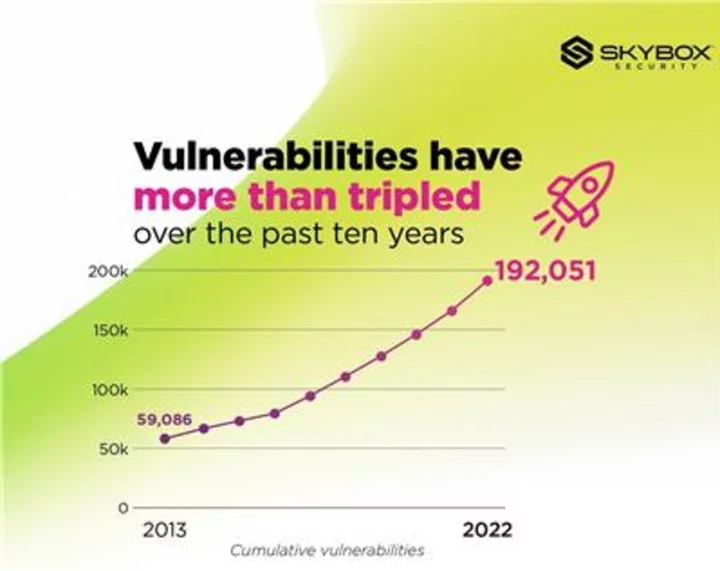
Skybox Security Report Unveils 25% Surge in New Vulnerabilities, Posing a Significant Challenge to Organizations
SAN JOSE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 23:27

OpenAI CEO suggests international agency like UN's nuclear watchdog could oversee AI
A key innovator is warning that artificial intelligence poses an “existential risk” to humanity
2023-06-06 23:26

NordVPN Partners With Mamenta to Streamline Global Digital Downloads
DENVER--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 22:58
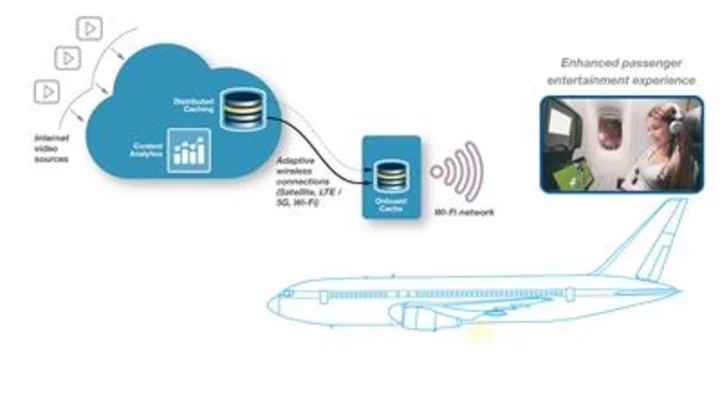
Thales and Netskrt Systems Working Together to Enhance the Passenger On-Demand Video Streaming Experience
VANCOUVER, British Columbia--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 22:24

New Ohmium Appointment Delivers on Sustainability and Safety Strategic Priorities
FREMONT, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 22:20
You Might Like...

Lunaphore to Get Acquired by Bio-Techne

Clari to Acquire Groove, Cementing Revenue Platform Leadership
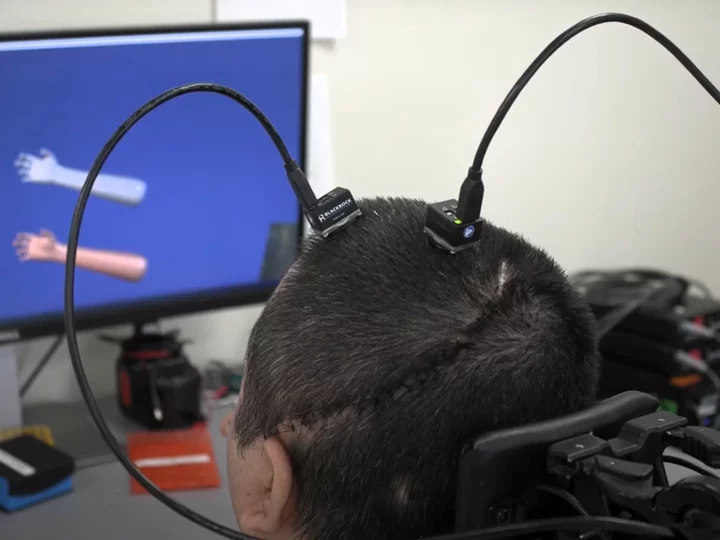

Paralysed man regains feeling and movement with AI brain implant
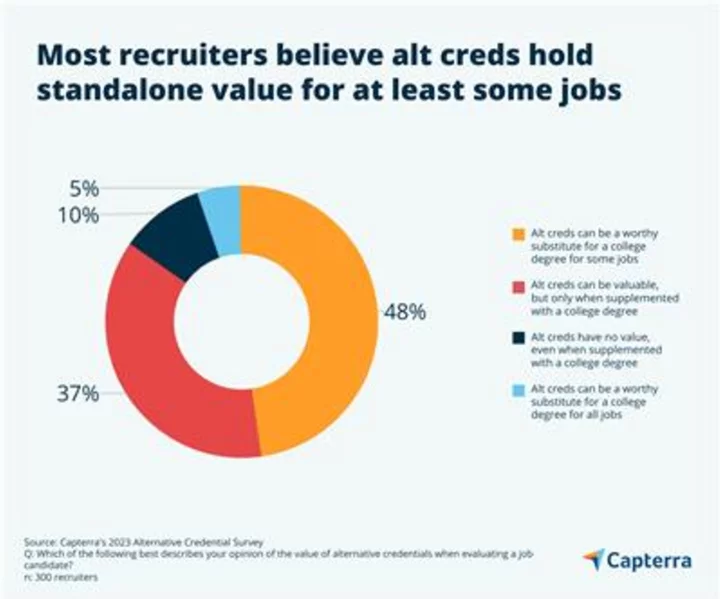
Recruiters Say Alternative Credentials Can Land You a Job, But Validating Them is a Challenge

Cleo Names Sameer Katiyar Chief Financial Officer

Terrifying video shows how long leaders have to act after a nuclear weapons launch

Microsoft ‘Bears Responsibility’ For China-Tied Hacks, Senator Says

When and where to watch Tesla’s highly anticipated Cybertruck delivery event
