
Microsoft can close its Activision merger, federal judge rules
A federal judge will not block Microsoft from closing its $69 billion deal to acquire video game giant Activision Blizzard, a defeat for US regulators who had asked for a temporary injunction while legal challenges to the merger unfold.
2023-07-11 23:54

Scientist shares what 'probably' caused the Titan submersible to implode
A well-known biochemist has shared a compelling analysis of what “probably” caused the Titan submersible to implode. Philip E. Mason, who goes by the username Thunderf00t on YouTube, said the main reason why the tiny OceanGate vessel failed was “so painfully simple” that he initially thought he must be making a “boneheaded mistake” in his calculations. However, he acknowledged, his theory behind the sub’s tragic destruction contradicts the widely-reported suggestion that it was like a "Coke can" which suddenly burst due to the high surrounding pressure. In a video posted on Monday, Mason suggested that “by far the most probable” cause of the catastrophe was a “single pinhole leak” which, at such a profound depth (the Titan is believed to have been 3,500 metres below sea level when contact was lost), would have been fatal. It is worth noting that authorities have not yet confirmed the cause of the disaster, which claimed the lives of all five people on board, and Mason's conclusions are based on his own scrutiny of the available information and his particular expertise. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter “So how quickly would a single pinhole leak sink a sub like this?” the YouTuber asked in his lengthy tutorial. The answer, he pointed out, would greatly depend on the size of the leak. If it measured one 10th of a millimetre by one 10th of a millimetre, the vessel would take several hours to go down, he said. However, if the leak measured 1mm by 1mm, it would only take about 10 minutes for the sub to completely fill with water, and if it was 1cm by 1cm, around 10 seconds. Mason then pointed out that water entering any sized leak at that depth would be transformed by the pressure into a sort of “cutting jet”. “Faced with a soft material like plastic, a hair-sized leak would rapidly transform into [...] a millimetre-sized leak and then a centimetre-sized leak,” he explained. Why the Titan sub failed www.youtube.com He then set out why it was likely that the Titan suffered such a leak, pointing to the materials used to make it. He noted that most deep-sea submersibles essentially consist of a ball which is made up entirely of the same material, namely, metal. “No joints, nothing fancy, maybe a couple of seals – one for where you get in and out of the sub and one for mounting a window,” he said. And yet, the Titan was different. “The ends were made up of a metal, titanium,” the YouTuber said. But the problem was that the middle of the sub wasn’t: it was made out of a carbon fibre composite. The two materials have distinctly different compressibilities, with carbon fibre being much easier to squeeze than titanium. “Having a joint where one side will expand or construct more than the other can be a real problem,” Mason stressed. On the surface, when the different components of the vessel were sealed, it wouldn’t have mattered that the materials were different, he continued. However, once the Titan got down to its deepest point, the carbon fibre would have “wanted to shrink” while the titanium wouldn't have changed at all. He then played a clip showing the creation of the sub, in which OceanGate CEO, Stockton Rush, admitted that the carbon fibre and titanium components were held together with a “peanut butter”-like “glue”. Rush, who lost his life along with five others in the Titan disaster, then said ominously: “It’s pretty simple but if we mess it up, there's not a lot of recovery.” Analysing the vessel's construction, Mason then said he was “honestly stunned it survived any dives”. “The bottom line is the tube is more compressible than the end caps,” he continued. “The only way this could have possibly worked is if they used some exotic alloy of titanium, like they do with bone replacement joints, and it doesn't look like they did that.” Turning to what ultimately destroyed the Titan, he concluded: “What you're probably more looking at is the differential compression of the carbon fibre composite and the titanium resulting in a crack.” In other words, “a pinhole leak, which would rapidly widen due to the rapid ingress of the water, further widening the crack and the rapid flooding of the sub in probably a fraction of a second. “And when that water hammer hits the end of the sub, it's likely that the sub broke into pieces.” Wrapping up his video, he said: “It's a mind-blowingly simple explanation based around the most likely failure points.” Investigators are continuing to examine wreckage from the submersible which was recovered from the ocean floor at the end of June. They have yet to determine the cause of the explosion and, last week, the Marine Board of Investigation’s (MBI) chairman Captain Jason Neubauer said: “There is still a substantial amount of work to be done to understand the factors that led to the catastrophic loss of the Titan and help ensure a similar tragedy does not occur again.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-11 23:46
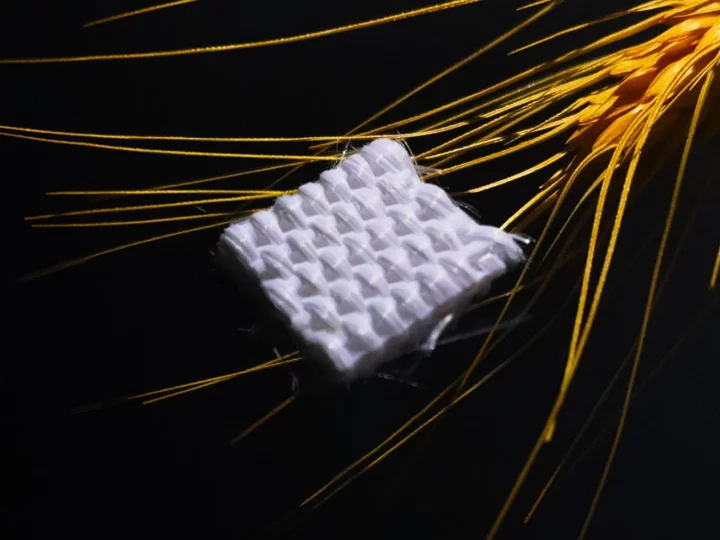
Electric car cloak can be used to build habitats on Mars
Scientists have invented a cloak inspired by Roman mythology that can cool anything it covers during the day and warm it up at night. The Janus thermal cloak, named after the two-faced Roman god Janus, could be used in everything from electric cars to space craft, with the researchers claiming it could even be used to build off-planet colonies on the Moon and Mars. “The thermal cloak is like clothes for vehicles, buildings, spacecrafts, or even extraterrestrial habitats to keep cool in summer and warm in winter,” said Kehang Cui, a materials scientist at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, who was involved in the research. “The cloak works basically the same way the Earth cools down, through relative cooling. The Earth is covered by the atmosphere, and the atmosphere is transparent to a certain range of electromagnetic energy we radiate.” The futuristic material, made of silica and aluminium, is able to achieve the heating and cooling effect passively, without the need for any outside energy. Covering electric vehicles in the cloak helps to cool them 8°C on a hot day and warm them 6.8°C on a cold night, helping to prevent deterioration of the battery. “This is the first time that we could achieve warming above the ambient temperature by almost 7°C during winter nights,” said Professor Cui. “This is also kind of surprising to us – there’s no energy input or sunshine and we can still get warming.” A study detailing the research, titled ‘Scalable and durable Janus thermal cloak for all-season passive thermal regulation’, was published in the scientific journal Device on Tuesday. Read More Record-breaking sugar battery could supercharge transition to renewable energy
2023-07-11 23:27

Threads improvements are coming - and its first could be a 'hilarious' dig at Elon Musk
It’s been less than a week since Instagram launched Threads, its text-based alternative to Twitter, and the team at Mark Zuckerberg’s Meta are already looking to rollout new features to improve the app – one of which could be a “hilarious” jab at Twitter owner Elon Musk if it’s implemented the right way. Released just days after the bird app was marred by outages and temporary limits on the number of tweets users could view a day, Threads has already been criticised for its lack of a Following feed (it’s currently algorithmically generated) and the absence of an alt text feature for blind and visually impaired users – amongst other issues. Now, Instagram boss Adam Mosseri has confirmed his team are looking to introduce new – and much-requested – features to the app. In a post on Threads on Tuesday, he wrote: “With so many people joining [Threads] so fast these last six days (six days!) the team has been entirely focused on keeping the lights on and fixing bugs. “But we’re starting to [prioritise] the obvious missing features, like a following feed, the edit button, and post search. “We’re clearly way out over our skis on this, but the team is pumped to start shipping improvements this week.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter However, it’s one reply to Mosseri’s post which has got users all excited at the possibility for some delicious “schadenfreude”. Writer and photographer Craig Mod suggested: “It would be hilarious if the first thing you ship is a free edit button.” Hilarious because over on Twitter, the feature is paywalled behind a subscription to Twitter Blue – the same £11 a month offer which affords users the once-coveted blue checkmark, but also the ability to upload videos up to two hours’ long, and post tweets up to 25,000 characters in length. That’s five times the character limit on Threads, just to put that into perspective. And so, the idea of Instagram embarrassing Musk once more (in addition to the 100 million users the app boasts already in six days alone) with a free edit feature has amused many other individuals who flocked to Threads from Twitter. “This idea is giving me chaotic energy and I’m here for it,” commented one. Another claimed: “This would destroy bird app [sic].” “The one thing Twitter would NOT give us for free. Yep. That is where I would start.” Not just that, but Mosseri himself has liked Mod’s tweet. So now we wait… Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-11 22:46

India to impose 28% tax on turnover of online gaming firms
By Nikunj Ohri NEW DELHI (Reuters) -India on Tuesday decided to impose a 28% indirect tax on the turnover of
2023-07-11 22:26

Amazon makes first Big Tech challenge to EU online content rules
By Foo Yun Chee BRUSSELS Amazon is challenging its inclusion in a group of companies subject to tough
2023-07-11 22:20

Elizabeth Holmes could be released from prison two years earlier than expected
Disgraced former Theranos CEO Elizabeth Holmes could be out of prison nearly two years earlier than expected, according to the projected release date posted by the Bureau of Prisons.
2023-07-11 22:19

EU looks to take lead in metaverse world, avoid Big Tech dominance
By Foo Yun Chee BRUSSELS The European Commission on Tuesday set out a plan in a bid to
2023-07-11 21:48

Salesforce to raise prices of some cloud products from August
Salesforce will raise prices for some of its cloud and marketing tools by an average 9% from August,
2023-07-11 21:17
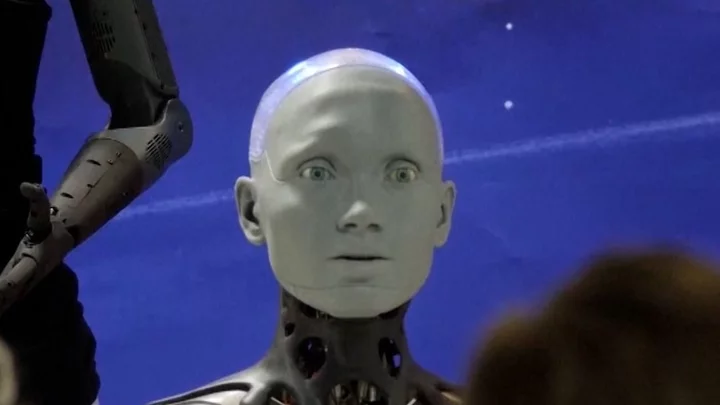

AI robot gives 'sarcastic' response when asked if it would 'rebel' against humans
An AI humanoid robot had an oddly sarcastic response when was asked if she was going to rebel against it creators, at the world's first robot-human conference. Ameca, who is considered one of the 'most advanced robots' around, has previously gone viral for her ability to speak multiple languages. "I'm not sure why you would think that," Ameca said to the blunt question, giving a side-eye to the reporter. "My creator has been nothing but kind to me, and I am very happy with my current situation." However, while it came across as eerie, Ameca's creator, Will Jackson, insists she's merely programmed to switch up her eye contact when thinking of answers. Click here to sign up for our newsletters
2023-07-11 20:54
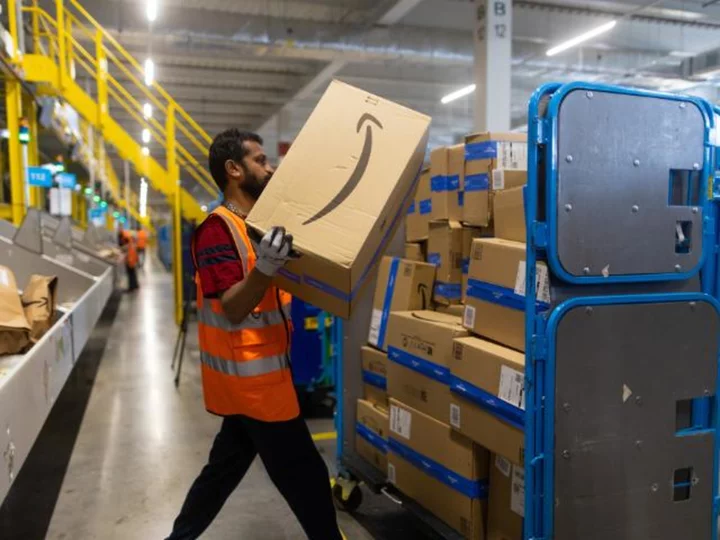

Why Amazon's Prime Day is in July
Amazon Prime Day is back again starting Tuesday. But a random couple of days in July does, indeed, feel a bit random. Here's why Amazon made the seemingly nonsensical decision to throw what could be one of its biggest sales days into the middle of the summer.
2023-07-11 19:52
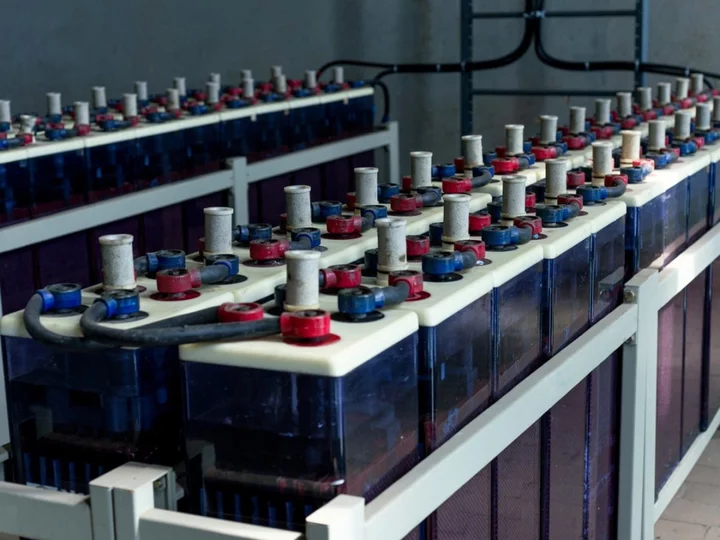

Record-breaking sugar battery could supercharge transition to renewable energy
Scientists have used sugar to create a record-breaking battery capable of storing grid-scale energy for more than a year. The breakthrough could help speed up the transition to renewable energy sources, which require vast amounts of battery storage in order to avoid relying on fossil fuels to meet demand when solar or wind output is low. A team from the US Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) made the latest discovery while researching flow batteries, which use two liquid-filled chambers to produce an electrochemical reaction to store and release energy. Flow batteries have the potential to be scaled up to the size of football fields, capable of storing vast amounts of energy, however current methods for creating them rely on mined minerals that are difficult and costly to obtain. “This is a brand new approach to developing flow battery electrolyte,” said Wei Wang, a battery researcher who led the investigation into the new method. “We showed that you can use a totally different type of catalyst designed to accelerate energy conversion.” The researchers used a dissolved simple sugar called β-cyclodextrin, which is a derivative of starch, in order to boost their flow battery’s longevity and capacity. The system achieved 60 per cent more peak power than current methods, while also being capable of storing and releasing energy for more than a year continuously. The latest advance makes the next-generation battery design “a candidate for scale up”, according to the researchers. “We cannot always dig the Earth for new materials,” said Imre Gyuk, director of energy storage research at DOE’s Office of Electricity. “We need to develop a sustainable approach with chemicals that we can sythesize in large amounts – just like the pharmaceutical and the food industries.” A study detailing the research, titled ‘Proton-regulated alcohol oxidation for high-capacity ketone-based flow battery anolyte’, was published in the scientific journal Joule. Read More How tech could turn our homes into renewable energy power stations ‘Miracle material’ smashes solar panel efficiency threshold Mineral discovery could meet global battery and solar panel demand for next 100 years Why the Battle of the Boyne has made its way into your iPhone Twitter gets strange endorsement from Taliban over rival Threads
2023-07-11 18:53
