
US judge dismisses Republican National Committee's email spam suit against Google
By Kanishka Singh WASHINGTON A U.S. judge on Thursday dismissed a lawsuit against Alphabet Inc's Google that was
2023-08-25 06:46
AI Startup Hugging Face Valued at $4.5 Billion After Raising Funding From Google, Nvidia
Hugging Face Inc., a startup that makes artificial intelligence software and hosts it for other companies, said it
2023-08-25 03:52

US sues SpaceX, alleges hiring discrimination against asylum seekers, refugees
By Kanishka Singh WASHINGTON (Reuters) -The U.S. Justice Department sued Elon Musk-owned rocket and satellite company SpaceX on Thursday for
2023-08-25 01:59
Dropbox Ends Unlimited Cloud Storage Following Google Change
Dropbox Inc., a provider of online data storage, is ending its unlimited option, saying a small handful of
2023-08-25 01:18

Google Axes Bad Reviews of Tracker Exposing Uyghur Forced Labor
Alphabet Inc.’s Google has removed hundreds of negative reviews for a tracker that identifies apparel brands linked to
2023-08-25 00:55
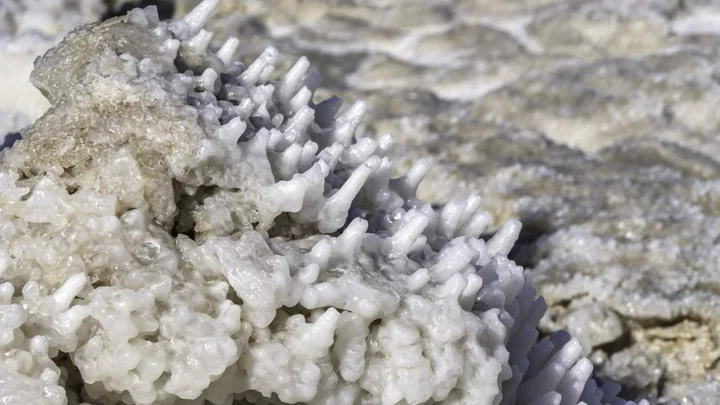

150 million year old water trapped in salt contains secrets to our ocean history
The key to discovering the secrets of life at the bottom of the ocean 150 million years ago has been discovered, and it was trapped inside ancient salt formations this whole time. Experts have been able to uncover the Earth's geological history y studying tiny water particles which have been preserved in crystals for millions of years. It’s all to do with analysing the amount of lithium which is trapped in samples rock salt. As it turns out, the level of lithium can tell us far more about atmospheric conditions in the oceans over the ages than most of us previously realised. Geochemists Mebrahtu Weldeghebriel of Princeton University and Binghamton University and Tim Lowenstein of Binghamton University have published their findings in a new study. The rock salt they studied, known as marine halite, came from across the world including the US, Europe, Asia and Africa. A total of 639 samples were taken from 65 halite crystals dating back to 150 million years ago. "There is a close link between ocean chemistry and atmospheric chemistry," Weldeghebriel said. “Whatever changes happen in the ocean also reflect what's happening in the atmosphere." "The oceans and atmosphere are connected to one another, and how they change is related," Lowenstein added. "Everything is connected." Most notably, their findings have helped to create a better understanding of tectonic movement on the seafloor. The reason the presence of lithium was so important is due to what it tells us about hydrothermal activity. The amount in the water indicates the levels of chemicals and heat which was being released into the oceans by vents between tectonic plates. As tectonic plate activity declined, there was a global drop in lithium levels. Instead, it was replaced by a rise in magnesium and calcium. The reduction in activity would also have meant less carbon dioxide being released into the atmosphere, which could potentially have been a factor in the temperature drop which resulted in the ice age. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 00:48

Mastercard, Binance to end crypto card partnership
By Elizabeth Howcroft LONDON (Reuters) -Mastercard and crypto exchange Binance will end their four crypto card programmes in Argentina, Brazil,
2023-08-25 00:47
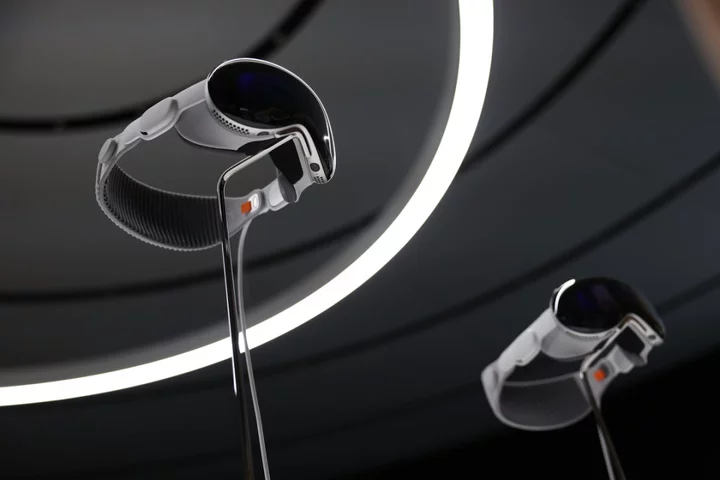

‘Audible gasp’: Apple says developers have been shocked by augmented reality headset
Developers say they “audibly gasped” when first using Apple’s upcoming augmented reality headset, the company has said. Apple announced the Vision Pro headset in June, when it said it would arrive early next year and cost $3,500. In the wake of that announcement, it allowed some journalists to use the headset, including The Independent. Since then, however, Apple has kept its Vision Pro largely hidden. Some units have been shipped out to developers, and it is offering special sessions where they can try out their apps in Apple’s buildings, but those taking part have been asked to sign expansive non-disclosure agreements that mean they cannot talk about those experiences. Now Apple has published some comments from some of those early users, however, who have detailed the first experience of using the headset. Actually strapping the headset on is fundamentally different from using it in the simulator that Apple has provided so that developers can start work on their augmented reality apps, they said. “I’d been staring at this thing in the simulator for weeks and getting a general sense of how it works, but that was in a box,” said David Smith, the developer of the app Widgetsmith. “The first time you see your own app running for real, that’s when you get the audible gasp.” Another developer said that it changed the experience of using his app. Michael Simmons – who runs Flexibits, which creates apps such as calendar tool Fantastical, said that using the kit was a surprise. “It was like seeing Fantastical for the first time,” he said. “It felt like I was part of the app.” Using the app in augmented reality meant that he was already thinking of new ways to get past the “limiting” nature of a screen with a border, he said in Apple’s post. “Experiencing spatial computing not only validated the designs we’d been thinking about — it helped us start thinking not just about left to right or up and down, but beyond borders at all.” Slack employee Chris Delbuck also said that he had come to think about the way the app might work in three dimensions in new ways. “I wouldn’t have been able to do that without having the device in hand,” Apple quoted him as saying. Apple is allowing any adult developer to apply to attend one of its “Vision Pro labs” for free, which are being held in a range of cities across the world. Developers must bring either an app they are working on for the Vision Pro, or an iPhone or iPad app that they want to see in augmented reality. Some reports have suggested that Apple has seen less interest for the labs than it might have hoped, possibly in part because it is not offering the labs on the east coast of the US. The labs have been “under-filled”, Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman reported earlier this month – which might explain why the company is so keen to stress the importance of attending the sessions. Read More iPhone 15 could bring two major changes to fix battery life iPhone owners to receive payouts from Apple iPhone 15: Global smartphone demand collapses as Apple aims to take top spot
2023-08-24 23:47

Swipebuster: New website lets you check whether someone is using Tinder
A new website claims to let its users find out whether people they know are using Tinder. Using public data, Swipebuster says it can reveal whether someone is using the dating app, even revealing their location, profile pictures and bio. Swipebuster charges $4.99 (£3.50) for three searches, and requires users to enter the first name, gender and age of the person they want to check in on, as well as the rough location where they may have last used the app. Although it sounds dodgy, what Swipebuster is doing is completely above board - it uses Tinder's API to access the information, which is typically used by developers building other services to integrate with the app. Swipebuster doesn't make any explicit assumptions about why people would use the site, but the fact its homepage instructs users to "tell us who you want to bust" suggests it's been built with suspicious partners in mind. The site's anonymous creator tells a different story. Speaking to Vanity Fair, he said: "There is too much data about people that people themselves don't know is available." "Not only are people oversharing and putting out a lot of information about themselves, but companies are also not doing enough to let people know they're doing it." Although he claims the site is raising awareness about the importance of data security, a number of people have suggested Swipebuster could by abusive partners or obsessive exes to harass their victims. Tinder is surprisingly unfazed about the site. A spokeswoman told Vanity Fair that "searchable information on the website is public information that Tinder users have on their profiles." "If you want to see who's on Tinder we recommend saving your money and downloading the app for free." There's nothing that can be discovered through Swipebuster that isn't visible on the app, although there's a difference between instantly finding a profile through a search and coming across it after swiping through thousands of profiles. The information shown on Swipebuster isn't secret, although some users will be worried their Tinder use isn't as discreet as before. Read More Read moreTinder reveals the 15 most right-swiped jobs for men and women Terrifying Facebook posts are scaring people into sharing them, fact checkers warn Nvidia sales hit record high as AI chip demand soars Why India’s moon landing is about a lot more than exploring the lunar surface
2023-08-24 22:26
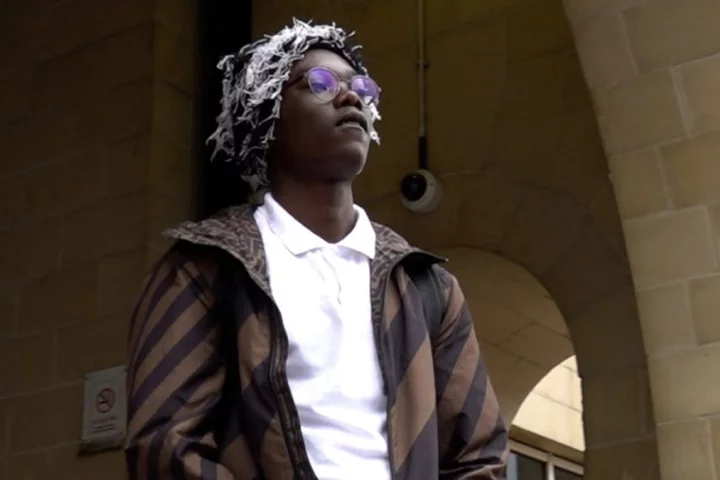

TikTok star Mizzy bailed again over prank videos
TikTok prankster Mizzy has again been released on bail after he was accused of posting videos on social media without the consent of the people featured in them. The star, real name Bacari-Bronze O’Garro, appeared at Stratford Magistrates’ Court in east London on Thursday morning. He was listed for trial on three counts of breaching a criminal behaviour order but his case was adjourned because he has now been accused of engaging in further “criminal activities”, according to a joint submission by prosecution and defence lawyers. The case was previously adjourned on July 19 at the same court. O’Garro was initially placed on bail for the offences at a hearing at Thames Magistrates’ Court in May. The 18-year-old spoke to the PA news agency outside court on Thursday, saying society is “out to get me” and adding: “We will conquer.” One of the alleged offences took place on May 25 when O’Garro visited the Westfield Centre in Stratford, which he is not permitted to do under the criminal behaviour order. He told PA after a previous hearing that he was unaware he was in breach because he had not been given a map of the out-of-bounds area. The two other offences relate to videos posted on May 25 and May 26 allegedly without the consent of the people involved. O’Garro will appear at Stratford Magistrates’ Court again on September 21. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live
2023-08-24 22:26

T-Mobile to lay off 5,000 employees
T-Mobile on Thursday announced it plans to lay off 5,000 employees, or around 7% of its total staff, over the next five weeks.
2023-08-24 22:17

A new 'Antarctica' accent has been discovered by scientists
Antarctica might be the only continent on Earth with no natural human habitation, but it’s emerged that an “Antarctica accent” is very much a thing. Despite having no locals, thousands of scientists have made up an ever-changing population in research stations over the years. The continent is so isolated and the level of interaction between researchers is so intense, that a common accent is beginning to emerge there despite people coming from different parts of the world. At its busiest points in the year during the summer, Antarctica is home to around 5,000 people. Only around 1,000 people live there during the winter months. The idea of accents changing due to human interaction on Antarctica is no different to the phenomenon seen throughout history at a glacial pace. However, given the very specific sample size, it’s an opportunity for scientists to study it at a much quicker rate and on a much smaller scale. Experts at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich published a study in 2019 which focused on the change in accents observed in 11 people who took part in the British Antarctic Survey. @human.1011 There’s an Antarctic Accent! #language #linguistics #english #antarctica Of the 11 who were studied, eight came from England, one from the US, one from Germany and one from Iceland. Their voices were recorded every six weeks, and the team found that over time they developed longer vowel sounds. There was a physical change too, with participants pronouncing the “ou” sound in the front of their mouths rather than the back of their throats. Speaking to IFL Science, Jonathan Harrington, study author and Professor of Phonetics and Speech Processing at the Ludwig-Maximilians University of Munich said: "The Antarctic accent is not really perceptible as such – it would take much longer for it to become so – but it is acoustically measurable. "It's mostly an amalgamation of some aspects of the spoken accents of the winterers before they went to Antarctica, together with an innovation. It's far more embryonic [than conventional English accents] given that it had only a short time to develop and also, of course, because it's only distributed across a small group of speakers.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-24 20:51
