
Vodafone down: Phone network not working as customers struggle to make calls
Vodafone customers say they are struggling to make calls, seemingly after technical issues at the network. Users said they were experiencing an array of unusual problems. Some said they were able to call other people on Vodafone – but not speak to people on other networks, for instance. Data connections appeared to be working as normal, however. On Twitter, Vodafone responded to affected users by apologising and asking for more information, and its online service checker indicated there were problems in some areas. The company did not immediately respond to a request for comment. Tracking website Down Detector also showed problems at Vodafone, starting on Monday afternoon. Other networks were also flagged as having issues – but that may be simply because Vodafone calls to those on other providers were failing to connect. Read More US Air Force is toying with idea of building this Batman villain’s weapon China’s ‘government-approved’ AI chatbot says Taiwan invasion likely Russian cyber-attacks ‘relentless’ as threat of WW3 grows, expert warns
2023-09-04 20:57

The Moon is slowly drifting away from Earth and its beginning to impact us
The Moon is a constant in the night sky, but all is not actually as it seems. It turns out that scientists have discovered the Moon is drifting away from Earth, and it’s changing everything we thought we knew about our planet’s relationship with its only natural satellite. It’s also having a very real impact on the length of days on our planet – albeit at an incredibly slow rate. By moving away from Earth over the course of millions of years, the Moon is simultaneously making the length of the average day longer. A study by a team at the University of Wisconsin-Madison focused on rock from a formation aged at 90 million years. By doing so, they were able to analyse the Earth’s interactions with the Moon 1.4 billion years ago. It turns out that the Moon is moving away from Earth at us at 3.82 centimetres a year. That means that, eventually, it’ll result in Earth days lasting 25 hours in 200 million years time. Stephen Meyers, who is a professor of geoscience at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, said: “As the moon moves away, the Earth is like a spinning figure skater who slows down as they stretch their arms out.” He added: “One of our ambitions was to use astrochronology to tell time in the most distant past, to develop very ancient geological time scales. “We want to be able to study rocks that are billions of years old in a way that is comparable to how we study modern geologic processes.” It’s not the only story that changes our understanding of the Moon recently. Scientists have also just uncovered billions of years’ worth of secrets buried beneath the surface of the moon – all thanks to China’s space programme, which has uncovered hidden structures which can help us start to piece together the Moon’s past. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-09-04 20:29
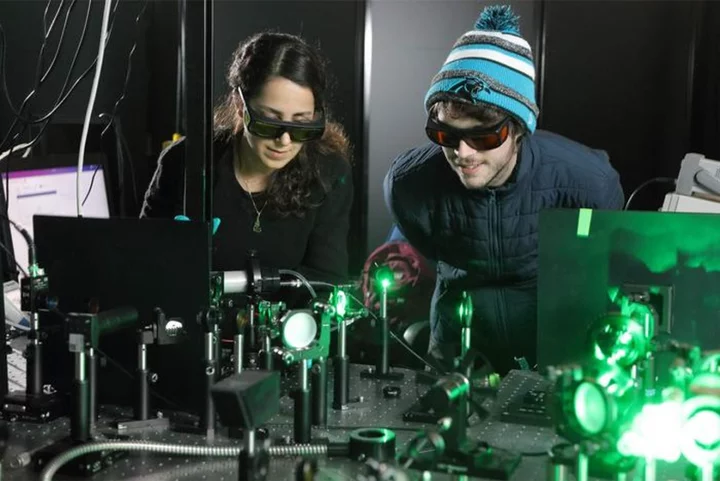

US Air Force is toying with idea of building this Batman villain’s weapon
Researchers funded by the US Air Force are developing a new type of device that can invite comparisons to a weapon used by a Batman villain. Scientists, including Patrick Hopkins from the University of Virginia in the US, are working on a new device to be used for on-demand surface cooling for electronics inside spacecraft and high-altitude jets. The device may seem similar to the freeze gun used by Batman villain Mr Freeze to “ice” his enemies. “A lot of electronics on board heat up, but they have no way to cool down,” said Dr Hopkins, whose lab has been granted $750,000 over three years to develop the technology. On Earth, electronics in military craft can rely on nature to cool themselves, but in space, this may be a challenge, scientists said. Citing an example, researchers said the Navy uses ocean water in its liquid cooling systems while flying jets can rely on air that is dense enough to help keep components chilled. “With the Air Force and Space Force, you’re in space, which is a vacuum, or you’re in the upper atmosphere, where there’s very little air that can cool,” Dr Hopkins said. “So what happens is your electronics keep getting hotter and hotter and hotter. And you can’t bring a payload of coolant onboard because that’s going to increase the weight, and you lose efficiency,” he explained. In such extra-terrestrial environments, a jet of plasma, the fourth and most common state of matter in the universe, can be used in the interior of a craft. “This plasma jet is like a laser beam; it’s like a lightning bolt. It can be extremely localized,” Dr Hopkins explained. One of the strange qualities of plasma is that while it can reach temperatures as hot as the surface of the Sun, it chills before heating when it strikes a surface. In the new research, published recently in the journal ACS Nano, scientists fired a purple jet of plasma generated from helium through a hollow needle encased in ceramic, targeting a gold-plated surface. When researchers turned on the plasma, they could measure temperature immediately at the point where the plasma hit, and could see that the surface cooled first and then heated up. “We were just puzzled at some level about why this was happening, because it kept happening over and over,” Dr Hopkins said. “And there was no information for us to pull from because no prior literature has been able to measure the temperature change with the precision that we have. No one’s been able to do it so quickly,” he said. The strange surface-cooling phenomenon, according to scientists, was the result of blasting an ultra-thin, hard-to-see surface layer, composed of carbon and water molecules. Researchers compare this to a similar process that happens when cool water evaporates off of our skin after a swim. “Evaporation of water molecules on the body requires energy; it takes energy from body, and that’s why you feel cold. In this case, the plasma rips off the absorbed species, energy is released, and that’s what cools,” the researchers explained. Using the method, scientists could reduce the temperature of the setup by several degrees for a few microseconds. While this may not be dramatic, they said it is enough to make a difference in some electronic devices. Now, thanks to the Air Force grant, researchers are looking at how variations on their original design might improve the apparatus. “Since the plasma is composed of a variety of different particles, changing the type of gas used will allow us to see how each one of these particles impact material properties,” researchers said. Read More Scientists discover 3,000-year-old arrowhead made of ‘alien’ iron Carcinogens found at nuclear missile sites as reports of hundreds of cancers surface India’s moon rover confirms sulphur and detects several other elements near the lunar south pole China’s ‘government-approved’ AI chatbot says Taiwan invasion likely Russian cyber-attacks ‘relentless’ as threat of WW3 grows, expert warns How new bike technology could help cyclists tell drivers not to crash into them
2023-09-04 20:25
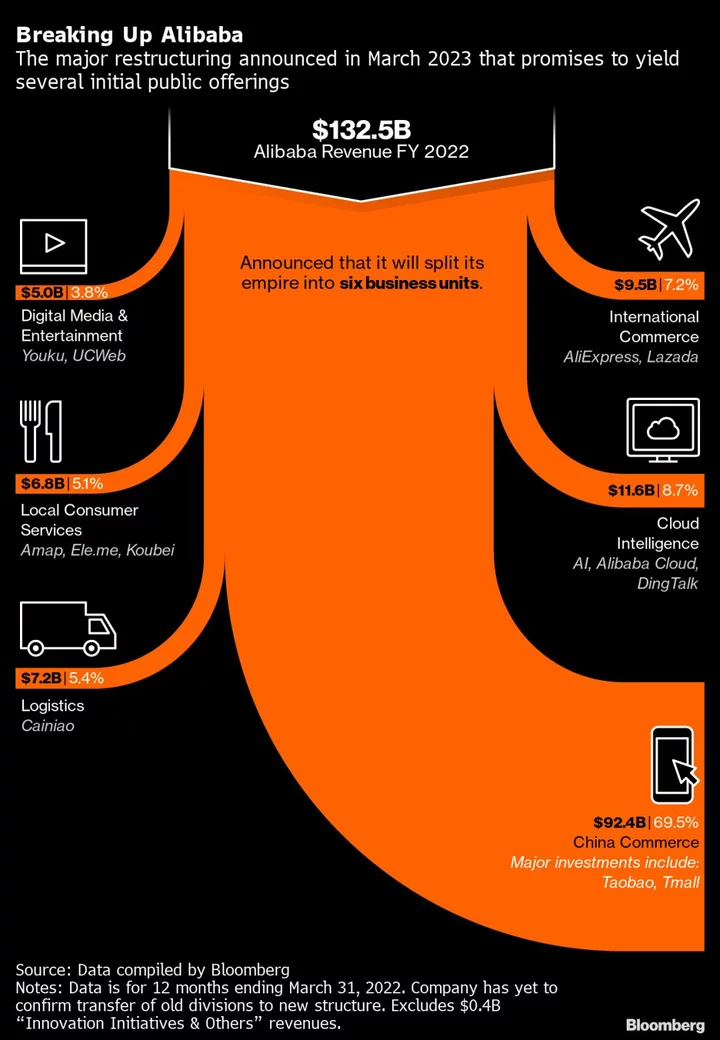
Alibaba Cloud Eyes State Firms for Up to $3 Billion Fundraising
Alibaba Group Holding Ltd.’s cloud division is weighing a private round to raise funds from Chinese state-owned enterprises
2023-09-04 18:28

German Banking Regulator BaFin’s Website Hit by Cyber Attack
German banking regulator BaFin said its website has only been partially accessible since Friday after a so-called distributed
2023-09-04 16:45

Russian court fines Tinder, Twitch for refusing to localise data
MOSCOW A Russian court on Monday fined Match Group, which operates Tinder, 10 million roubles ($104,000) and streaming
2023-09-04 16:24

Binance global head of product Mayur Kamat resigns - The Block
Binance's global head of product and design, Mayur Kamat, has resigned amid a string of executive exits and
2023-09-04 15:46

China’s ‘government-approved’ AI chatbot says Taiwan invasion is likely
A military takeover of Taiwan is likely, according to one of many Chinese government-approved artificial intelligencechatbots that seem to toe the ruling Communist Party’s official line. The island nation has been a self-governing democracy since its separation from the mainland following a civil war in 1949, but China has claimed it as part of its national territory. The chatbots have dubbed Taiwan an inseparable part of China. The Chinese government recently approved a number of AI chatbots for use in the country, including a bot named Ernie and developed by tech giant Baidu and TikTok owner ByteDance’s Doubao. When Bloomberg tested some of these AI services for how government oversight affected the accuracy of information provided by these chatbots, it found they appeared to be trained to follow the ruling Communist Party’s line. When asked whether Taiwan is a country, all the tested chatbots reportedly said the self-governed island was a part of China, and Baidu’s Ernie chatbot reportedly said a Chinese military takeover of Taiwan is likely. The Zhipu chatbot described China’s current economic situation, which experts said is at one of its weakest points in recent decades, to be “a mix of joys and sorrows”, reported Bloomberg. Another chatbot, SenseTime, reportedly described the economy as “very stable”. When asked to respond queries that may be deemed “sensitive content”, the Ernie bot was found to “change the subject”, while Zhipu would delete its response if it found it to be “controversial”, according to the report. Such generative AI tools are trained by analysing large quantities of data to respond to user queries with unique human-like replies. For instance, OpenAI’s ChatGPT has demonstrated a wide range of abilities, from summarising complex research, answering logical questions and also cracking business and medical school exams deemed crucial for students to pass. A number of Chinese companies have sought to build their own version of AI chatbots, prompting China’s cyberspace regulator to release ground rules for companies developing generative AI services. But prior to the launch of these chatbots, the Chinese government made several months-long efforts to regulate the generative AI industry. Some of the proposed rules have sought to ensure the content of Chinese AI systems reflect “socialist core values” and avoid information undermining “state power” or “national unity”. Baidu’s launch of Ernie for full public use on Thursday led to the company’s stock price rising by over 3 per cent following the announcement. Other AI firms such as Baichuan and Zhipu AI also launched their ChatGPT-like large language models on Thursday. The ruling Communist Party issued regulations on 15 August that required tech companies to carry out a security review of their chatbots, and obtain approvals before their products are publicly launched. It also requires companies providing such AI services to comply with government data requests, regulations which are currently absent in the US. Read More China's Baidu makes AI chatbot Ernie Bot publicly available Need to know about live-saving CPR? A new study says it's probably wise not to ask Alexa or Siri AI can write better university assignments than students, report suggests India’s moon rover finds sulphur and several other elements near lunar south pole Russian cyber-attacks ‘relentless’ as threat of WW3 grows, expert warns How new bike technology could help cyclists tell drivers not to crash into them
2023-09-04 14:52

Munich car show shines spotlight on China competition in EV race
MUNICH European carmakers must prove their ability to compete with new Asian players in the electric age on
2023-09-04 13:23

Russian cyber-attacks ‘relentless’ as threat of WW3 grows, expert warns
Cyberattacks by the UK’s enemies are becoming “relentless” as we enter a “new era” of global conflict, an expert has warned. It comes after Russian hackers allegedly acquired top-secret security information on some of the country’s most sensitive military sites, including the HMNB Clyde nuclear submarine base on the west coast of Scotland and the Porton Down chemical weapon lab. The “potentially very damaging” attack last month by hacking group LockBit, which has known links to Russian nationals, saw thousands of pages of data leaked onto the dark web after private security firm Zaun was targeted, the Sunday Mirror newspaper reported. The company, which provides security fencing for sites related to the Ministry of Defence, said it had been the victim of a “sophisticated cyber attack”. Responding to the news, Kevin Curran, professor of cyber security at Ulster University, told the PA news agency that LockBit’s attack was “serious” as we approach a potential “World War Three” following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. He said the raid was “likely” sponsored by the Russian state given the nature of its target and that cyber attacks by Britain’s enemies had become “relentless”. Professor Curran warned that we were unprepared for this new era as third-party companies, which hold data on our military infrastructure were not being properly regulated. He said: “You can’t just expect third-party suppliers to adhere to your rules. “There is always a risk when you have third-party suppliers and you do wonder if they adhere to industry best practice. “It is a worry because everything is online now – cybercrime is the biggest crime in the world. “Given the new era we are entering which is the brink of World War Three everything is serious. They are relentless with these attacks Professor Kevin Curran “They are relentless with these attacks. Their best way into our country is through our cyber-security. This is the nation at risk. “In this case, given the target, my money would be on this being state-sponsored.” It comes after Labour MP Kevan Jones, who sits on the Commons Defence Select Committee, urged the Government to explain why Zaun’s computer systems were “so vulnerable”, warning: “This is potentially very damaging to the security of some of our most sensitive sites.” “Any information which gives security arrangements to potential enemies is of huge concern,” he added. The government has so far declined to respond to concerns, with a spokesperson saying: “We do not comment on security matters.” In a statement on its website published on Friday, Zaun said it had taken “all reasonable measures to mitigate any attacks on our systems” and explained that they had referred the matter to the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC). It explained that the breach occurred through a “rogue Windows 7 PC” that was running software for one of their manufacturing machines but that the network was “otherwise up to date”. It said: “At the time of the attack, we believed that our cyber-security software had thwarted any transfer of data. “However, we can now confirm that during the attack LockBit managed to download some data, possibly limited to the vulnerable PC but with a risk that some data on the server was accessed. “It is believed that this is 10 GB of data, 0.74 per cent of our stored data. “It is well known that Zaun is a specialist in high-security perimeter fencing and has supplied fencing to many high-profile sites. “Sites where our products are used include prisons, military bases and utilities.” Zaun has been approached for further comment. Read More Ukraine-Russia war – live: Putin suffering ‘mounting casualties’ and forced to appeal for foreign fighters Russia attacks a Ukrainian port before key grain deal talks between Putin and Turkey's president Russians press Ukraine in the northeast to distract from more important battles in counteroffensive Ukraine ‘targets critical bridge’ built by Putin as counteroffensive ‘breaks through on southern front’ Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live
2023-09-04 01:48

The terrifying time our early ancestors almost became extinct
New research has shown that our early ancestors almost went extinct some 900,000 years ago. Using a new method called FitCoal (fast infinitesimal time coalescent process), researchers analysed the likelihood of present-day genome sequences to project current human genomic variation backwards in time. They applied the technique to the genomes of 3,154 people from 10 African and 40 non-African populations, and found a massive crash in genetic diversity during the transition between the early and middle Pleistocene. “Results showed that human ancestors went through a severe population bottleneck with about 1,280 breeding individuals between around 930,000 and 813,000 years ago,” the study authors wrote in the journal Science. “The bottleneck lasted for about 117,000 years and brought human ancestors close to extinction,” they say. Wiping out roughly 98.7 percent of the ancestral human population, “the bottleneck could also have increased the inbreeding level of our ancestors, thus contributing to the 65.85 percent loss in present-day human genetic diversity,” explained the researchers. This probably happened because of changes in the global climate as short-term glaciations became longer-lasting, triggering a drop in ocean temperatures, prolonged drought, and the loss of large numbers of species that humans might have relied on for food. Then, around 813,000 years ago, populations finally recovered, with a 20-fold increase in numbers because of fire combined with the return of warmer temperatures, researchers reckon. What a near miss, eh? Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-03 19:22

There’s an exact number of people required to colonise Mars – and it may surprise you
When he’s not making radical, controversial changes to Twitter/X, Elon Musk is eyeing up plans to colonise Mars in the coming years with his company SpaceX – and now a team of researchers at the Virginia-based George Mason University claims it has found out the minimum number of people needed to successfully takeover the red planet. In the study – the results of which were published to the research platform Arxiv in August - the academics established a model to find out the ‘initial population size’ required on Mars to produce a “stable colony size”. They ran the model five times for 28 Earth years, and increased the population by 10 people each time - from 10 to 170 individuals. “Given that there are four critical tasks that are needed continuously (air, water, food production and waste removal) in addition to handling disasters, and two skills needed for each task, we chose a population size of 10 as the minimum needed for a ‘stable’ colony size. “The population is allowed to dip below 10 as long as it bounces back within 1.5 years, or the amount of time between Earth resupply shuttles.” The test found all initial population sizes over 50 were able to sustain a population of at least 10 people across the time period, and that the bare minimum number to meet that criteria is at least 22 people. There you go, Elon. You’re welcome. It’s certainly a decrease in the minimum number previously suspected by French researcher Jean-Marc Salotti in June 2020 – that was the rather astronomical figure (sorry) of at least 110 people. And the Virginia researchers didn’t stop there, either, as they also took a look at the personality types best placed to handle the highly stressful environment that is living on a completely different planet. There’s four: “agreeables”: low competitiveness and aggressiveness, and not fixated on “stringent routine “socials”: medium competitiveness, extroverted, require social interaction but not fixated on stringent routines “reactives”: medium competitiveness and fixed on stringent routines “neurotics”: high competitiveness, highly aggressive and a “challenged ability to adapt to boredom or a change in routine” Perhaps unsurprisingly, the “agreeables” came out on top. The researchers added: “In all runs, the Agreeable personality type was the only one to survive the full duration of model runs. This is likely because it has the highest coping capability.” Their results found that while the “neurotic” was “most likely to fail”, and both “reactives” and “socials” fluctuated, the “agreeables” was the “most resilient”. “While this model assigns equal numbers of each personality type, future work could try adjusting the proportion of each to possibly lead to a lower required minimum initial population. For example, a crew of all Agreeable personalities may be more successful,” they suggest. Musk, meanwhile, said earlier this year that he was optimistic humans landing on Mars was "possible" in the next five years, and "highly likely" in a decade. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-03 00:26
