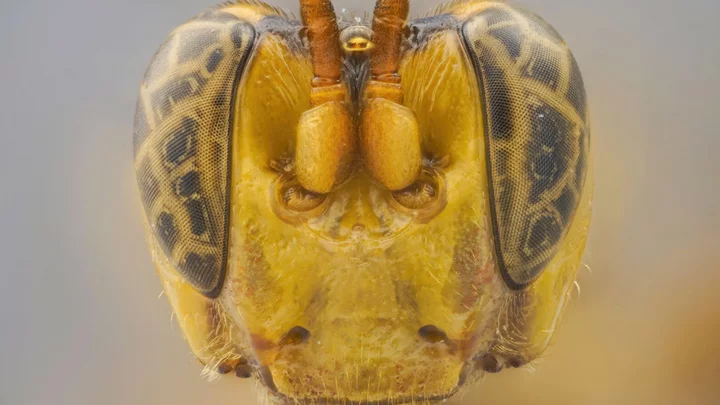

A parasitic wasp with a giant head has been discovered and it's the stuff of nightmares
Scientists have unearthed a new species of wasp in the Amazon – and it's rather terrifying. The alien-looking parasitic creature came to light when a team at Utah State University were researching Allpahuayo-Mishana National Reserve in Peru. The wasp, known as Capitojoppa amazonica, has a giant almond-shaped head and is known to latch on to prey before sucking its blood and then eating it from the inside. It does so by laying eggs in its victims including caterpillars, beetles and spiders. The study’s lead author, biologist Brandon Claridge called the practice a "solitary endoparasitoid". "Once the host is located and mounted, the female will frantically stroke it with her antennae," Claridge told Live Science in an email. "If acceptable, the female will deposit a single egg inside the host by piercing it with her ovipositor (a tube-like, egg-laying organ)." He went on to explain that in some instances, "females will even stab the host with the ovipositor and feed without laying an egg as it helps with gaining nutrients for egg maturation." This isn't the first horrifying discovery, with researchers recently finding a new species of tarantula in Thailand that is characterised with illuminous blue legs. The spider is one of the rarest in the world, with Dr Narin Chomphuphuang explaining how it lurks in hollow trees. "The difficulty of catching an electric-blue tarantula lies in the need to climb a tree and lure it out of a complex of hollows," he explained. "During our expedition, we walked in the evening and at night during low tide, managing to collect only two of them." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-17 18:23

Adobe unveils futuristic ‘digital dress’ that changes patterns on the go
Software company Adobe unveiled a new futuristic “digital dress” that lets wearers change patterns on its surface on the fly with the click of a button. The dress, created under Adobe’s “Project Primrose”, is made of sequins which are “reflective light-diffuser modules” built using liquid crystals such as those in smart lighting. Researchers say the sequins are basically tiny screens built using smart materials. The dress was unveiled for the first time for the audience at Adobe’s MAX conference last week with the software company describing it as bringing “fabric to life”. Video from the conference showed Adobe researcher Christine Dierk wearing the strapless outfit, which appeared like an average cocktail dress on first impression, but the patterns on it begin to shift immediately with the touch of a remote button. “Unlike traditional clothing, which is static, Primrose allows me to refresh my look in a moment,” the Adobe scientist said while demonstrating that its colors can go from light to dark in a moment. The researcher-turned-model also showed that the dress not only had static changes, but also animated designs with patterns fading in and out. Ms Dierk, who not only designed the dress but also stitched it herself, demonstrated that the outfit will even respond to movement. Researchers say the dress is built using “reflective-backed polymer-dispersed liquid crystal (PDLC)” a material commonly used in smart windows. “This low-power non-emissive material can be cut to any shape, and dynamically diffuses light,” scientists wrote in a study presented at a tech conference last year, but it remains unclear how heavy the dress can actually get. “Designers can layer this technology into clothing, furniture, and other surfaces to unlock infinite style possibilities – such as the ability to download and wear the latest design from a favorite designer,” Adobe noted. They said the high-tech sequins are also used for smaller products part of Project Primrose including a handbag and a canvas. “We hope this work inspires future designers of flexible displays,” scientists said. Read More Photo giant Getty took a leading AI image-maker to court. Now it's also embracing the technology John Warnock, who helped invent the PDF and co-founded Adobe Systems, dies at age 82 In closed forum, tech titans to give senators advice on artificial intelligence Tell us if you think price is the biggest problem with electric cars Sadiq Khan, Met Commissioner to ask phone companies to ‘design out’ theft TikTok details plans for Israel-Hamas war posts
2023-10-17 17:51

Amazon to launch online shopping service in South Africa in 2024
JOHANNESBURG (Reuters) -U.S. ecommerce firm Amazon said on Tuesday it would launch its online shopping service in South Africa in
2023-10-17 16:59

Tesla to recall nearly 55,000 Model X vehicles, auto regulator says
The U.S. auto regulator on Tuesday said Tesla will recall 54,676 Model X vehicles manufactured between 2021-2023, as
2023-10-17 16:18
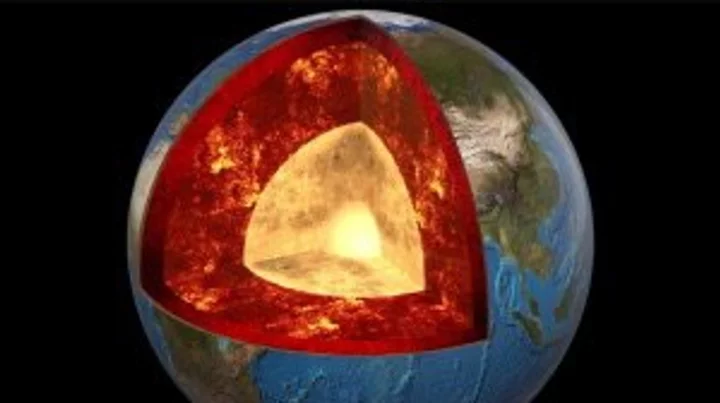
Scientists have discovered two giant mystery structures lurking under Africa
Many of us look to the stars for answers to life’s most complex questions. But actually, some of the greatest mysteries lie beneath our very feet. One might think we’d know the Earth pretty well by now but, in fact, our planet’s core remains shrouded in enigma. Indeed, there are two gigantic blobs located beneath Africa and the Pacific Ocean that occupy around six per cent of the world’s entire volume. And yet, we’re still not entirely sure what they’re made of or where they came from. There are a number of hypotheses, including that they are piles of oceanic crust that have accumulated over billions of years. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter But a more interesting theory is that they are huge chunks of an ancient planet that hit the Earth around 4.5 billion years ago. To give an indication of just how massive these things are, the structure under Africa – an area known as Tuzo – is thought to be around 800km (497 miles) tall – the equivalent of some 90 Mount Everests stacked on top of one another, as IFLScience notes. The problem with determining the origin of these monster formations is that there are no direct ways of observing the Earth’s core. The deepest hole humans have ever dug – branded the "entrance to hell" – reached a pretty staggering 12,263m (40,230ft), but that doesn’t even come close to breaking through the crust to the layers beneath. Our most effective tool for analysing what lies beneath the ground is a technique called seismic tomography, which looks at how waves of energy travel when earthquakes occur. Since rocks and liquids have different densities, the waves move through them at different speeds. By measuring the tremors from different points on the surface, geologists can determine what kind of material the waves are travelling through and, in so doing, map out the Earth’s interior. It was by using this technique that the two unusual structures – known as large low shear velocity provinces (LLSVPs) – were found. Waves travel more slowly in these areas – fondly known as “blobs” – than through the surrounding lower mantle, indicating that they’re made of something different. We can’t tell what this material is based on seismic tomography data alone, but some scientists like to believe that they are the remnants of an ancient planet called Theia – an idea known as the “giant impact hypothesis”. According to this hypothesis, around 4.5 billion years ago, a Mars-sized object collided with the Earth. This impact not only created the planet we call home today, but also threw off enough rock to form the moon that lights up our night skies. Some scientists suggest that some of Theia’s leftovers also sunk to the bottom of the planet, probably settling somewhere above the core – thereby forming at least one of the two LLSVPs. More Updates About Strange Blob Structures Inside Planet Earth youtu.be Experts have been investigating the area for decades but there’s still no way of knowing for sure just what these two giant blobs are. Still, studies into Theia have offered important insights into how the possible collision might have kickstarted key plate tectonic and mantle motion inside our planet – crucial processes for establishing the world on which we live. It’s also a useful reminder that we still have so much to learn about our planet and where we came from. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-17 14:56

Baidu says its AI is in the same league as GPT-4
Chinese tech giant Baidu is officially taking on GPT-4.
2023-10-17 14:15

This is why time ‘speeds up’ when we get older, according to scientists
We've all heard and probably have used the saying "time flies," but why does this expression resonate more and more as we get older? From being a happy-go-lucky child counting down the days of school left until the summer holidays to finding ourselves in adulthood with responsibilities like a full-time job and bills to pay, everything changes in what feels like a blink of an eye. While there isn't any scientific evidence that explains why we feel time moves faster as we age, there is a theory that may provide the answer. "One is that when we are older, we tend to have lives that are more structured around routines, and fewer of the big landmark events that we use to demarcate different epochs of the 'time of our lives,'" Cindy Lustig, a professor of psychology at the University of Michigan, told the Daily Mail. She explained how as children we have fewer experiences to reflect on. And so 20 per cent of a five-year-old's life is just one year and in this year there are momentous milestones and life experiences. While the same duration of time only two per cent of a 50-year-old's life who wouldn't have as many new experiences within this period. The professor added how our brains often merge similar days and weeks together and this blending of memories means that many of us can remember something they've done once rather than recalling the hundred times they have done it before. Well, there you go - something to think about whenever we feel old and like time is passing us by. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-17 14:15

Cryptoverse: Winter is coming as ether funds flounder in fall
By Lisa Pauline Mattackal The weak crypto market is wobbling through autumn. And winter's on its way. The
2023-10-17 13:51

Sadiq Khan, Met Commissioner to ask phone companies to ‘design out’ theft
The Mayor of London and the Metropolitan Police Commissioner will meet with leading mobile phone companies on Tuesday to ask them to commit to “design out” mobile phone robbery. Apple, Samsung and Google will join representatives from major UK mobile phone network providers at the meeting, which will focus on how the police, City Hall and the mobile phone industry can work better together to find the most effective deterrent and ultimately significantly reduce mobile phone robberies in London and beyond. Figures from the Met Police show there has been a 28% increase in mobile phone robbery in London and a 22% increase in theft of mobile phones over the last 12 months. This represents a total of 57,174 mobile phones reported stolen and equates to an average of 157 mobile phones stolen every day in the capital. This meeting is an important milestone to developing a practical and long-term solution to ending the menace of mobile phone crime which we know is driving violence and criminality in our communities - not just in London but across the UK Sadiq Khan London Mayor Sadiq Khan said the meeting is a step towards making London “safer for everyone”. He said: “This meeting is an important milestone to developing a practical and long-term solution to ending the menace of mobile phone crime, which we know is driving violence and criminality in our communities – not just in London but across the UK. “Right now, it is far too easy and profitable for criminals to repurpose and sell on stolen phones. “That must change and is why, alongside strengthening neighbourhood policing and record investment in supporting the police to go after the worst offenders, the Commissioner and I are now working closely with mobile phone industry to develop innovative and technological solutions that make a stolen phone far less desirable and usable by thieves.” Met Commissioner Sir Mark Rowley said the force made “multiple arrests and seized more than 70 stolen phones at a shop selling them onwards” over the past weekend. “But until we design out the ability for phones to be used in the way they currently are, we will be stuck in a vicious circle,” he added. Hamish MacLeod, chief executive of Mobile UK, said: “Mobile operators and the device and operating system manufacturers have several capabilities and measures to deter the theft of mobile phones, including the provision of capabilities which customers can enable, allowing them to track and disable mobile handsets. “We welcome today’s roundtable to discuss with the Mayor of London and the Metropolitan Police further actions, including prioritising mobile theft and prosecutions to deter and reduce these crimes.” Read More Microsoft gets go-ahead to buy Call of Duty maker Activision Incels using TikTok to spread ‘hateful beliefs’, research suggests Duke and Duchess of Sussex call for overhaul of social media Google to trial AI in UK traffic light systems to reduce stop-and-go emissions Broadband customers face £150 hikes because of ‘outrageous’ rises – Which? Rise of AI chatbots ‘worrying’ after man urged to kill Queen, psychologist warns
2023-10-17 13:47

TSMC third-quarter profit to slide 30%, focus on how much growth to come
By Sarah Wu and Ben Blanchard TAIPEI Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co Ltd is expected to report a 30%
2023-10-17 11:50

China's Baidu unveils latest version of its Ernie AI model
BEIJING Baidu on Tuesday unveiled the newest version of its generative artificial intelligence (AI) model, Ernie 4.0. Ernie
2023-10-17 10:18

Climate Tech Investing Slides More Than 40% Over Past 12 Months
Climate tech is no longer a bright spot in a challenging investment landscape. Private market equity and grant
2023-10-17 09:46
