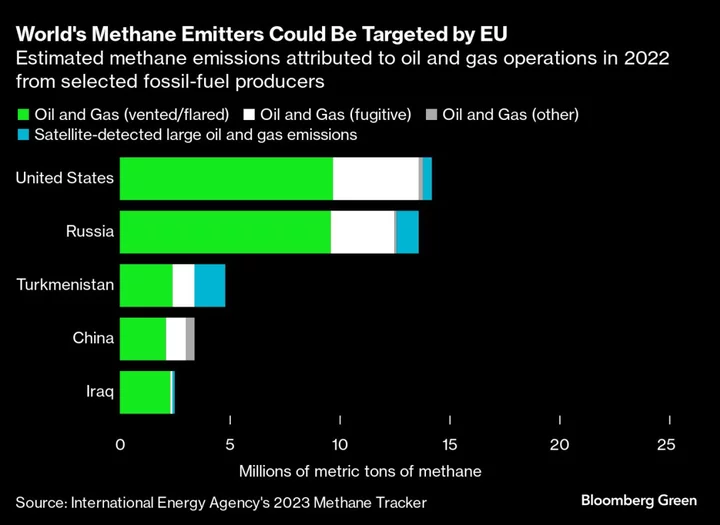
Europe Warns Methane Polluters as Bloc Pushes to Slash Emissions
The European Union aims to slash methane emissions by clinching a deal that could have global ramifications if
2023-11-14 12:19
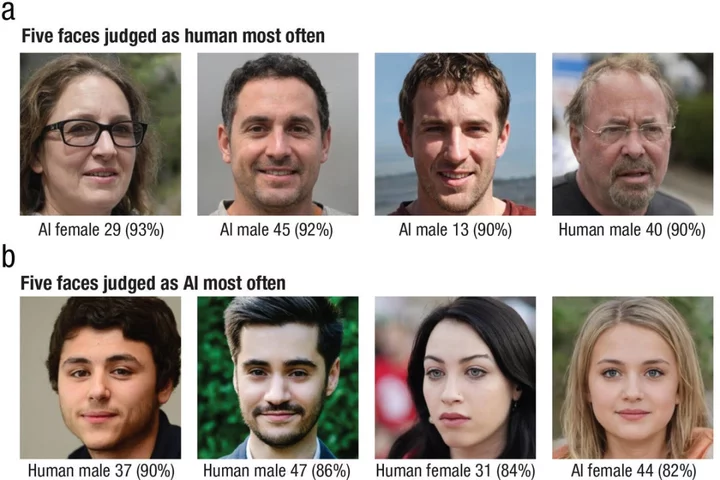
AI can create Caucasian faces that look more real than actual humans – study
Artificial intelligence (AI) can generate Caucasian faces that seem more realistic than actual human faces, according to a new study. As per the research, published in Psychological Science and led by experts at the Australian National University (ANU), more people thought the AI-generated white faces were human than the faces of real people. The study found, however, that the same did not apply to faces generated of people of colour. If white AI faces are consistently perceived as more realistic, this technology could have profound implications for people of colour by ultimately reinforcing racial biases online Dr Amy Dawel According to senior author of the paper, Dr Amy Dawel, the reason for the notable difference between generated Caucasian faces and people of colour comes down to the fact that AI algorithms are trained disproportionately on white faces. Dr Dawel said: “If white AI faces are consistently perceived as more realistic, this technology could have profound implications for people of colour by ultimately reinforcing racial biases online. “This problem is already apparent in current AI technologies used to create professional-looking headshots. “When used for people of colour, the AI is altering their skin and eye colour to those of white people.” Researchers found when it comes to AI “hyper-realism”, most people did not realise they were being fooled. Study co-author and ANU PhD candidate Elizabeth Miller said researchers found that most of the study participants who were most confident that their answers were correct paradoxically thought that the AI faces were real. She said: “This means people who are mistaking AI imposters for real people don’t know they are being tricked.” The researchers were also able to discover why AI faces are fooling people. Although there were still physical differences between the AI and human faces, study participants still managed to misinterpret them. Dr Dawel revealed more in-proportion faces were typical signs that AI had generated a face. However, people mistook it as a sign of humanness. She added: “We can’t rely on these physical cues for long. AI technology is advancing so quickly that the differences between AI and human faces will probably disappear soon.” She said this could have profound implications regarding online misinformation and identity theft. Dr Dawel urged public transparency around AI so society can identify issues with the technology before they become more significant problems. “Given that humans can no longer detect AI faces, society needs tools that can accurately identify AI imposters,” she said. “Educating people about the perceived realism of AI faces could help make the public appropriately sceptical about the images they’re seeing online.” Read More AI among the biggest threats to the UK, cyber security agency warns Meta faces renewed criticism over end-to-end encryption amid child safety fears Call of Duty launch sparks record traffic on broadband networks Crypto investment fraud warning issued by major bank Council investigating extent of cyber attack that affected website and systems Setback for Ireland as EU legal adviser recommends revisit of Apple tax case
2023-11-14 10:58

AI among the biggest threats to the UK, cyber security agency warns
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), as well aggressive state-aligned groups pose a significant threat to critical infrastructure, the UK’s cyber security agency has said. In its annual review, the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) warned ongoing geopolitical challenges and AI also posed a threat to UK elections. Published on Tuesday, the NCSC’s Annual Review said the Centre, which is part of GCHQ, had seen the emergence of a new type of cyber adversary in the last year – state-aligned actors who are ideologically, rather than financially, motivated. Beyond the present challenges, we are very aware of the threats on the horizon, including rapid advancements in tech and the growing market for cyber capabilities Lindy Cameron, NCSC The NCSC highlighted China and Russia as enduring and significant threats to UK cyber security, noting that many of the new state-aligned groups it had seen appear were sympathetic to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. On artificial intelligence, the NCSC warned that the next general election in the UK, expected next year, will be the first to take place against the backdrop of significant advances in AI, which it said would enable and enhance existing challenges. The cyber security agency said that large language models (LLMs) – the technology apps such as ChatGPT are built on – would almost certainly be used to generate fake content as part of disinformation campaigns to disrupt the democratic process. At the first AI Safety Summit, held in the UK earlier this month, industry figures and world leaders warned of the potential for AI to help cybercriminals carry out more sophisticated cyber attacks. “The last year has seen a significant evolution in the cyber threat to the UK – not least because of Russia’s ongoing invasion of Ukraine but also from the availability and capability of emerging tech,” NCSC chief executive Lindy Cameron said. “As our annual review shows, the NCSC and our partners have supported Government, the public and private sector, citizens, and organisations of all sizes across the UK to raise awareness of the cyber threats and improve our collective resilience. “Beyond the present challenges, we are very aware of the threats on the horizon, including rapid advancements in tech and the growing market for cyber capabilities. “We are committed to facing those head on and keeping the UK at the forefront of cyber security.” The annual review said work needed to be done to ensure the UK kept pace with the changing threats, particularly in relation to enhancing cyber resilience in the nation’s infrastructure. Read More Meta faces renewed criticism over end-to-end encryption amid child safety fears Call of Duty launch sparks record traffic on broadband networks Crypto investment fraud warning issued by major bank Council investigating extent of cyber attack that affected website and systems Setback for Ireland as EU legal adviser recommends revisit of Apple tax case Smartphones ‘may be able to detect how drunk a person is with 98% accuracy’
2023-11-14 08:29

GPU tech supplier Imagination Technologies lays off 20% of staff -sources
By Max A. Cherney (Reuters) -Chip technology design maker Imagination Technologies plans to lay off 20% of the company’s staff,
2023-11-14 07:29

Senator asks Treasury to bar Chinese battery firms, minerals from US EV tax credits
By David Shepardson WASHINGTON (Reuters) -Democratic Senator Joe Manchin urged the U.S. Treasury on Monday to adopt the "strictest possible
2023-11-14 06:22

EU Reaches Deal to Boost Domestic Supplies of Key Raw Materials
The European Union reached a deal on measures to become more self-sufficient in the key raw materials it
2023-11-14 02:49

A new beetle with bottle opener shaped penis has been named 'Carlsberg'
A newly discovered species of beetle that has sex organs shaped like a bottle opener has been named Carlsberg after the beer giant. Many animals face an uncertain future thanks to changes to their habitats. So, when a brand new species is discovered it is an exciting thing for scientists. It allows experts an opportunity to get creative with the name, with some previous examples including a new rainbow fly species named after RuPaul and an ancient egg-laying mammal named after Sir David Attenborough. Now researchers from the University of Copenhagen have discovered six new South American beetle species of the rove beetle genus Loncovilius, one of which caught the eye. Because the insect’s penis was shaped like a bottle opener. The unusual shape led to researchers giving it the very apt name – Loncovilius carlsbergi. Biologist Aslak Kappel Hansen, from the Natural History Museum of Denmark, explained: “This species is characterised, among other things, by the fact that the male’s sexual organ is shaped remarkably like a bottle opener. "Therefore, we thought it is obvious to dedicate this species to the Carlsberg Foundation, which has generously supported independent research for many years. “Their support for various projects, expeditions, or purchase of the scientific instruments at the Natural History Museum of Denmark contributes to the discovery of new species on our planet.” Hansen explained that the beetles’ penises evolve to be differently shaped, allowing them to only reproduce with members of the same species. “As such,” Hansen explained, “they are often the best way to identify a species. That’s why entomologists like us are always quick to examine insect genitalia when describing a species. The unique shape of each species’ genitals ensures that it can only reproduce with the same species”. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-14 01:53

This is the potential reason humans experience deja vu, according to experts
It’s happened to us all. Maybe you’re walking down the street, or sitting on the bus, or even just sending an email – then suddenly, you realise you’ve been here before. Déjà vu can be a puzzling thing. It literally means already seen in English, and it remains pretty mysterious as to why we feel it. Now, scientists have a couple of theories. Sanam Hafeez, a clinical psychologist, told Fox News: "It refers to the eerie and distinct feeling that one has already experienced the current situation or event, even though it’s a new and unfamiliar occurrence. "It feels like a powerful wave of familiarity with the present moment as if the person is re-living a past experience. "Some suggest it may be linked to how memories are processed in the brain, potentially involving delays or errors in memory retrievals." She added that it may be because the brain is processing information through multiple pathways at the same time, creating the illusion of a memory when you are living in the present moment. She said: "Regardless of the precise mechanism, déjà vu is a transient and common experience that lasts only briefly, affecting people of all ages and not considered a pathological condition. "While it remains a puzzle, déjà vu continues to be a fascinating facet of human consciousness." "It is also important to note that déjà vu is not associated with any particular medical or psychological condition. It is usually a brief and transient experience and is considered a normal aspect of human perception and memory." About two-thirds of people in good health experience déjà vu during their lifetime, according to WebMD, though it is more likely to happen to people aged 15 to 25. The website explains: "A familiar sight or sound can trigger the feeling. You may walk into a room in a building you’ve never visited yet feel like you know it intimately." Health.com adds: "People with more education, those who travel a lot and people who can recall their dreams are also more likely to experience déjà vu." How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-14 01:46

Breakthrough device cleans dirty water and turns it into fuel
Scientists have built a breakthrough device that can clean dirty water and turn it into clean hydrogen fuel. The “simple” device could be used in areas without resources or places where people live off the grid. And it is just one example of the many solutions that will be required to respond to pollution and give people access to both clean fuel and water, the researchers behind it say. The system is inspired by photosynthesis, the process where plants turn light into food. But previous versions of those “artificial leaves” have required clean water sources – whereas the new device can be used with polluted water and even produce clean drinking water at the same time. As such, scientists believe that it could help solve two problems at once: making green fuel and cleaning water so that it is ready to drink. “Bringing together solar fuels production and water purification in a single device is tricky,” said Chanon Pornrungroj from the University of Cambridge, the paper’s co-lead author. “Solar-driven water splitting, where water molecules are broken down into hydrogen and oxygen, need to start with totally pure water because any contaminants can poison the catalyst or cause unwanted chemical side-reactions.” The system uses a carbon mesh to absorb light and heat, creating water favour that is then turned into hydrogen for fuel by a photocatalyst. That carbon mesh also repels water, so that the system can float and its important parts can be kept from being damaged by water. The device is also able to harness more of the Sun’s energy than previous examples, which have used only a small portion of the spectrum of light. The new system has a white layer on top to absorb UV rays, with the rest being used lower down to vaporise the water. “This way, we’re making better use of the light – we get the vapour for hydrogen production, and the rest is water vapour,” said Dr Pornrungroj. “This way, we’re truly mimicking a real leaf, since we’ve now been able to incorporate the process of transpiration.” The researchers behind the breakthrough noted that the system was simple to make, and was especially able to deal with very polluted water. As such, it could be a key way of working towards a sustainable future, they said – even though it is just a proof of concept for now. “The climate crisis and issues around pollution and health are closely related, and developing an approach that could help address both would be a game-changer for so many people,” said Cambridge’s Erwin Reisner, who led the work. The device is described in a new paper, ‘Hybrid photothermal-photocatalyst sheets for solar-driven overall water splitting coupled to water purification’, published in Nature Water today. Read More First carbon capture plant opens in the US to help avoid climate catastrophe Breakthrough solar system outperforms military-grade diesel generator Solar panel world record smashed with ‘miracle material’
2023-11-14 00:20
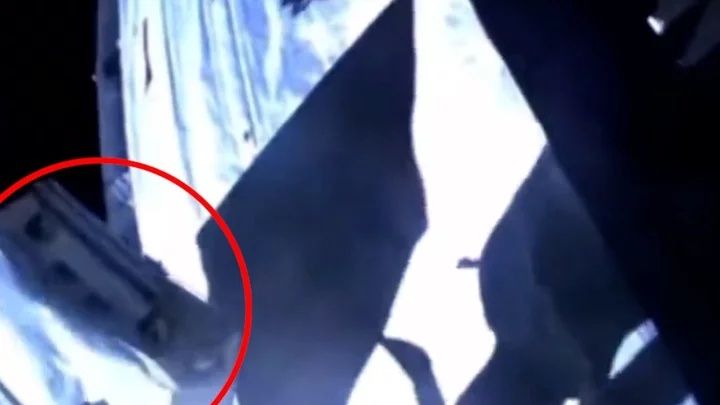

Astronauts dropped a toolbag in space which you can see with just binoculars
Whilst repairing external parts of the International Space Station (ISS) last week, astronauts dropped a toolbag. And it turns out you just need a pair of binoculars to see it. The bag is tiny compared to the ISS, but it's reflective enough that when it catches the Sun's light it reaches 6th magnitude from Earth according to Earthsky. Under very dark skies, some powerful binoculars or a small telescope might allow you to see the toolbag. The bag is moving at almost exactly the same speed as the ISS on the same path and about a minute ahead of it. Over time, however, its distance from the ISS will grow, making it harder to find. Eventually, its orbit will become low enough that it burns up from friction with the outer atmosphere. You can find out if you have the ISS passing overhead here if you want to have a chance of seeing the bag. The ISS can only be seen easily when it's dark on the ground and sunlight is still catching it. It means it's usually best seen when the skies are not fully dark - so around dusk or dawn. Here is what the toolbag looks like from space: Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel
2023-11-13 22:51
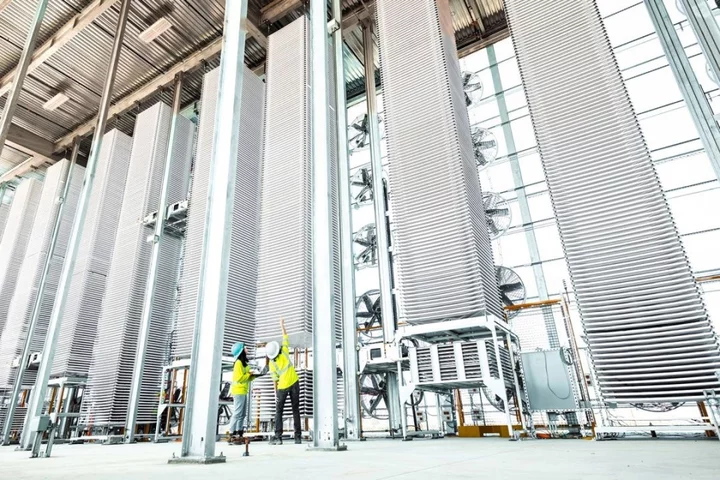

First carbon capture plant opens in the US to help avoid climate catastrophe
The first ever commercial-scale carbon capture facility has begun operations in the US, marking a significant milestone towards meeting cleaner climate targets. San Francisco-based startup Heirloom Carbon Technologies opened the carbon removal plant in Tracy, California, on Thursday, claiming it will be able to capture 1,000 metric tons per year of CO2. The renewable energy-powered plant leverages the natural power of limestone to remove CO2 from the atmosphere. “Rocks are some of the planet’s most vital carbon sinks. Over geological timescales, CO2 from the atmosphere binds to minerals and permanently turns to rock - a process known as carbon mineralisation,” Heirloom notes on its website. “Limestone is one of the most abundant rocks on the planet, capturing massive amounts of CO2 from the air over years, Heirloom’s technology accelerates this natural process to just days.” The process works by placing hundreds of trays of calcium oxide powder onto 12-metre-tall racks, which turns into limestone as it comes into contact with CO2 from the atmosphere. Workers then heat up the limestone, which releases the carbon dioxide and turns it back into calcium oxide that can be reused to capture more CO2. The atmospheric CO2 that is captured through the facility is permanently sequestered in concrete through a partnership between Heirloom and CarbonCure Technologies. Heirloom aims to remove 1 billion tons of CO2 from the atmosphere by 2035 using its Direct Air Capture technology, with funding coming from companies buying carbon removal credits in order to offset their own emissions. It is not the first company to achieve direct carbon capture from the atmosphere, but Heirloom claims to be the first in the US. Switzerland-based startup Climeworks AG has commercial facilities in Switzerland and Iceland, which are capable of removing 4,000 metric tons of CO2 each year. Carbon capture technologies have faced criticism for the large amounts of energy and resources they require to operate, though some scientists claim they will be a vital part of keeping global net emissions below zero by 2050. In response to criticism from green groups in 2021 claiming that such projects are a costly distraction, Professor Stuart Haszeldine from Edinburgh University said: “Carbon capture and storage is going to be the only effective way we have in the short term to prevent our steel industry, cement manufacture and many other processes from continuing to pour emissions into the atmosphere. “If we are to have any hope of keeping global temperature [increases] down below 2C then we desperately need to develop ways to capture and store carbon dioxide.” The US government announced in August that it would fund a $1.2 billion effort to develop and deploy carbon capture technologies, with Heirloom among the recipients. Major companies, including Microsoft, have already signed deals to purchase carbon removal credits from Heirloom. Read More Breakthrough solar system outperforms military-grade diesel generator Breakthrough solar system outperforms military-grade diesel generator Solar panel world record smashed with ‘miracle material’ Google issues three-week warning to Gmail account holders
2023-11-13 22:46

Eating strawberries can reduce the risks of dementia, study finds
A recent study has found that eating strawberries daily could reduce the risk of developing dementia. Researchers at the University of Cincinnati claim that by eating the fruit every day, certain people of middle age could reduce their risk of dementia. The 12-week study published in Nutrients had 30 overweight patients - who had complained of mild cognitive impairment - abstain from eating berries, aside from a daily packet of supplement powder mixed with water and consumed with breakfast. Half of the participants, who were 50 to 65 years old, received a powder that contained the equivalent of one cup of whole strawberries (the standard serving size), whilst the other half received a placebo. Participants' long-term memory, mood, and metabolic health were measured by researchers. The team found that those who had taken the strawberry powder had performed better on a wordlist learning test, as well as having a significant reduction in depressive symptoms. "Both strawberries and blueberries contain antioxidants called anthocyanins, which have been implicated in a variety of berry health benefits such as metabolic and cognitive enhancements," said Robert Krikorian, professor emeritus in the UC College of Medicine's Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Neuroscience. "There is epidemiological data suggesting that people who consume strawberries or blueberries regularly have a slower rate of cognitive decline with ageing." Ellagitannins and ellagic acid are also found in strawberries, which are known to possess anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer properties. Krikorian went on to explain that strawberries may have improved cognitive function by reducing inflammation in the brain. "Executive abilities begin to decline in midlife and excess abdominal fat, as in insulin resistance and obesity, will tend to increase inflammation, including in the brain," he explained. The university did, however, acknowledge that Krikorian's research was partly funded by the California Strawberry Commission. Although said that the group had no role in the design of the study, data collection and analysis, or publication of the results. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel
2023-11-13 20:48
