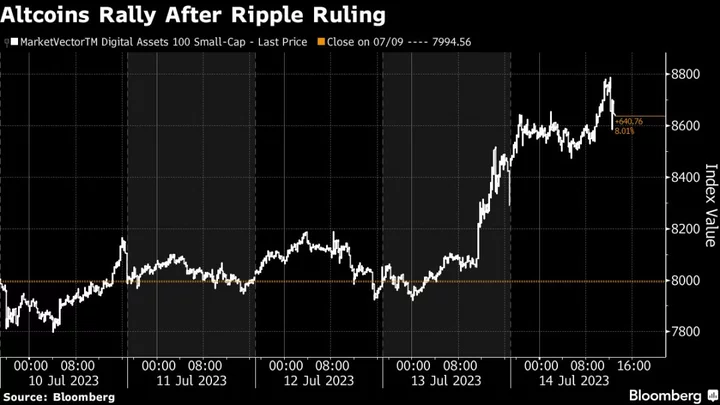
Crypto Altcoins Outperform as Ripple Court Ruling Spurs FOMO
Smaller, lesser-known digital tokens such as Solana and Avalanche are outperforming Bitcoin for a second day after a
2023-07-15 01:47

Microsoft changes its default typeface for only the second ever time
Microsoft is changing its default typeface for only the second ever time. For 15 years, Microsoft Office and other software has opened with one particular typeface: Calibri. By virtue of being the default look on some of the world’s most popular software, it might have been seen more than any other set of letters. Before that, Microsoft’s documents started with Times New Roman, a typeface that itself became famous largely as a result of being the default option. Now, however, Microsoft is moving on. Microsoft said that it had taken the decision in part because the technology used to display the typeface had changed, and that it needed to update for the higher resolution screens that are used today. And it is doing so with “Aptos”, a new font that was specially commissioned for the company, in a process it described as “exciting, but also intimidating”. It had done so with a view to finding a new font that could replace Calibre and have “sharpness, uniformity, and be great for display type”. Microsoft initially commissioned five new fonts, with the hope that one of them would become the default: Bierstadt, Grandview, Seaford, Skeena, and Tenorite. It added all of them to its software and allowed people to choose them from the picker and give feedback. Based on that information, Microsoft chose “Bierstadt”, and renamed it Aptos, though it will still live on under the old name too. The other fonts that lost out will also stay in the drop-down picker. Aptos will become the default typeface on Microsoft’s software, such as 365, which itself has replaced the well known Office suite. That will mean becoming the default font on Word, Outlook, PowerPoint and Excel and be seen by the hundreds of millions of people who use the software. The rollout will take place over the “next few months”, the company said. The font was named Aptos by its designer, Steve Matteson, after a town in Santa Cruz, where Microsoft said the “widely ranging landscape and climate epitomizes the font’s versatility”. The font was designed with “humanity”, Mr Matteson said, and with a view to allowing it to be “more universal and less mechanical or institutional”, he said in a blog post by Microsoft. For those that don’t like the new font, Microsoft has always offered the option to change the default font – including back to Calibri or Times New Roman. Read More Microsoft’s attempt to buy Call of Duty developer reaches huge new development Twitter starts making payments to its most controversial users What striking Hollywood writers and actors fear about AI replacing roles
2023-07-15 01:24

AT&T Falls to 29-Year Low Amid Concerns of Cleanup Costs
AT&T Inc. shares hit an almost three-decade low Friday amid growing concerns of the potentially high costs the
2023-07-15 00:52

US officials worry about 'chilling effect' on combating election disinformation after order limiting Biden administration contact with social platforms
A federal judge's move to limit how some US agencies communicate with social media companies could have a "chilling effect" on how the federal government and states address election-related disinformation just as the 2024 election cycle get underway, according to interviews with current and former US officials.
2023-07-14 23:52

Scientists have discovered how to reverse ageing
Ageing could soon be a thing of the past, following the latest development in chemical therapy and anti-ageing research. The research focuses on anti-ageing genes and adds to a previous study which won a Nobel Prize, focusing on small cell cultures. A team from Harvard Medical School is leading the study into genes called Yamanaka factors. The research focuses on turning cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which effectively turns the cell young again. If the research targeted cells in this fashion, it could ultimately reverse the physical impacts of ageing. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter There’s a great deal to consider when it comes to treatment like this, as the effect of ageing is a natural way the human body protects against harmful mutations like cancer. However, the new research published in the journal Aging claims that the process doesn’t create cells that are prone to cancer. The results showed that six chemical mixes were found that showed scientist could make cells biologically “younger” in the space of just seven days. After previous research conducted on mice, the team behind the study is looking to thake the study to human trials by 2024. David A. Sinclair is Professor in the Department of Genetics and lead scientist on the project. He released a statement saying: “Until recently, the best we could do was slow aging. New discoveries suggest we can now reverse it.” He added: “This process has previously required gene therapy, limiting its widespread use.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-14 23:19
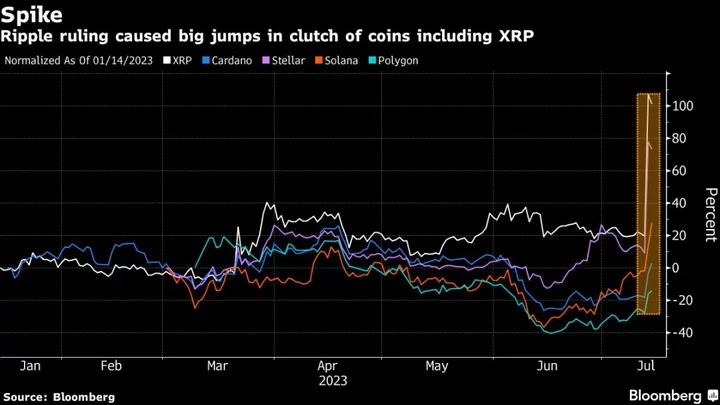
Crypto Market Is Celebrating SEC’s Setback in Ripple Suit. But the Case Is Far From Settled
A US Securities and Exchange Commission lawsuit against Ripple Labs Inc. has kept crypto on edge since 2020
2023-07-14 23:00

Nasa has found ‘diverse organic matter’ on surface of Mars
Nasa has discovered “diverse organic matter” on the surface of Mars, which could change our understanding of the red planet and the search for life in the universe. The Perseverance rover made the discovery in the Jezero Crater on Mars and a number of different explanations for the existence of the material have been posited. The materials could have been formed when water and dust interacted, or was dropped onto the planet by dust or meteors. Authors of the new study also refused to rule out that the materials are “biotic”, or came about due to the existence of life on the surface. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The findings could have a big impact on the continued search for alien life, with research into the organic matter on the surface telling us more about the existence of carbon sources on Mars. The Jezero crater has been explored by The Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals (Sherloc) instrument on the rover since February 2021. The crater is the site of an ancient lake basin and all 10 target sites explored within it came back with signs of organic molecules. Even if the materials are not biological in origin, research into them could be crucial in the search for alien life, according to the researchers. “Not all organics are biological in origin. Observing spatial relationships between minerals and organics is necessary when evaluating organic origins and potential biosignatures. Everything we know of life on Earth is limited to what is preserved in the rock-mineral record. On Earth, biosignatures are found in certain minerals and some minerals are better at preserving organics than others,” said Ashley E Murphy, a researcher at the Planetary Science Institute and co-author on the new paper. “Mars may have had a similar early geologic history to Earth so we use our knowledge of life as we know it on Earth for where to look for potential evidence of past life on Mars. Mapping organics allows for a better understanding of if the Martian carbon cycle is similar to or different from Earth, and the potential of Mars to host life.” Writing in the Nature journal, the authors said: “Our findings suggest there may be a diversity of aromatic molecules prevalent on the Martian surface, and these materials persist despite exposure to surface conditions. “These potential organic molecules are largely found within minerals linked to aqueous processes, indicating that these processes may have had a key role in organic synthesis, transport or preservation.” The findings are published in a new article, ‘Diverse organic-mineral associations in Jezero crater, Mars’, in Nature. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-14 22:48

Bitcoin near 13-month high as investors welcome Ripple ruling
By Tom Westbrook and Rae Wee SINGAPORE Bitcoin was hovering near its highest so far this year on
2023-07-14 22:22

Twitter starts making payments to its controversial users, including $20k to Andrew Tate
Elon Musk’s Twitter has started sending payments to some of its most most popular and controversial users. The scheme is part of what Twitter says is an ad revenue sharing programme, which will let people keep some of the money generated from showing advertising in the replies to their tweets. It is still not clear exactly how the size of the payments is decided, and some have reported receiving tens of thousands of dollars. Users must be subscribed to Twitter Blue and have at least five million impressions on their posts. The payments have gone to popular Twitter users that include some of the most controversial on the site. Andrew Tate, for instance, shared that he had received a payment of $20,000 from Twitter. Many of those who have received payouts have had their accounts boosted by Elon Musk in recent months. Mr Musk has often replied to some of the site’s users – especially those focused on politics – seemingly in an attempt to draw more attention to those accounts. Some critics of Mr Musk had suggested that he had favoured right-wing accounts in the first payouts. But the nature of the accounts may also be affected by the fact that users must pay for Twitter’s premium Blue membership – which has been embraced by many of Mr Musk’s political allies – and other non-political accounts did post that they had received payments. Mr Musk first announced the ad sharing plan in February, saying that the idea was to allow people to “create an interesting thread and get paid for it”. The payments that are being sent to the first users are based on the impressions their posts have gathered since that plan was first announced, he said in a recent tweet. In a thread, Twitter said that the scheme was intended to allow people to make a living directly on Twitter. Until now, users have had to monetise their following in other ways – usually by sending traffic to other platforms. “We’re expanding our creator monetisation offering to include ads revenue sharing for creators. This means that creators can get a share in ad revenue, starting in the replies to their posts,” the company wrote on its official account. “This is part of our effort to help people earn a living directly on Twitter. We’re rolling out the program more broadly later this month and all eligible creators will be able to apply. Go get yourself something nice!” Twitter said that it will soon launch an application process for ads revenue sharing. It is not clear how those who received early payments were chosen. After some users attempted to calculate how much money accounts were receiving per view, Mr Musk cautioned that the system includes some other controls. He said that the payouts are “not exactly per impression”, and were instead based on how many ads were shown to other verified users, which he said was done to ensure that people were not able to use bots to drive up their impressions. Mr Musk also said that he had given the money generated from his own tweets to the creator payout pool. Twitter’s announcement comes soon after Meta announced its own competitor to the site, in the form of Threads. That app has grown rapidly – and while it is still unclear how much it has affected the user base of Twitter, some away from the company have said that the site’s traffic is “tanking”.
2023-07-14 21:21

Scientists uncover supergiant ’space ghost’ in night sky
Scientists have been studying a “space ghost” which could be due to explode in just a few decades, changing the night sky forever – if it hasn’t already, that is. The object in question is a large star called Betelgeuse and the scientific community is divided over whether or not it’s already become a supernova. One theory states that the light from Betelgeuse takes so long to reach Earth it could mean the huge explosion has already taken place. Betelgeuse has been a supergiant red star for an estimated 40,000 years, but that could change relatively soon. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Michael Shara is the curator of astrophysics at the American Museum of Natural History. He told the US Sun: "Betelgeuse lies somewhere between about 450 and 550 light years from Earth." He went on to say: "Betelgeuse’s position appears to change slightly, as seen from Earth, between June and December, when the Earth is on opposite sides of its orbit around the Sun. "That tiny change in position is a direct measure of the distance to Betelgeuse." He went on to expand on the theory by saying: "Let's assume that Betelgeuse is precisely 500 light years distant. "If Betelgeuse exploded as a supernova anytime in the past 499 years, the light from that event has not yet had enough time to reach Earth…so we have no way of knowing if Betelgeuse has already blown up. "If, for example, Betelgeuse blew up in 1600 AD, we won’t know about it until the year 2100. But if it blew up on August 1, 1523, then on August 1, 2023 it will become about as bright as the full Moon. "The only naked eye supernova of the past century occurred in 1987… all astronomers would be thrilled and delighted if Betelgeuse (or another dying star) graced our night sky with a supernova in the coming decades." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-14 20:26
Why trolling the likes of Andrew Tate is actually earning them money
Since Elon Musk’s takeover of Twitter, many controversial users who were previously banned from the platform have been allowed back on and are flourishing. Users such as Andrew Tate have regained a platform to spout his harmful views to millions of users. But, while it may feel satisfying to troll such users, engaging with their tweets actually earns them money. Here’s why: Twitter recently announced it was paying out thousands of dollars in advertising revenue to users to “benefit” from their high engagement on tweets, earning more money the higher their engagement is. As part of Twitter’s Ad Revenue sharing program, users require “5M+ Tweet impressions in each month for the last 3 months”. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter On Thursday (13 July), some eligible users began receiving notifications of how much money they would receive. The highest earner, Dogecoin co-founder Billy Markus, known online as Shibetoshi Nakamoto, earned $37,050. Tate also revealed in a tweet that he earned $20,379 from ad revenue generated in the reply threads under his posts. The money comes from the ad revenue generated in their replies below the content they post on the platform, and is paid out via the Stripe account that the user registered for creator subscriptions with. Twitter staffer, Patrick Traughber, said: “Excited to start sending our first payments to creators for ads revenue sharing today. “Creators are the lifeblood of this platform, and it's great to see so many creators I follow getting paid today. The program will be expanding soon—more to come!” The cash payouts come just a week after Meta launched its rival text-based platform, Threads. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-14 19:49
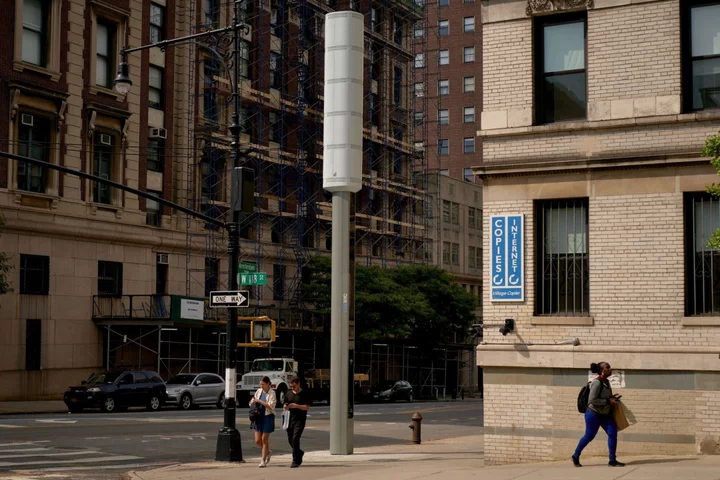

The Wealthy New York Enclave Fighting Against ‘Ugly’ 5G Towers
In New York, an Upper East Side enclave is fighting city plans for curbside 5G towers, calling them
2023-07-14 19:28
