
Dell Sales Top Estimates in Positive Signal for PC Market
Dell Technologies Inc. reported better-than-expected sales of personal computers and data center hardware, fueling hopes of a recovery
2023-09-01 04:56

Broadcom forecasts fourth-quarter revenue below Wall Street expectations
Broadcom forecast fourth-quarter revenue below Wall Street estimates on Thursday, on worries bleak enterprise spending and stiff competition
2023-09-01 04:25

Dell beats quarterly revenue estimates on AI strength, demand recovery
Dell Technologies beat quarterly revenue expectations on Thursday, as it benefited from the artificial intelligence (AI) boom and
2023-09-01 04:22

Intel Rallies on CEO Gelsinger’s Optimistic Comments
Intel Corp. Chief Executive Officer Pat Gelsinger said the chipmaker is on course to hit its third-quarter forecasts,
2023-09-01 03:48
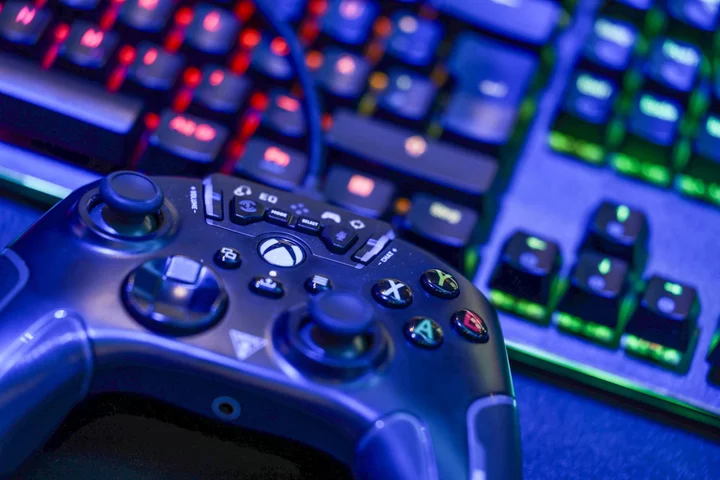

Microsoft’s Hotly Awaited ‘Starfield’ Game Scores With Critics
Microsoft Corp. shot for the sky with Starfield, its ambitious new space role-playing video game, and so far
2023-09-01 03:25

Virtu Sues to Block Tech Executive’s Move to Rival Clear Street
Market-making firm Virtu Financial Inc. sued to block its former head of client technology from accepting a senior
2023-09-01 01:47
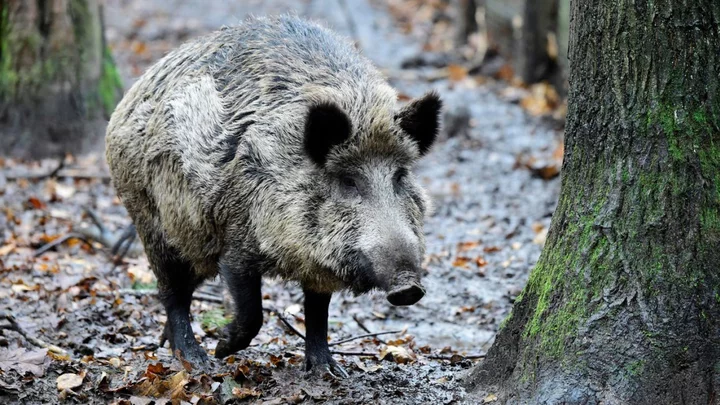

Wild boar in Germany are strangely radioactive – now scientists know why
Wild boar in southeastern Germany have long contained high levels of radioactive substances, which has been attributed to the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster. But as radioactivity levels have fallen in other animals, they have stayed much the same among boar. Now, scientists have worked out the secret behind the so-called “wild boar paradox”. Research shows there is another culprit for the high levels of radioactivity: nuclear weapons tests from the mid-20th century. And both the weapons and the nuclear reactor meltdown continue contaminating the boar because of their diet. While the muscular boar seem healthy, the dangerous levels of radioactive caesium, the main contaminator, have prompted people to stop hunting them. In turn, there is now an overpopulation issue. “Our work reveals deeper insights into the notorious radio-cesium contamination in Bavarian wild boars beyond the total radionuclide quantification only,” radioecologist Felix Stäger from Leibniz University Hannover wrote in a paper. After a nuclear incident, radioactive materials can pose a significant threat to ecosystems. This happened after the Chernobyl meltdown in 1986, where there was an increase in radioactive caesium contamination. The main component of this, caesium-137, has a half-life of about 30 years, meaning it loses its radioactivity fairly quickly. However, caesium-135, which is created via nuclear fission, is far more stable. It has a half-life of more than 2m years. The ratio of cesium-135 compared to cesium-137 can help us work out where the cesium came from. A high ratio indicates nuclear weapon explosions, while a low ratio points to nuclear reactors like Chernobyl. So the researchers analysed caesium levels from 48 wild boar meat samples from 11 regions of Bavaria. It turns out that nuclear weapons testing was responsible for between 12 per cent and 68 per cent of the unsafe contamination in the samples. “All samples exhibit signatures of mixing,” wrote the researchers. “Nuclear weapons fallout and [Chernobyl] have mixed in the Bavarian soil, the release maxima of which were about 20−30 years apart.” So while Chernobyl remains the main source of caesium in wild boar, about a quarter of the samples showed enough contributions from weapons fallout to exceed safety limits even before the reactor meltdown comes into account. And because wild boar eat so many truffles, it has been exacerbated. The fungus absorbs high levels of contamination from both sources. Wild boars' diets, which include underground truffles, have absorbed varying levels of contamination from both sources, which has contributed to the animals' persistent radioactivity. “This study illustrates that strategic decisions to conduct atmospheric nuclear tests 60−80 years ago still impact remote natural environments, wildlife, and a human food source today,” the authors concluded. The study was published in Environmental Science & Technology. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-01 00:53

Twitter/X indicates it will start collecting ‘biometric information’ and ‘employment history’
X, formerly known as Twitter, wants to start collecting “biometric information” about its users, as well as their employment history. Elon Musk’s company is seemingly giving itself permission to fingerprints or facial features, or the other kind of information about people’s bodies that are usually used in biometrics. That is according to a change to its privacy policy that was first reported by Bloomberg. “Based on your consent, we may collect and use your biometric information for safety, security, and identification purposes,” the new rules state. They will go into effect at the end of the month. The policy also allows X to collect “your employment history, educational history, employment preferences, skills and abilities, job search activity and engagement”. The policy does not give any details about where the information will be used, and the company has not elaborated elsewhere. But it has been looking into using biometric data for some features. Earlier this month, for instance, security researcher Nima Owji found that the site was testing a way for users of the premium Twitter Blue service to verify who they are by using a government-issued ID and taking a selfie. A screenshot of the feature showed users being asked to click a button to confirm they “consent to X sharing images of my ID, including biometric data” with authentication companies. Elon Musk has also suggested that X could be used for hiring in the future, which may be the purpose of collecting employment information. Last week, X announced a new feature called “X Hiring” which allows companies that pay for the verified badge to include job ads on their profiles. That appears to be part of his plan to turn X into the “everything app”. He has suggested that it could include payments in the future, and he is soon to roll out audio and video calls that will be made with people’s username rather than their phone number. Read More Tesla reportedly under probe over mysterious project to build ‘glass house’ for Musk Elon Musk booed at video games contest as crowds shout: ‘Bring back Twitter!’ Meta could finally launch Threads feature everyone is waiting for
2023-09-01 00:21
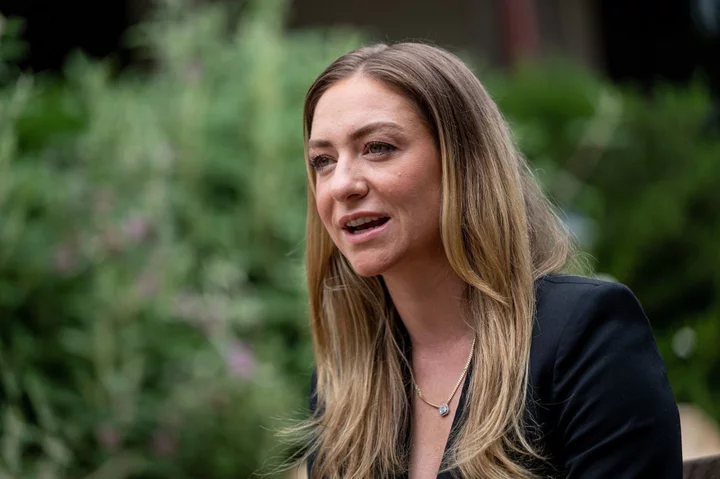

Bumble CEO Predicts AI Dating Coach Will Teach You How to Flirt
There are many predictions about our AI future that veer into Black Mirror territory, but perhaps the most
2023-08-31 23:18
Broadcom’s Earnings Will Test Whether AI Euphoria Is Fading
Having unlocked stock market riches in 2023, the “artificial intelligence” catchphrase faces a shift in sentiment — and
2023-08-31 22:21

'Altcoins' central to Hong Kong crypto firm HashKey’s first liquid fund
(Corrects company name HashKey with capitalisation of letter K) By Summer Zhen HONG KONG (Reuters) -The first secondary crypto market
2023-08-31 21:29
Scientists may have just found a cure for alcoholism
Alcohol addiction ruins millions of lives every year, but scientists may have found a cure for this terrible affliction. A new treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD) has been trialled in monkeys with impressive results and, if these translate to human trials, the impact could be monumental. A team of neuroscientists and physiologists from across the US tested a new type of gene therapy to see if they could directly target the underlying brain circuitry associated with sustained heavy drinking. As they noted, in the journal Nature Medicine, people suffering from AUD commonly return to alcohol use even if they attempt to quit. This is largely to do with what’s known as mesolimbic dopamine (DA) signalling – meaning how the central nervous system circuit communicates the feelgood neurotransmitter dopamine. A protein called glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is key to keeping these neurons in this reward circuitry functioning. However, experts have found that levels of GDNF are reduced in people with AUD during periods of alcohol abstinence, most notably in a region of the brain called the ventral tegmental area (VTA), as IFLScience notes. Therefore, the researchers decided to test whether using gene therapy to deliver more GDNF to the VTA could help reinforce this crucial dopaminergic signalling and prevent patients from suffering an alcoholic relapse. The team of scientists explained how alcohol consumption in non-addicts prompts the release of dopamine, creating a pleasurable buzz feeling, but chronic alcohol use causes the brain to adapt and stop releasing so much dopamine. “So when people are addicted to alcohol, they don’t really feel more pleasure in drinking,” Dr Kathleen Grant, a senior co-author of the study, said in a statement. “It seems that they’re drinking more because they feel a need to maintain an intoxicated state.” For their research, Dr Grant and her colleagues used eight rhesus macaque monkeys, who were exposed to increasing concentrations of alcohol over four 30-day “induction” periods. The monkeys then had free access to alcohol and water for 21 hours a day for six months, during which they developed heavy drinking behaviours. This was then followed by a 12-week abstinence phase, with the GDNF treatment performed four weeks in for half of the subjects. The gene therapy was delivered using a a viral vector containing a copy of the human GDNF gene injected directly into the primate’s VTA, according to IFLScience. And the results were truly jaw-dropping. “Drinking went down to almost zero,” Dr Grant said. “For months on end, these animals would choose to drink water and just avoid drinking alcohol altogether. They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.” The most exciting aspect of their findings is the suggestion that gene therapy could offer a permanent solution for people with the most severe cases of AUD. This will be a welcome glimmer of hope to many, given that some 29.5 million people were diagnosed with AUD in the US alone in 2021, according to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Of these 29.5 million sufferers, almost a million (894,000) were aged between 12 and 17. It’ll likely be some time before we know for sure whether the gene therapy can be rolled out in humans, but it’s an important first step in tackling this devastating disorder. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 19:46
