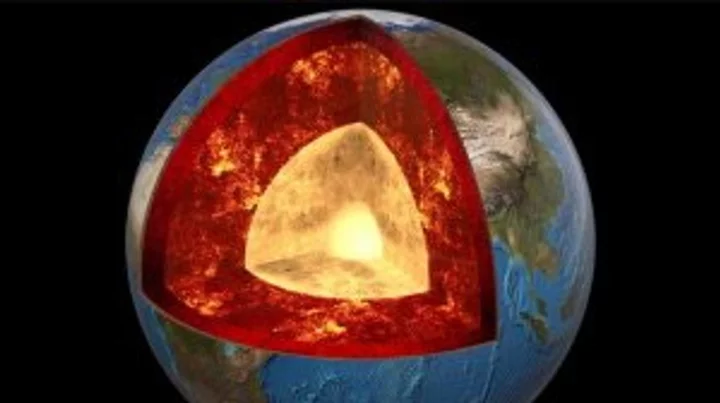
'Mountains' taller than Everest discovered on 'ancient structure' around Earth's core
A new study into the Earth beneath our feet has discovered that an ancient ocean floor structure could be wrapped around the planet's core which could be taller that Mount Everest in some areas. A brand new high-resolution mapping of the core has uncovered things that scientists previously didn't know according to a study that was first published in April. The discovery found that a thin but dense layer sits at around 2,900 kilometers below the surface at the Core Mantle Boundary where rocks meet the molten outer core of the planet. Geologist Samantha Hansen from the University of Alabama is quoted in the study saying: "Seismic investigations, such as ours, provide the highest resolution imaging of the interior structure of our planet, and we are finding that this structure is vastly more complicated than once thought." She adds: "Our research provides important connections between shallow and deep Earth structure and the overall processes driving our planet.” Hansen and her team conducted the research from 15 different stations in Antarctica by using seismic waves created by Earthquakes to create a map of what the inside of the planet looks like. The team identified the unexpected energy within seconds of the boundary-reflected wave from the seismic data. The findings show that although the layer is very thin it does spread for many, many kilometers and has been called the ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZs) due to its strong wave speed reductions. Due to the properties of the ULVZs the experts believe that the layer could vary dramatically in height. Geophysicist Edward Garnero from Arizona State University adds: "The material's thickness varies from a few kilometers to [tens] of kilometers. This suggests we are seeing mountains on the core, in some places up to five times taller than Mt. Everest." These underground mountains could play a significant role in how heat escapes from the Earth's core and power magnetic fields and volcanic eruptions. The team's studies suggest that the layer could encase all of the core but further research will have to be carried out to determine if that is the case. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-10 19:21

G-20 Broadens Debate on AI Risks and Mulls Global Oversight
Leaders at the Group of 20 summit discussed how to harness artificial intelligence for economic development while protecting
2023-09-10 18:23
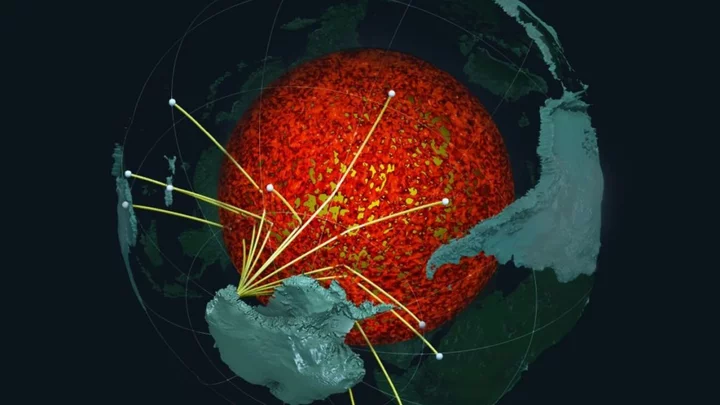
Underground 'mountains' discovered on Earth's core five-times taller than Mt. Everest
A new study into the Earth beneath our feet has discovered that an ancient ocean floor structure could be wrapped around the planet's core which could be taller that Mount Everest in some areas. A brand new high-resolution mapping of the core has uncovered things that scientists previously didn't know according to a study that was first published in April. The discovery found that a thin but dense layer sits at around 2,900 kilometers below the surface at the Core Mantle Boundary where rocks meet the molten outer core of the planet. Geologist Samantha Hansen from the University of Alabama is quoted in the study saying: "Seismic investigations, such as ours, provide the highest resolution imaging of the interior structure of our planet, and we are finding that this structure is vastly more complicated than once thought." She adds: "Our research provides important connections between shallow and deep Earth structure and the overall processes driving our planet.” Hansen and her team conducted the research from 15 different stations in Antarctica by using seismic waves created by Earthquakes to create a map of what the inside of the planet looks like. The team identified the unexpected energy within seconds of the boundary-reflected wave from the seismic data. The findings show that although the layer is very thin it does spread for many, many kilometers and has been called the ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZs) due to its strong wave speed reductions. Due to the properties of the ULVZs the experts believe that the layer could vary dramatically in height. Geophysicist Edward Garnero from Arizona State University adds: "The material's thickness varies from a few kilometers to [tens] of kilometers. This suggests we are seeing mountains on the core, in some places up to five times taller than Mt. Everest." These underground mountains could play a significant role in how heat escapes from the Earth's core and power magnetic fields and volcanic eruptions. The team's studies suggest that the layer could encase all of the core but further research will have to be carried out to determine if that is the case. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-09 19:49

G-20 Welcomes African Union as Member in Nod to Emerging World
The Group of 20 nations agreed to grant the African Union permanent membership status in a move aimed
2023-09-09 14:55

Court eases curbs on Biden administration's contacts with social media firms
By Nate Raymond and Jonathan Stempel (Reuters) -A federal appeals court on Friday ordered the White House, the FBI and
2023-09-09 08:00

Elon Musk's X Corp sues California to undo content moderation law
By Jonathan Stempel Elon Musk's X Corp sued California on Friday, challenging the constitutionality of a state law
2023-09-09 05:28

Uber Working on TaskRabbit-Like Service in Potential Expansion
Uber Technologies Inc. is working on a TaskRabbit-like service that will let app users hire people to conduct
2023-09-09 05:23

Musk’s X Sues California Over Content Moderation Legislation
Elon Musk’s X Corp. sued California over a law requiring social media companies to explain how their content
2023-09-09 04:46
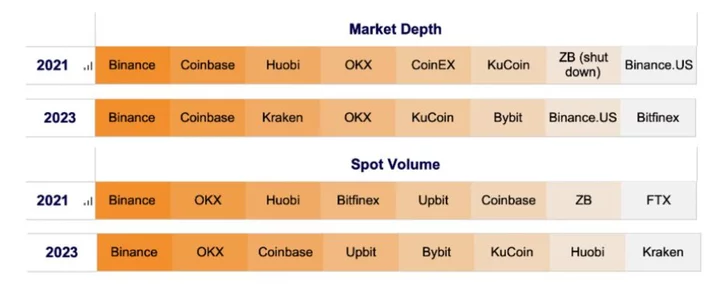
Just Eight Exchanges Handle 90% of All Crypto Trading Volume
In cryptocurrency markets, liquidity is uber-concentrated and has become more so over time, with nearly all of it
2023-09-09 02:48
iPhone Hacked Using NSO Group’s Pegasus Spyware
An iPhone belonging to a staffer at a Washington-based civil society organization was hacked remotely with spyware created
2023-09-09 00:48
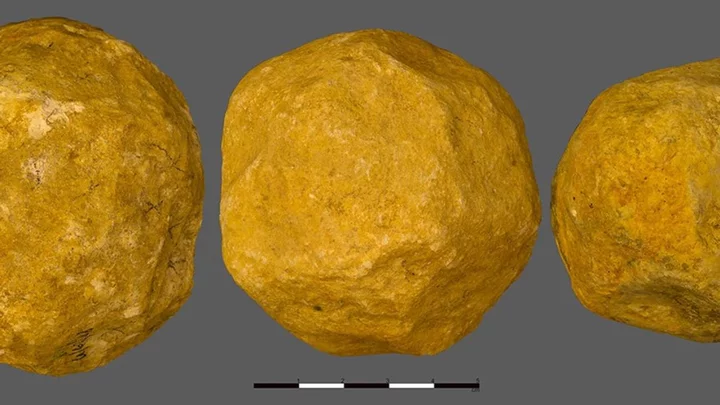

New study shows that early humans deliberately made stones in spheres
A study of 150 stones dating back 1.4m years shows early humans were deliberately crafting spherical shapes – but nobody knows why. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem made findings after analysing the limestone balls which were unearthed in Ubeidiya, a dig site in Israel’s Jordan Rift Valley. Scientists have previously speculated that the stones, which were discovered in the 1960s and serve no discernable purpose, became round after being used as hammers. But the university’s team reconstructed the steps required to create the so-called spheroids and found they were part of a “preconceived goal to make a sphere”. The researchers used 3D analysis to retrace how they were made based on the markings and geometry of the spheroids. They concluded that the objects were intentionally “knapped”, the technique used to shape stone by hitting it with other objects. Antoine Muller, a researcher at the university’s Institute of Archaeology, said: “The main significance of the findings is that these spheroids from ‘Ubeidiya appear to be intentionally made, with the goal of achieving a sphere. “This suggests an appreciation of geometry and symmetry by hominins 1.4 million years ago.” Early humans clearly had some reason for making the balls, but what exactly that is remains a mystery. He said: “We still can’t be confident about what they were used for. A lot of work needs to be done to narrow down their functionality.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-09 00:29

iPhone 15 price: New Apple handset could be by far most expensive ever
Apple’s upcoming iPhone 15 Pro Max could be easily its most expensive ever, according to numerous reports. A number of analysts have suggested that Apple could push the price of the more expensive phones up by $200, partly as a response to inflation but also because of a new strategy. Rumours have suggested that Apple is looking to offer new options at the very expensive end of its line-up, in an attempt to encourage growth of its profits. Tim Cook, Apple’s chief executive, appeared to confirmed that strategy during an earnings call earlier this year in which he said that he thought “people are willing to really stretch to get the best they can afford in that category”. Apple has already seemingly attempted that strategy with the Apple Watch Ultra, a new and more expensive version of the wearable, which was released last year. It was a marked change from previous releases, which have seen Apple offer cheaper “SE” versions of the Watch and iPhone, as well as much smaller handsets. Various reports have suggested that Apple is planning to do the same with its iPhone line-up. That could eventually bring an “Ultra” version of the iPhone, reports have suggested, presumably with premium features and other changes intended to encourage customers to buy it. This time around, however, Apple will offer the same line-up as it did with the iPhone 14: a smaller and larger version of both the normal iPhone 15 and the premium iPhone 15 Pro. The larger version of the latter – the iPhone 15 Pro Max – will be the most expensive. This year, the iPhone 15 Pro Max could have even more features that set it apart from the rest of the line-up. Rumours have indicated that Apple is adding a “periscope lens” to the larger phone, which would allow it to offer more zoom without taking up more space. Numerous analysts and reports have suggested that those changes could bring additional cost to the price of the iPhone. The iPhone 14 Pro Max currently costs $1,099 and the new model could be $200 more than that, analysts have indicated. The changes are also set to raise the average selling price of an iPhone, according to a new report from analyst Dan Ives at Wedbush and reported by 9to5mac. It would take the average selling price to $900-$925, he suggested. Apple will reveal the new iPhones – and their price – at an event on Tuesday, 12 September. They are expected to go on sale the following week. The base iPhone 15 is expected to largely be brought in line with the current iPhone 14 Pro, borrowing its chip and the “Dynamic Island” at the top of the display. The iPhone 15 Pro is expected to get a new, more powerful chip, thinner bezels around the display, and an “action button” on the side of the phone. Apple is also expected to move the port at the bottom of of all the new phones from the current Lightning to USB-C. Read More Could China be about to take a big bite out of Apple’s iPhone business? Update your iPhone immediately Apple is dropping leather from iPhone cases and Watch bands, report claims
2023-09-09 00:26
