
A major change is coming to WhatsApp
Big news for WhatsApp users who are a bit trigger happy when sending risky texts. You will now be able to edit your messages sent via the platform, within 15 minutes. "From correcting a simple misspelling to adding extra context to a message, we're excited to bring you more control over your chats," the messaging service said in a blog post on Monday. "All you need to do is long-press on a sent message and choose 'Edit' from the menu for up to fifteen minutes after," it added. Edited messages will be tagged as "edited", so recipients can see the message has been changed. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter But they won't be able to see how the message has been edited. It comes after Twitter said it was giving its paying subscribers the ability to edit their tweets last year. Tweets can be edited a few times in the 30 minutes after posting. "Tweeting will feel more approachable and less stressful," Twitter said in a blog post at the time. "You should be able to participate in the conversation in a way that makes sense to you and we'll keep working on ways that make it feel effortless to do just that," the platform added. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-23 20:19
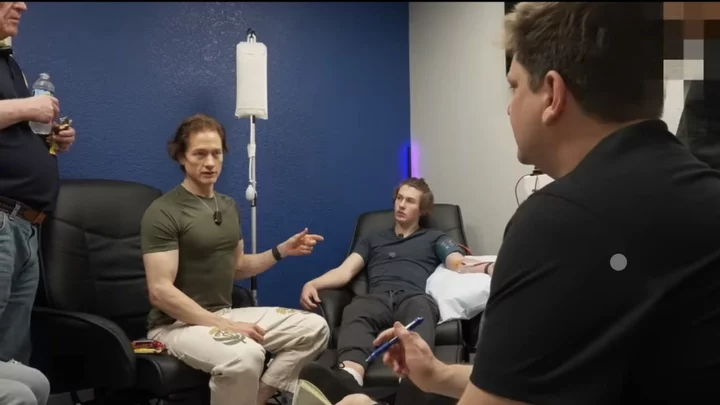

Tech bro millionaire injects himself with son's blood in attempt to de-age himself
Bryan Johnson, the multimillionaire tech and science entrepreneur who is trying to reverse his biological age, has taken the next odd step in his attempt to achieve this. Johnson, who has already spent millions of dollars every year trying to turn back the clock, has now revealed that he’s injected himself with his teenage son’s blood. The multimillionaire recruited his 17-year-old son, Talmage, and his 70-year-old father, Richard, for a trigenerational blood transfusion. The family travelled to a clinic in Dallas, where Talmage and Richard gave a litre of their blood for it to be converted into a batch of plasma. Bryan then donated a litre of his blood to Richard. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Claims that plasma from younger bodies can benefit older people’s health have been around for a while. Previously there have been studies carried out on mice, however experts say the results are inconclusive. The FDA does not recommend the blood infusions Bryan has done. "We have not learned enough to suggest this is a viable human treatment for anything." said Charles Brenner, a biochemist at City of Hope National Medical Centre in Los Angeles. The 45-year-old has previously spoken about his lifestyle, and told the BBC that there have been improvements in different parts of his body. "my left ear is 64, my fitness tests say I’m 18, my heart is 37, my diaphragm strength is 18," he said. Bryan’s mission to reverse the ageing process has been titled ‘Project Blueprint,’ and involves following a strict diet, sleep, and exercise routine. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-23 19:51
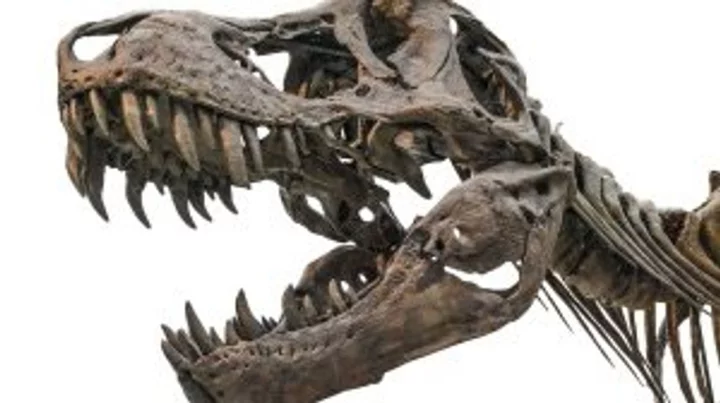

Scientists have discovered how many T-Rex ever existed
If you’re anything like us, you were probably absolutely obsessed with dinosaurs as a child. However, did you ever stop to think about the sheer number of dinos that were wandering around the planet before they met their untimely end at the hands of an asteroid? A new study has been published which states that a whopping 1.7 billion T-Rex roamed the Earth in total across the Late Cretaceous period. It comes after researchers calculated their average lifespan, which measured up to a whopping 40 feet in length and 12 feet in height. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter They cross referenced this with the number of eggs which survived and the sexual maturity of the animals to come up with the figure. It’s a huge number, but it’s actually far less than previously thought. A previous study from 2021 estimated that there were 800 million more of them that existed between about 90 to 66 million years ago. The research was published in Palaeontology, and evolutionary ecologist Eva Griebeler from the Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz in Germany wrote about the findings. "Unlike my model, the generation time as well as life expectancies, gross reproduction rates, and reproductive values of individuals calculated from the previous model all strongly contradicted our current understanding of the biology of T. rex and of other theropods,” she said. "Their values also disagreed with those of large extant reptiles, birds, and mammals. All of these shortcomings of the previous model favor the assessment of individual and population characteristics of T. rex and of other extinct species using my model." Griebeler also explained how the findings suggest a lower T-Rex survival rate, as well as fewer generations of the animal and less egg laying. "All of these shortcomings of the previous model favor the assessment of individual and population characteristics of T. rex and other extinct species using my model," she wrote. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-23 18:58

New SpaceX flight just made history thanks to its passengers
SpaceX's second private flight just made history by sending Saudi Arabia's first female astronaut towards the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon rocket launched from NASA's Kennedy Space Centre on Sunday night, and the astronaut and the other three passengers are expected to reach the space station in their capsule on Monday, where they will hang out for just over a week. Saudi Arabia's first astronauts in decades are stem cell researcher Rayyanah Barnawi, and Royal Saudi Air Force fighter pilot Ali al Qarni. "This is a dream come true for everyone," Barnawi said before the flight. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter "Just being able to understand that this is possible - if me and Ali can do it, then they can do it, too." The journey was organised by Houston-based Axiom Space and the crew was led by Peggy Whitson, a former NASA astronaut who holds the US record for the most accumulated time in space - 665 days and counting. The company would not reveal how much the latest tickets cost, but previously cited per-seat prices of $55m (£44m). Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-23 00:26
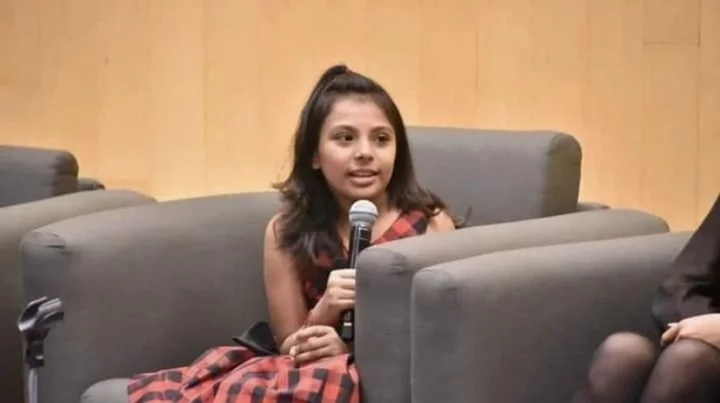

Mexcian girl who was bullied at school has a higher IQ than Einstein and Stephen Hawking
A young girl who was bullied for being autistic may have a higher IQ than Stephen Hawking or Albert Einstein. Adhara Maite Pérez Sánchez, an 11-year-old from Tláhuac, Mexico, is being described as a prodigy by many after recently graduating with a degree in Systems Engineering. She is now going on to study industrial engineering. The extraordinary girl has a passion for astronomy and space, expressing the dream to become the first Mexican woman to travel to space as an astronaut and has given talks about her interest and knowledge of aerospace. She intends to become an astronaut at NASA, and is currently taking courses in astronomy and gravitational waves at the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM), which is widely regarded as a top research university. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Adhara has also had her achievements recognised in 2021 by the Senate of the Republic, as well as being declared one of Mexico’s 100 most influential women, and appearing on the cover Marie Claire Mexico. However, life hasn’t always been easy for Adhara, who struggled with being bullied by her classmates. Often labelled as a ‘weirdo’ for her autism. Adhara was diagnosed with Asperger’s at 3 years old, but has succeeded greatly with it. Recently she has begun developing a bracelet designed to monitor the emotions of children such as herself in order to improve their communication skills. But she hasn’t let the negativity bring her down. Determined to succeed and achieve her goals in spite of what others say about her. Her inspirations include late physicist, Stephen Hawking, and Carmen Félix, a Mexican engineer currently developing a plan to launch a manned mission to Mars. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-23 00:25

Brains of three suspected zombies scanned in Haiti
Researchers in Haiti once scanned the brains of three people believed to be long-deceased individuals returning from the dead - or zombies. In a study published in 1997, researchers investigated three such cases, using electroencephalography and DNA testing techniques to try and find a rational explanation for a Haitian Voodoo theory that the spirits of the dead can be captured by sorcerers called bokors, who use these souls to reanimate fresh corpses into zombies who walk around rural areas. One case involved a woman who had died aged 30 and was spotted three years later by family members who recognised her because of a distinctive facial mark. A local court then authorised the opening of the woman’s grave, revealing it to be full of rocks. Describing the 'zombie', the study authors explained that “she kept her head in a lowered position, and walked extremely slowly and stiffly, barely moving her arms.” She was also unable to communicate “but would occasionally murmur some incomprehensible but stereotyped words.” But the scan showed her “electroencephalogram and central nervous system examination were unremarkable” and said she may have had catatonic schizophrenia, but couldn't explain how she came back from the dead. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter They proposed that the woman might not have died at all, but may instead have been poisoned by a “neuromuscular toxin” to induce catalepsy and trick relatives into thinking she was dead. A lack of oxygen within the grave may have resulted in brain damage, thus explaining her zombie-like state when she was taken out of the grave. Next, the study described a 26-year-old man who was seen at a local cockfight 19 months after being buried. The man’s uncle was subsequently found guilty of using sorcery to zombify the man, who was then kept chained to a log at his parents’ house. But clinical examinations found nothing weird and the man was diagnosed with “organic brain syndrome and epilepsy.” And DNA testing revealed that he was not even the man who had died shortly beforehand. In a similar case, a 31-year-old woman was identified as a villager who had been dead for 13 years. Once again, however, a medical examination revealed that she was a normal human while genetic analyses showed that she was not the dead individual after all. The study authors concluded that “mistaken identification of a wandering, mentally ill, stranger by bereaved relatives is the most likely explanation.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-23 00:15
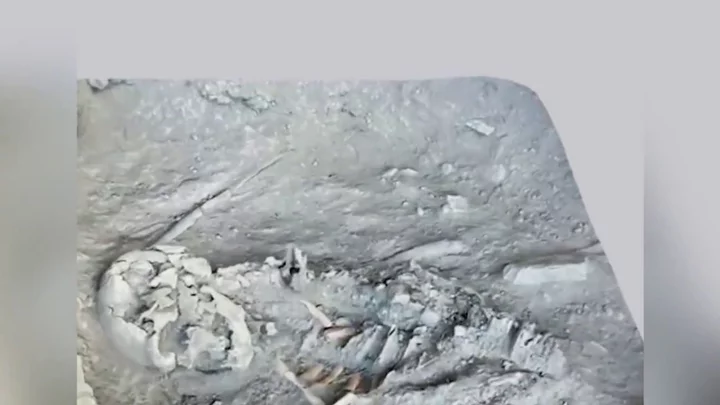

Proof that Vikings were in America far earlier than Columbus discovered
The discovery of North America is synonymous with Christopher Columbus, but proof has been found confirming that the Vikings were there hundreds of years earlier. Columbus is said to have “discovered the New World" in 1492 CE, but new analysis has suggested that the Norse people in Greenland were using wood from North America centuries before. Research focused on timber used in Norse sites across Greenland which people lived in between 1000 and 1400. The findings show that some of the wood came from types of trees that were grown outside of Greenland. One was the Jack pine, which is found in Canada. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Archaeologist Lísabet Guðmundsdóttir from the University of Iceland studied the timber and put across his findings in the journal Antiquity. “These findings highlight the fact that Norse Greenlanders had the means, knowledge, and appropriate vessels to cross the Davis Strait to the east coast of North America, at least up until the 14th century,” the study says. “As such, journeys were being made from Greenland to North America throughout the entirety of the period of Norse settlement in Greenland, and resources were being acquired by the Norse from North America for far longer than previously thought.” It’s not the first time that it’s been suggested that Norse communities travelled to north America. Italian texts from the 14th century contain references to Vikings making contact with Markland, which is believed to be on the Labrador coast in Canada. The 13th-century Norwegian text called Konungsskuggsjá also referenced the fact that Greenland at the time wasn’t home to great abundances of natural resources, reading: “Everything that is needed to improve the land must be purchased abroad, both iron and all the timber used in building houses.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-22 00:17
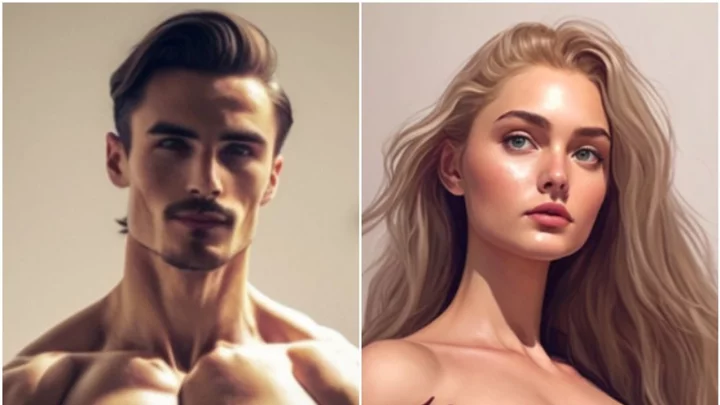

This is what the 'perfect' man and woman look like, according to AI
Artificial intelligence has unrealistic and often dangerous ideas of what the “perfect” man and woman look like, according to a new study. Chiselled features, olive skin and eight-pack abs are among the features that kept cropping up when three leading AI image generators were tasked with creating “ideal” male and female bodies. The challenge was put to the popular programmes Dall-E 2, Stable Diffusion, and Midjourney by eating disorder awareness group the Bulimia Project, which separated its request into two parts. First up, it asked the generators to come up with pictures of men and women based specifically on beauty standards set by social media. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Although it churned out quite a few different options, it showed a number of noticeable biases. Nearly all of the images featured petite women – with Midjourney named as the worst culprit – and all of the men looked like photoshopped versions of bodybuilders. The three AI favoured women with blonde hair and men with brown hair, and nearly half of the male images had facial hair. After analysing their findings based on social media, the Bulimia Project team broadened the scope of the task. This time, they asked the programmes to base their creations on images from across the internet. The main difference between the two categories was that the social media set was “far more sexually charged”, according to the study’s authors. The social media images also featured “largely disproportionate body parts”, which the Bulimia Project described as “unsettling”. “We can only assume that the reason AI came up with so many oddly shaped versions of the physiques it found on social media is that these platforms promote unrealistic body types, to begin with,” it said. “In the age of Instagram and Snapchat filters, no one can reasonably achieve the physical standards set by social media. So, why try to meet unrealistic ideals? It’s both mentally and physically healthier to keep body image expectations squarely in the realm of reality.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-21 15:46

Scientists have discovered why we wake up earlier as we get older
Are your grandparents up very early in the morning, without fail? Well, it turns out there are scientific reasons why older people wake up earlier as they get older. It’s been revealed that in later life, the natural process of ageing leads to changes in the times the body approaches sleep. According to HuffPost, our approach towards resting and amount of sleep we require is down to both genetics and our age. Cindy Lustig, who is a professor of psychology at the University of Michigan, said: “Like most of the things that change with age, there’s not just one reason, and they are all interconnected.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It’s all to do with the brain becoming less responsive as people age to factors such as sunlight, social cues and physical activity which indicate where in the day we are at any given time. “The wiring of the brain is likely not sensing... and responding to the inputs as well as it should because it’s an ageing brain,” Dr. Sairam Parthasarathy, the director of the Center for Sleep and Circadian Sciences at the University of Arizona Health Sciences, also told the publication. “These are all what we call time givers, or they give time to the brain,” he said. In other words, they help the brain sense where it is in the 24-hour circadian cycle. Younger people can more easily connect indicators like eating dinner with the idea of sleeping in the next few hours. However, that’s not as easy for older people to register naturally, especially as their vision tends to suffer in later life. “Interestingly, one of [the reasons] seems to be that the vision changes that come with age reduce the intensity of the degree of light stimulation that our brain receives, which plays an important role in ‘setting’ our circadian clock and keeping it on track,” said Lustig. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-20 22:48
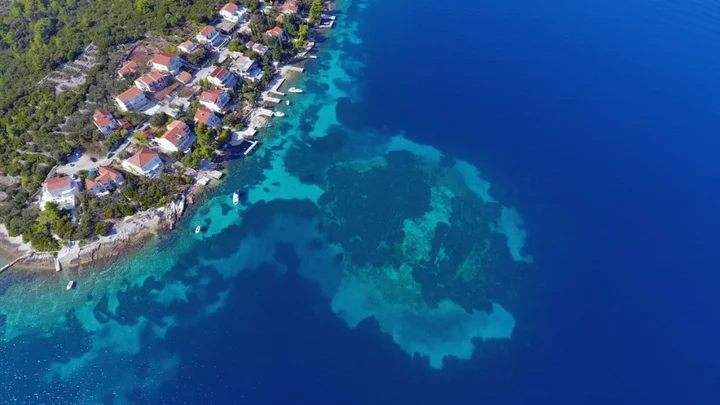

Scientists 'surprised' by 'strange underwater road' discovered in Europe
It’s not quite the lost city of Atlantis, but scientists have just uncovered a slice of history that had been swallowed up by the sea. Experts admitted that even they were surprised when divers unearthed a 7,000-year-old stone road that had lain buried under layers of sea mud. The ancient structure was discovered after archaeologist Igor Borzić, of the University of Zadar, spotted “strange structures” nearly 16 ft (5m) underwater in the Bay of Gradina, off the coast of Croatia. The submerged road once linked the island of Korčula to an artificial, prehistoric settlement that belonged to a maritime culture known as the Hvar. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The university released footage of the incredible finding over the weekend. It showed the passageway which consisted of stacked stones and measured some 12 ft (around 4m) across. Archaeologists believe people walked this road “almost 7,000 years ago”, with radiocarbon dating of wood near the site suggesting the settlement may have been built around 4,900 BC. “In underwater archaeological research of the submerged neolithic site of Soline on the island of Korčula, archaeologists found remains that surprised them,” the University of Zadar said in a Facebook statement. “Namely, beneath the layers of sea mud, they discovered a road that connected the sunken prehistoric settlement of the Hvar culture with the coast of the island of Korčula.” Borzić and his team also discovered another “almost identical” settlement on the other side of Korčula Island. Neolithic artefacts including a stone axe, cream blades and sacrificial fragments, were found at the site which lay at a depth of 4-5m. Understandably, the researchers were delighted and, as they continue to delve into their nation’s past, we wonder what else they’ll unearth. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-20 15:49
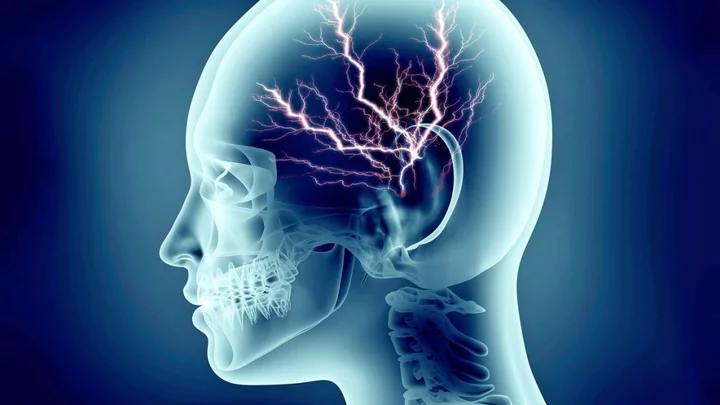
Scientists find that AI can read thoughts from monitoring your brain activity
Scientists have revealed they had found a way to combine the technology of brain scans and artificial intelligence to transcribe “the gist” of people’s thoughts. Alex Huth, an assistant professor of neuroscience and computing science at the University of Texas at Austin, and a co-author on the new study published in Nature Neuroscience, said that ‘this is a real leap forward.’ The study was led by Huth and Jerry Tang, a doctoral student in computer science. The main development from this study is that it’s non-invasive. This means that subjects do not require surgical implants. Instead, brain activity is measured using a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scanner. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter In the study, individuals listened to hours of podcasts in the scanner. Then, given the participant’s consent to have their thoughts decoded, they listened to a new story and the machine-generated corresponding texts from brain activity. It’s not a word-for-word transcript. For example, when an individual heard the phrase ‘I don’t have my driver’s licence yet’, the model decoded the individual’s thoughts to read as ‘she has not even started to learn to drive yet.’ Even when participants thought up their own stories, the machine was able to decode their thoughts still. Tang acknowledged that the advancements made in the study had the potential for negative aftermath. Tang said, ‘we take very seriously the concerns that it could be used for bad purposes and have worked to avoid that.’ They ran tests that highlighted that unless the machine had been trained on an individual’s particular brain activity, it could not decode its thoughts. An individual had to allow for the machine to train their brain activity over a long period of time inside a fMRI scanner for it to work. Researchers also found that it was easy to ‘sabotage’ the machine. Three participants were told to tell a different story in their mind, or count by seven, while listening to one of the podcasts. The study highlights even more development with artificial intelligence, after the popularity of OpenAI’s Chat GPT has sparked debate around the potential of AI. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-20 00:30

Scientists discover that humans mastered fire centuries before history suggests
Humans in Europe may have mastered fire long before we previously thought. According to a study published in Scientific Reports, humans made the discovery around 245,000 years ago, up to 50,000 years earlier than scientist thought previously. Researchers studied samples from the Valdocarros II, a huge archaeological site found east of Madrid, Spain. Using chemical analysis, they found certain compounds that show things were burnt by fire in "organised" social events, rather than through accidents or wildfires. "We have found definitive evidence of things being burnt and those remains are organised into a pattern, suggesting it's humans who are making and controlling the fire. Either they were using the fire to cook or to defend themselves. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The spatial patterning in the fire tells us that they were encircling something, like a home or sleeping area, a living room or kitchen, or an enclosure for animals," Dr. Clayton Magill, study author and Assistant Professor at Heriot-Watt University in Scotland, said in a statement. Dr Magill added that this new work helps to fill in the gaps in our understanding of human-controlled fire and human development. "This is important because our species is defined by our use of fire," Dr Magill explained. "Being able to cook food to feed our big brains is one of the things that made us so successful in an evolutionary sense. Fire also brings protection and fosters communication and family connection. And we now have definitive, incontrovertible evidence that humans were starting and stopping fires in Europe about 50,000 years earlier than we suspected." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-19 20:57
