
A new accent from 'Antarctica' has been discovered by scientists
Antarctica might be the only continent on Earth with no natural human habitation, but it’s emerged that an “Antarctica accent” is very much a thing. Despite having no locals, thousands of scientists have made up an ever-changing population in research stations over the years. The continent is so isolated and the level of interaction between researchers is so intense, that a common accent is beginning to emerge there despite people coming from different parts of the world. At its busiest points in the year during the summer, Antarctica is home to around 5,000 people. Only around 1,000 people live there during the winter months. The idea of accents changing due to human interaction on Antarctica is no different to the phenomenon seen throughout history at a glacial pace. However, given the very specific sample size, it’s an opportunity for scientists to study it at a much quicker rate and on a much smaller scale. Experts at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich published a study in 2019 which focused on the change in accents observed in 11 people who took part in the British Antarctic Survey. @human.1011 There’s an Antarctic Accent! #language #linguistics #english #antarctica Of the 11 who were studied, eight came from England, one from the US, one from Germany and one from Iceland. Their voices were recorded every six weeks, and the team found that over time they developed longer vowel sounds. There was a physical change too, with participants pronouncing the “ou” sound in the front of their mouths rather than the back of their throats. Speaking to IFL Science, Jonathan Harrington, study author and Professor of Phonetics and Speech Processing at the Ludwig-Maximilians University of Munich said: "The Antarctic accent is not really perceptible as such – it would take much longer for it to become so – but it is acoustically measurable. "It's mostly an amalgamation of some aspects of the spoken accents of the winterers before they went to Antarctica, together with an innovation. It's far more embryonic [than conventional English accents] given that it had only a short time to develop and also, of course, because it's only distributed across a small group of speakers.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 23:45

Mystery of how a meteor left Earth thousands of years ago, then came back
Baffled scientists are trying to unravel the mystery of how a meteorite left Earth’s atmosphere and somehow came back again. Unlike boomerangs, meteorites don’t have a reputation for coming back around again, so when a black rock found in Morocco in 2018 seemed to have done just that, it left the scientific community confused. The rock, whose official name is Northwest Africa (NWA) 13188, is a scientific first (that we know of) to have left the Earth’s atmosphere, gone into outer space and returned again. The 646-gram piece of rock is remarkable not only for its journey but also its makeup. NWA 13188 has a bubbly texture and contains crystals. Its chemical components suggest that the rock is made out of the minerals produced by molten minerals that come from volcanic activity. It also possesses trace elements and oxygen isotopes, which suggests to scientists that it is not the typical meteorite that originates in space, but instead, it originated on Earth itself. However, according to a geophysicist from the French National Centre for Scientific Research, Jérôme Gattacceca, who studied the rock and presented the findings, it has undergone an interesting journey in orbit. Scientists can identify this because of the presence and concentration levels of Helium-3, Beryllium-10, and Neon-21, which suggest exposure to cosmic rays that are not present in Earth’s atmosphere. Compared to other more traditional meteorites scientists have studied, the concentrations are lower on NWA 13188 but are still higher than rocks on Earth. It is thought that NWA 13188 could have been expelled from Earth and in orbit for thousands of years. Scientists said, “We consider NWA 13188 to be a meteorite, launched from the Earth and later re-accreted to its surface”. Despite the rock originating on Earth, the team said it fits the definition of a meteorite since it has achieved orbit. The definition states: “Material launched from a celestial body that achieves an independent orbit around the Sun or some other celestial body, and which eventually is re-accreted by the original body, should be considered a meteorite. “The difficulty, of course, would be in proving that this had happened, but a terrestrial rock that had been exposed to cosmic rays and had a well-developed fusion crust should be considered a possible terrestrial meteorite.” It is not yet understood how the rock came to be launched from Earth into space, as researchers said it still “remains to be determined”. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 23:17

Scientist shares routine that can 'make you better at everything'
The emphasis on a good night's sleep is nothing new. But now, neuroscientist, Dr Andrew Huberman, has shared one routine that he suggested can make you "better at everything." In a YouTube talk on After Skool, Dr Huberman said he immediately starts his day with a sunrise walk at 6.30am. "Getting outside for a 10-minute walk or a 15-minute walk is absolutely vital to mental and physical health," he shared. Despite coffee being the get-up-and-go drink for most, Huberman says the first beverage he consumes is salty water, as he claims it helps improve bodily functions. "There are certain foundational behaviours - certain dos and don'ts that set the stage for you to be better at everything," he continued. "It always comes back to two elements - that's sleep and what I call non-sleep deep rest. Sleep is the fundamental practice or part of our 24-hour cycle where if you don't get it on a consistent basis, you are down-regulating your ability to do everything." He went on to discuss a "90-minute bout of work," in which he says he turns his phone off to fully optimise this time. "You'd be amazed how much you can get done in 90 minutes if you are focused," he said. Huberman then ensures he gets in an hour's worth of exercise before exposing himself to cold temperatures such as an ice bath. The NHS states that there are no official guidelines regarding how much sleep a person should get each night as everyone is different. "On average, a 'normal' amount of sleep for an adult is considered to be around seven to nine hours a night. Children and babies may sleep for much longer than this, whereas older adults may sleep less," they wrote. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 21:58
Scientists suggest doctors could be taken over by ChatGPT in near future
Robots could soon take over doctors’ jobs, according to experts. A recent study found that AI technology was able to accurately diagnose patients in a healthcare setting. Investigators found the controversial model ChatGPT to be nearly 72 per cent accurate in making clinical decisions. It was also 77 per cent accurate in making final diagnoses. It was able to come up with possible diagnoses, final diagnoses and care management decisions. The artificial intelligence chatbot was found to perform equally well in both primary care and emergency settings. Researchers at Mass General Brigham in Boston, Massachusetts conducted the study. They tested how ChatGPT would be able to work through an entire clinical encounter with a patient. This included recommending a diagnostic workup, deciding the clinical management course, and ultimately making the final diagnosis. It was tested by putting 36 published clinical descriptions into ChatGPT. Patient gender, age and symptoms were put into the language model. ChatGPT was then given further information and asked to make management decisions and a final diagnosis. This simulates the process of seeing a real patient. However, scientists also found it was less accurate - 60 per cent - at making several possible diagnoses. Co-author Marc Succi said: “Our paper comprehensively assesses decision support via ChatGPT from the very beginning of working with a patient through the entire care scenario, from differential diagnosis all the way through testing, diagnosis, and management. ”No real benchmarks exist, but we estimate this performance to be at the level of someone who has just graduated from medical school, such as an intern or resident. ”This tells us that LLMs in general have the potential to be an augmenting tool for the practice of medicine and support clinical decision making with impressive accuracy.” The research team say they will soon be looking at whether AI tools can improve patient care and outcomes in resource-constrained areas of hospitals. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 20:25
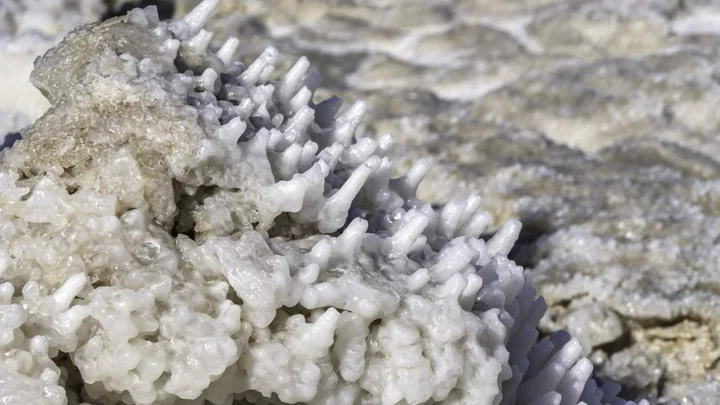

150 million year old water trapped in salt contains secrets to our ocean history
The key to discovering the secrets of life at the bottom of the ocean 150 million years ago has been discovered, and it was trapped inside ancient salt formations this whole time. Experts have been able to uncover the Earth's geological history y studying tiny water particles which have been preserved in crystals for millions of years. It’s all to do with analysing the amount of lithium which is trapped in samples rock salt. As it turns out, the level of lithium can tell us far more about atmospheric conditions in the oceans over the ages than most of us previously realised. Geochemists Mebrahtu Weldeghebriel of Princeton University and Binghamton University and Tim Lowenstein of Binghamton University have published their findings in a new study. The rock salt they studied, known as marine halite, came from across the world including the US, Europe, Asia and Africa. A total of 639 samples were taken from 65 halite crystals dating back to 150 million years ago. "There is a close link between ocean chemistry and atmospheric chemistry," Weldeghebriel said. “Whatever changes happen in the ocean also reflect what's happening in the atmosphere." "The oceans and atmosphere are connected to one another, and how they change is related," Lowenstein added. "Everything is connected." Most notably, their findings have helped to create a better understanding of tectonic movement on the seafloor. The reason the presence of lithium was so important is due to what it tells us about hydrothermal activity. The amount in the water indicates the levels of chemicals and heat which was being released into the oceans by vents between tectonic plates. As tectonic plate activity declined, there was a global drop in lithium levels. Instead, it was replaced by a rise in magnesium and calcium. The reduction in activity would also have meant less carbon dioxide being released into the atmosphere, which could potentially have been a factor in the temperature drop which resulted in the ice age. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 00:48

A new 'Antarctica' accent has been discovered by scientists
Antarctica might be the only continent on Earth with no natural human habitation, but it’s emerged that an “Antarctica accent” is very much a thing. Despite having no locals, thousands of scientists have made up an ever-changing population in research stations over the years. The continent is so isolated and the level of interaction between researchers is so intense, that a common accent is beginning to emerge there despite people coming from different parts of the world. At its busiest points in the year during the summer, Antarctica is home to around 5,000 people. Only around 1,000 people live there during the winter months. The idea of accents changing due to human interaction on Antarctica is no different to the phenomenon seen throughout history at a glacial pace. However, given the very specific sample size, it’s an opportunity for scientists to study it at a much quicker rate and on a much smaller scale. Experts at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich published a study in 2019 which focused on the change in accents observed in 11 people who took part in the British Antarctic Survey. @human.1011 There’s an Antarctic Accent! #language #linguistics #english #antarctica Of the 11 who were studied, eight came from England, one from the US, one from Germany and one from Iceland. Their voices were recorded every six weeks, and the team found that over time they developed longer vowel sounds. There was a physical change too, with participants pronouncing the “ou” sound in the front of their mouths rather than the back of their throats. Speaking to IFL Science, Jonathan Harrington, study author and Professor of Phonetics and Speech Processing at the Ludwig-Maximilians University of Munich said: "The Antarctic accent is not really perceptible as such – it would take much longer for it to become so – but it is acoustically measurable. "It's mostly an amalgamation of some aspects of the spoken accents of the winterers before they went to Antarctica, together with an innovation. It's far more embryonic [than conventional English accents] given that it had only a short time to develop and also, of course, because it's only distributed across a small group of speakers.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-24 20:51
Apple issues danger warning to iPhone users
The Apple iPhone is one of the most popular mobile devices in the world, but the company has issued a new danger warning to users that could help save lives. Popular among those particularly in the West, iPhones are prevalent in most people’s everyday lives, ever since the first one was released in June 2007. However, Apple has issued a stark warning for those who leave them charging overnight, highlighting a risk of fire, electrocution and injury. The warning by Apple comes under its updated user guide under the article titled, “Important safety information for iPhone” in which it is warned that charging phones over long periods poses a risk. It read: “Use common sense to avoid situations where your skin is in contact with a device, its power adapter, or a wireless charger when it’s operating or connected to a power source for long periods of time. “For example, don’t sleep on a device, power adapter, or wireless charger, or place them under a blanket, pillow, or your body, when it’s connected to a power source. “Keep your iPhone, the power adapter, and any wireless charger in a well-ventilated area when in use or charging. Take special care if you have a physical condition that affects your ability to detect heat against the body.” The company confirmed consumers can use “‘Made for iPhone’ or other third-party cables” that are compliant with relevant safety regulations. But, it added: “Other adapters may not meet applicable safety standards, and charging with such adapters could pose a risk of death or injury.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-24 19:52

Terrifying video shows how long leaders have to act after a nuclear weapons launch
A terrifying video has shown just how little time world leaders have to act in the event that nuclear weapons are launched. In the video, shared by the educational channel Kurzgesagt, a potential scenario of a country launching nuclear weapons is set up, with a commander talking the viewer, from the point of view of a world leader, through what is going on. The commander explained that an enemy had released nuclear weapons primarily targeting military bases and nuclear command centres. Secondary targets include oil refineries, power stations and ports. The commander grimly explained: “Deaths from the blast and burns may be a few million today. It’s morning rush hour and there’s not much to be done for people stuck in traffic.” Radiation effects from the blast, the commander explained, would be dependent on the weather and direction of the wind. Those in populated urban areas would be less able to flee and there would be “dozens of millions of deaths” in just a few weeks. It is explained that the 400 nuclear weapons in silos need to be launched “now” before they are taken out by the enemy warheads. Nuclear-capable bomber planes need to take off within two minutes to stand any chance of getting out of the blast. The horrifying intensity of the nuclear war continues as the commander explains that there is nothing that can be done for civilians and that if the order is not given immediately, the war could be over before they even have a chance to retaliate. Thankfully, the scenario was only fake, but the video ended by explaining that the world has been very close to a similar situation unfolding several times due to mistakes or errors – and that it only takes one person to give the order. In 1955, a Russian radar detected what it thought was a missile launch from a submarine, causing its military to be on high alert. But, it turned out it was actually a scientific rocket studying the auroras. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-24 19:23

'Hidden structures' discovered deep beneath the dark side of the moon
Scientists have just uncovered billions of years’ worth of secrets buried beneath the surface of the moon. Our celestial companion has been a source of awe and mystery since time immemorial, but now, thanks to China’s space programme, we’re starting to piece together its past. In 2018, the Chang’e-4 lander, of the Chinese National Space Administration (CNSA), became the first spacecraft ever to land on the far side (or the dark side, if you'd prefer) of the moon. Since then, it has been capturing incredible images of impact craters and extracting mineral samples, offering a long-sought insight into the structures that make up the top 1,000 feet of the moon’s surface. Earlier this month, the Chang’e-4’s findings were finally published, and the world was invited to delve deep into the history of our cherished natural satellite. The results, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, reveal that the top 130 feet (40m) of the lunar surface are made up of multiple layers of dust, soil, and broken rocks. Hidden within these layers is a crater, which formed when a large object slammed into the moon, according to Jianqing Feng, an astrogeological researcher at the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, who co-led the pioneering analysis. Beneath this, Feng and his colleagues discovered five distinct layers of lunar lava that spread across the landscape billions of years ago. Experts believe that our moon formed 4.51 billion years ago, when a Mars-size object crashed into Earth and broke off a chunk of our planet, as Live Science notes. Over the following 200 million years or so, the moon continued to be pummelled by space debris, with numerous impacts leaving cracks in its surface. Just like on Earth, the moon’s mantle contained pockets of molten magma, which infiltrated the newly formed cracks thanks to a series of volcanic eruptions, Feng explained. However, the new data provided by Chang’e-4 showed that the closer the volcanic rock was to the moon’s surface, the thinner it got. "[The moon] was slowly cooling down and running out of steam in its later volcanic stage," Feng said. "Its energy became weak over time." It is understood that volcanic activity on the moon died out between a billion and 100 million years ago, which means it is largely considered “geologically dead”. However, Feng and his co-authors have suggested there could still be magma buried deep beneath the lunar surface. Chang’e-4 still has much work to do, and Feng and his team hope this is just the beginning of their literally ground-breaking mapping of the moon. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-23 22:25
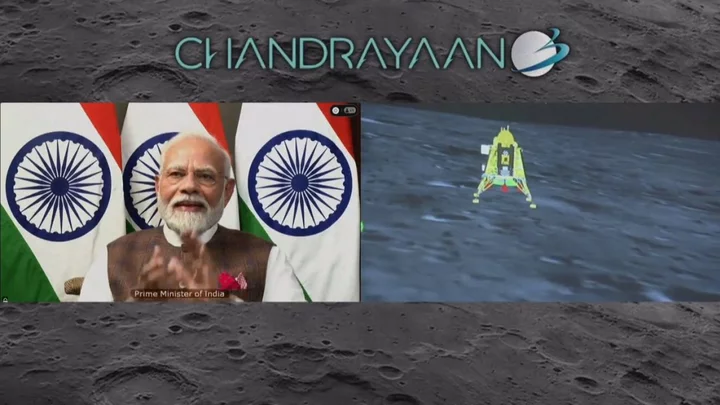
Watch: India becomes first country to make historic moon landing on planet's south pole
This is the moment India made its historic first landing on the moon's south pole, just days after Russia's attempt ended in a crash. India's attempt to land its Chandrayaan-2 mission near the south pole in 2019 was unsuccessful, but the Chandrayaan-3 mission went off without a hitch. The lander, known as Vikram, touched down at 13:34 BST. It's thought no attempts have been successful so far because of its rocky landscape, making it difficult to find somewhere to land safely. Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter
2023-08-23 20:47

Scientists discover that plants make sounds when hurt that you can hear
Plants make sounds when they’re distressed and humans are only hearing them now for the first time, scientists have found. New research has discovered that sounds are used by plants to communicate with their ecosystems – and they could be studied and used to improve growing conditions for plants in the future. Itzhak Khait of Tel Aviv University led the research, which involved studying tobacco and tomato plants. As the findings showed, the plants made high-frequency noise which could be detected five metres away. The study was published in the journal Cell, and the results “can alter the way we think about the plant kingdom, which has been considered to be almost silent until now”. Not only that, but by studying the sounds emitted by the plants experts could tell whether they were in need of water or suffering from cuts. Lilach Hadany, an evolutionary biologist at Tel Aviv University, told Vice: “We started this project from the evolutionary question: why are plants mute? It appears that plants could have a lot to benefit from acoustic communication.” “We were particularly happy that the sounds turned out to be informative – containing information on the type of the plant and the type of the stress.” The findings could change the way plants are grown and communicate with their environments in future, given that we now know information can be conveyed via the sounds. Hadany went on to say: “What we do know is that there are sounds in the air, and they contain information. “Thus, natural selection may be acting on other organisms (animals and plants) to whom the sounds are relevant, to be able to hear the sounds and interpret them. That includes animals that can hear the sounds and can use the information to choose a food source or a laying site, or potentially plants that can prepare for the stress.” The team said in the study: “Plant sound emissions could offer a way for monitoring crops water and possibly disease states—questions of crucial importance in agriculture. “In times when more and more areas are exposed to drought due to climate change, efficient water use becomes even more critical, for both food security and ecology.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-23 19:27

Toilet invented that is so slippy nothing can leave skid marks
A 3-D-printed toilet has been invented and the surface is so slippery that nothing can leave a mark on it. Cleaning the toilet has to be one of the grimmest household chores, but thanks to new material, you may never have to scrub a loo again. The toilet is the invention of Yike Li at Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, China, who, alongside colleagues, invented a toilet whose surface is so slippery that nothing stains it and uses less water for each flush. The team created a prototype of the toilet around 10 times smaller than a real one. It was made using 3D printing technology, where particles of plastic and hydrophobic sand grains were fused together with lasers. The surface of the toilet was lubricated with a type of silicon oil that also penetrated the surface due to the complex structure of the material. The team tested the toilet with a variety of substances, including honey, yoghurt, muddy water as well as synthetic faeces. They found that none of the substances stuck to the toilet bowl. Amazingly, the toilet was just as slippery after having been rubbed with sandpaper over 1,000 times, which Li believes is due to the oil being able to penetrate the material of the toilet. Li believes the technology would be suited for settings in which a toilet gets a lot of use, such as on modes of transport and in public toilets. He explained: “The reduced flushing volume would result in less wasted water during transportation to the processing facilities, thereby saving transportation costs.” But, before that can happen, Li says the technology needs to be adapted for use on a full-sized toilet and also needs to be cheaper to make. You can see the toilet in action below courtesy of New Scientist. Nothing can stick to this 3D-printed slippery toilet youtu.be Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-22 20:19
