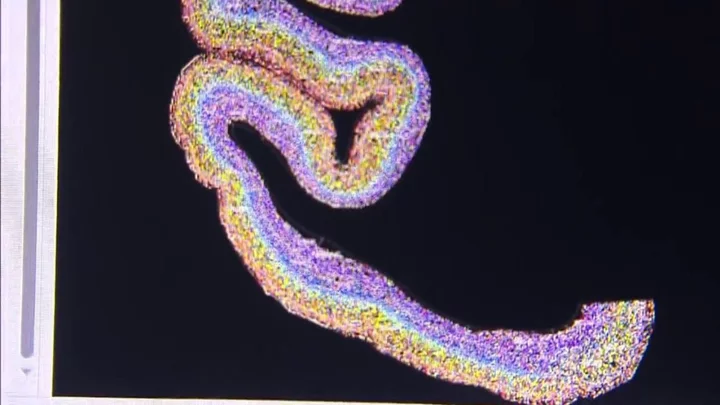
Scientists discover strange 'mathematical pattern' in the human body
The human body is a marvel of science and researchers have discovered a strange reoccurring mathematical pattern within its cells. Our bodies are made up of a massive variety of individual cells with countless different functions, from neurons in our nervous system to the oxygen carriers that all work in harmony to keep us alive. Experts from scientific research institutions in Germany, Canada, Spain, and the US have worked together on a study to determine just how many cells of each type there are in the human body and the results are staggering. They found that most adult males possess around 36 trillion cells, while adult females have in the region of 28 trillion cells. For a 10-year-old child, they have around 17 trillion. Interestingly though, scientists discovered that, regardless of the total number of cells, if they are grouped according to their function, the proportions for each individual remain the same. The researchers explained in their findings: “These patterns are suggestive of a whole-organism trade-off between cell size and count and imply the existence of cell-size homeostasis across cell types.” Scientists believe there is a natural balancing act at play between different cell types with new cells being produced to maintain the balance. The body produces fewer larger cells (such as muscle fibres) and more smaller cells (like blood cells). It is hoped that future studies will be able to uncover exactly how this happens and how bodies seem to naturally regulate cells. They explained that all cells are perfectly sized for their roles and any deviation from their scale can indicate the presence of disease. Experts have made their data, analysis and results public in the hopes that future studies into biology will be able to utilise their research. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-22 23:21
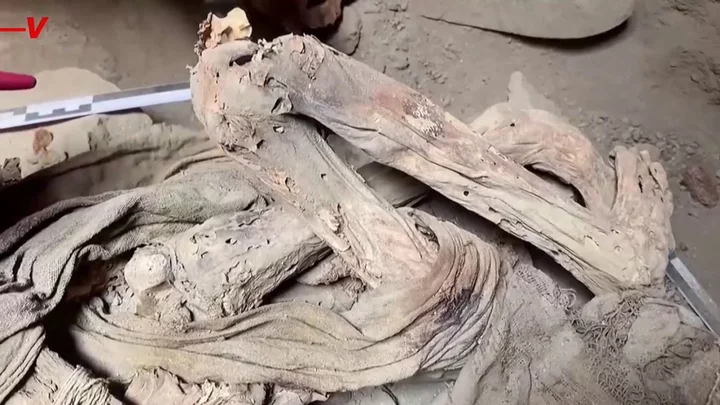

Scientists baffled by discovery of completely mummified man just 16 days after he was last seen alive
Warning: This article does contain images some readers might find disturbing. Investigators have been left puzzled after finding a man’s body in a stage of “complete mummification” just 16 days after he was last seen alive. The man was found alongside a railway line in Bulgaria on 3 September. Identity checks later found he was 34 when he died, with a history of alcoholism, and was last seen alive on 16 August. However, his insides had been reduced to “structureless masses”, and case workers have been unable to explain how the body reached such an advanced state of mummification so quickly. A report published in Cureus journal shows a full set of pictures of the corpse – linked at the foot of this article. Trigger warning, they’re pretty gruesome. It has got scientists fascinated though. The report’s authors reveal that the “skin surface showed coloration ranging from light to dark brown, and it was hard and leathery.” “The internal examination of the body showed that the internal organs in the cranial, thoracic, and abdominal cavities had decayed into dried, brownish-black masses,” they write. Researchers stressed that natural mummification “usually takes several weeks to 6-12 months”, and that such a fast transformation would only normally happen in extreme heat. The temperature in Sofia has ranged from 16 to 33 degrees Celsius in the time period, which scientists said is not hot enough. The authors speculated that passing trains could have created a windy environment that could have contributed to drying out the body and causing bodily fluids to evaporate. They said it almost certainly wasn’t the weather in Sofia that caused the bizarrely fast mummification process. As of yet, it remains a mystery. Here’s the journal article. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-22 17:17

Missing nuclear bomb off the US coast could still explode
On February 5, 1958, two Air Force jets collided in mid-air during a train mission. Fortunately, all involved survived the crash, but one of the jets carried a Mark 15 thermonuclear bomb, as was "common practice" during training missions. The weapon is now believed to be hidden 13 to 55 feet below the ocean and sand, and the Air Force and Navy divers have been looking for it ever since. The nuclear weapon is somewhere off the coast of Tybee Island, Georgia, and every once in a while, a high reading of radioactivity is recorded in the area. This causes the US government to scramble in efforts to find the bomb, likely buried in the seafloor. For two months after the jets collided, the Air Force and Navy divers searched a 24-square mile area in the Wassaw Sound, a bay of the Atlantic Ocean near Savannah, using handheld sonar. On April 16 1958, the military decided the bomb was "irretrievably lost." The Air Force said the weapon wasn't fully assembled and "there was no danger of an explosion or radioactivity." Forty years later, a retired Air Force officer began to search for it. "It's this legacy of the Cold War," said Stephen Schwartz, author of 'Atomic Audit: The Costs and Consequences of US Nuclear Weapons Since 1940'. "This is kind of hanging out there as a reminder of how untidy things were and how dangerous things were." However, some experts say that the bomb may be better left buried, even if someone finds it. Whilst there was little chance of the bomb spontaneously exploding, there was a chance of it exploding during retrieval, and experts would have to remove and dispose of the uranium first. A 2001 report on the bomb suggested recovery cost would start at $5 million. "The whole Air Force perspective is, it's just not worth it," Schwartz said. "Trying to move it could create bigger problems than if we just leave it where it is." Schwartz said the only way the weapon will be found is by chance or if a powerful storm dredges it up. "I won't say it's lost for the ages because I don't think it is," he said, but "so many people have searched for it for so long using some fairly sophisticated equipment and not found it." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-22 00:24
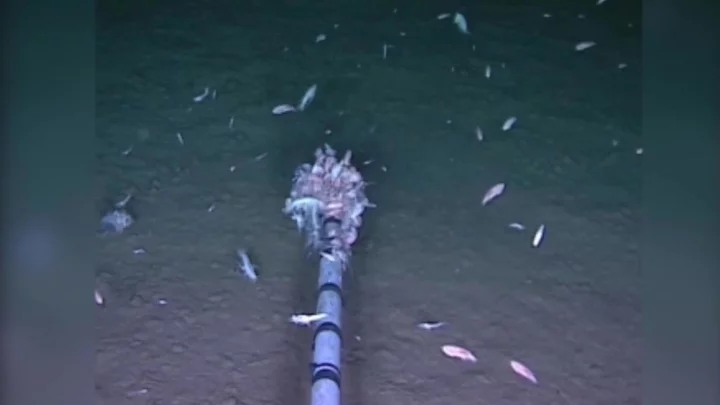

Scientists have found a novel virus at the bottom of the ocean
Scientists have discovered a new virus in the Pacific that is thought to be the deepest ever found in Earth’s oceans. The so-called bacteriophage virus infects and replicates inside bacteria, and was found in the Mariana Trench, which is the Pacific’s deepest point. Bacteriophages are among the world’s most abundant life forms, and are important for regulating population sizes in the oceans and releasing nutrients. This one, the catchily named vB_HmeY_H4907, was picked up at 8,900 metres below sea level. That is still some way off the 11,000 metre floor of the trench. Min Wang, a marine virologist from the Ocean University of China, said: “To our best knowledge, this is the deepest known isolated phage in the global ocean.” “Wherever there’s life, you can bet there are regulators at work. Viruses, in this case.” Scientists think this virus is likely to be distributed widely in the world’s oceans, despite the fact it has only been discovered. It has a similar structure to its host bacteria group halomonas. These are usually found in sediments and geyser-like openings on the seafloor. They also think the virus is lysogenic, which means it infects the host but does not kill it. Dr Wang said the discovery could inform further research about how viruses survive in the world’s harshest environments. “Extreme environments offer optimal prospects for unearthing novel viruses,” he added. The virus was found in the so-called hadal zone, which the study’s authors said is “the planet’s least explored and most mysterious environment, and it is the deepest habitat for life on Earth’s surface”. The area is named after Hades, the Greek god of the underworld. Researchers wrote in the study: “These findings expand our understanding of the phylogenetic diversity and genomic features of hadal lysogenic phages, provide essential information for further studies of phage-host interactions and evolution, and may reveal new insights into the lysogenic lifestyles of viruses inhabiting the hadal ocean.” The findings were published in the journal Microbiology Spectrum. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 20:48
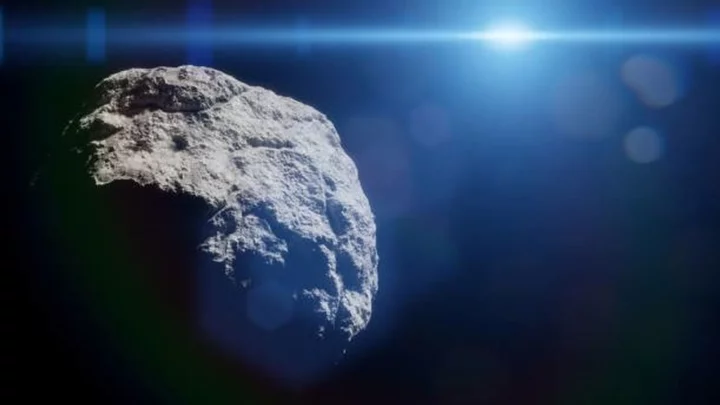

Scientists issue warning about asteroid heading to Earth with force of 24 atomic bombs
Scientists are on alert after NASA confirmed there is a chance an asteroid the size of the Empire State Building could come smashing into Earth. The asteroid is named Bennu after the ancient Egyptian bird god and has been on the space agency’s radar for a long time as they try to prevent it from coming crashing into our planet. Bennu has been categorised as one of the two “most hazardous known asteroids” and, despite the chance of impact standing at 1-in-2,700, it could strike the Earth with the force of 24 times that of the largest nuclear bomb – 1,200 megatons of energy. The carbon-based asteroid is approximately 510 metres wide and experts predict that it will come closest to hitting Earth on September 24, 2182. While the asteroid is quite sizeable, it is not quite as sizeable as the six-mile-wide asteroid which almost completely wiped out the dinosaurs. But, NASA warns that Bennu “could cause continental devastation if it became an Earth impactor”. A space mission launched using NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft has successfully taken a sample from Bennu in order for scientists to better understand the potentially dangerous asteroid. On Sunday (24 September) a capsule of the material will be dropped by OSIRIS-REx and returned to Earth where it will be retrieved and the matter inside studied. Davide Farnocchia of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory told the Science Journal: “We improved our knowledge of Bennu's trajectory by a factor of 20.” As scientists work to investigate how much of a risk it could cause, Farnocchia added: “In 2135, we'll know for sure.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 20:28

Former Elon Musk employee speaks out on 'ridiclous' death of Neuralink's monkeys
A new report from Wired has alleged that Elon Musk's Neuralink - a neurotechnology company developing a brain-computer interface - euthanised the company's macaque subjects after they suffered various complications from the implant. The report comes after human-test subjects were recently approved for Neuralink's clinical trial. Elon Musk had claimed earlier this month that "no monkey has died as a result of a Neuralink implant, but public documents obtained by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (PCRM) and seen by Wired, suggest that the primate subjects suffered complications including "bloody diarrhoea, partial paralysis, and cerebral edema." Musk had acknowledged the deaths on September 10 on Twitter/X, denying the deaths were "a result of a Neuralink implant", and that researchers had selected subjects who were already "close to death." However an anonymous former employee called this "ridiculous" if not a "straight fabrication." However, the public records reviewed by Wired suggest a different story. The PCRM, a nonprofit aiming to abolish live animal testing, claim that Musk knew his comments about the primate subjects deaths "to be false". They write that investors deserve to hear the truth about the safety, "and thus the marketability," of Neuralink's product. A December 2019 experiment outlined in one of the documents mentioned a subject known as Animal 15. The documents said that the subject "began to press her head against the floor for no apparent reason" just days after receiving the implant. Her condition only worsened as she "began to lose coordination" and "would shake uncontrollably when she saw lab workers." Staff finally euthanised her months later. Last year, the PCRM filed a complaint with the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) alleging that Neuralink's practices violate the Animal Welfare Act. The US Department of Transportation is also investigating Neuralink over allegations contimanted devices that were removed from monkeys' brains were illegally transported. Indy100 have reached out to Neuralink for comment. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 17:59
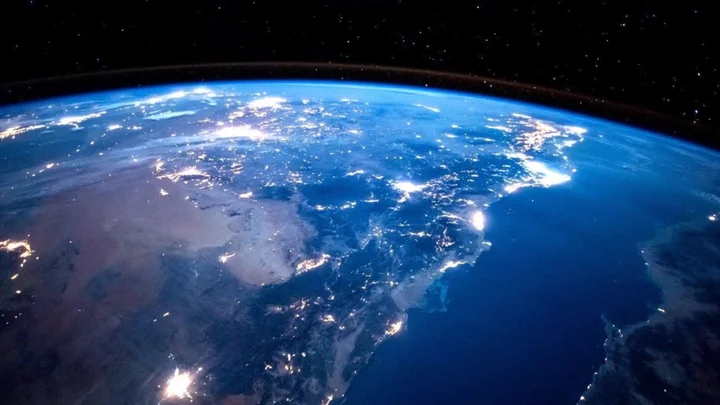

A scientist has discovered when Earth's first continent was formed
A researcher has figured out that the Earth’s first continent was formed 3bn years ago, in a new paper that sheds fresh light on the early stages of the planet’s life. Jane Greaves, an astronomy professor in the School of Physics and Astronomy at Cardiff University in Wales, was examining continent formation on distant stars and planets. It is thought that exoplanets with continents that formed in a similar way to Earth’s are more likely to be habitable, and perhaps even contain alien life. In the process, she calculated when several distant planets’ continents were born, as well as those a little closer to home. Continents on Earth sit on top of the planet’s hot, viscous mantle. Heat from the inner core stops the mantle from solidifying. The reason the core is hot is because it contains radioactive elements that came from neutron star collisions billions of years ago such as forms of Uranium, Thorium and Potassium. By analysing how many materials like this are present on Earth and on other planets, we are also able to estimate when the continents formed. On Earth, that was about 9.5 billion years since the beginning of the universe. Meanwhile, in Greaves' sample, the first continents appeared 2bn years before Earth’s on the exoplanets of younger, so-called thin disk stars. Older, thick disk stars analysed in her work produced rocky planets with continents that appeared even earlier: about 4 to 5bn years before Earth’s. “The outlook seems very promising for finding rocky exoplanets with continents, given that nearby Sun-like stars have already produced a few candidate hosts,” she wrote. The study, “When were the First Exocontinents?” is published in Research Notes of the American Astronomical SocietySign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 17:19
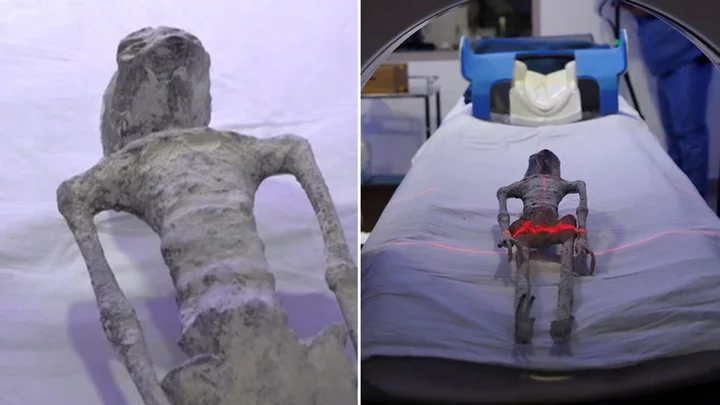

Scientists confirm that one of Mexican aliens is 'alive' after controversial research
Scientists in Mexico have given their verdict on the supposed 'aliens' that were presented to the country's congress last week. Much controversy existed around the aliens who were presented by a man named Jaime Maussan who has previously been accused of using the mummified beings, apparently found in Peru, as part of an elaborate hoax. Despite spawning dozens of memes, the aliens are apparently being treated seriously enough that they have now been studied by scientists who have said that the figures are ‘single skeletons’ and also have 'eggs' inside of them. The two aliens have been named Clara and Mauricio and have reportedly been studied in a lab at the Noor Clinic in Mexico. Lead researcher Dr Jose de Jesus Zalce Benitez, a former navy forensics doctor, who added that as well as being "a single skeleton" the aliens are also a "complete organic being." He also denied that the aliens were part of a hoax and even said that Clara was "alive, was intact, was biological and was in gestation." However, much like the alien bodies themselves, the research has been clouded in controversy and scepticism as the research has yet to be officially verified, with Nasa scientist Dr David Spergel questioning why the findings haven't been made public, as per the BBC. Spergel said: "He said: "If you have something strange, make samples available to the world scientific community and we'll see what's there." Benitez did add in his address at the press conference: "We are facing the paradigm of describing a new species or given the opportunity to accept that there has been contact with other beings, non-humans, that were drawn and marked in the past by diverse cultures throughout the world." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-20 16:23

Vatican comes to Nasa's aid in historic space mission
A Vatican astronomer has come to the help of NASA with a historic mission to study an asteroid. Meteorite expert and Vatican astronomer, Jesuit Brother Bob Macke, came to the aid of the US space agency after building a custom device that would allow the study of material of a sample collected from an asteroid. The mission is that of the unmanned spacecraft, Osiris-Rex, which was launched in 2016 in order to collect samples on an asteroid named Bennu. Bennu is located close to Earth and Osiris-Rex successfully collected a cup of material from the asteroid in 2020. Now, the vessel is approaching Earth and is due to release the sample in a return capsule on 24 September before continuing its orbit of the sun. Macke was contacted by the lead of the mission’s sample analysis working group, Andrew Ryan, who asked him to build the device that was needed in order to analyse the sample of the Bennu asteroid. The device has been devised so that it can analyse the density and porosity of the samples to help identify the make up of the asteroid surface. It is known as a pycnometer and NASA has strict requirements for the device, though other companies contacted were not willing to custom make one. Macke, however, took up the task and was able to build it in five weeks thanks to the assistance of students at the University of Arizona who collaborate with the Vatican Observatory’s advanced technology telescope in Tucson. In March it was delivered to the NASA Johnson Space Center in Houston for a test run and is hoped to be used for the real thing when the sample arrives from space. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-19 22:27
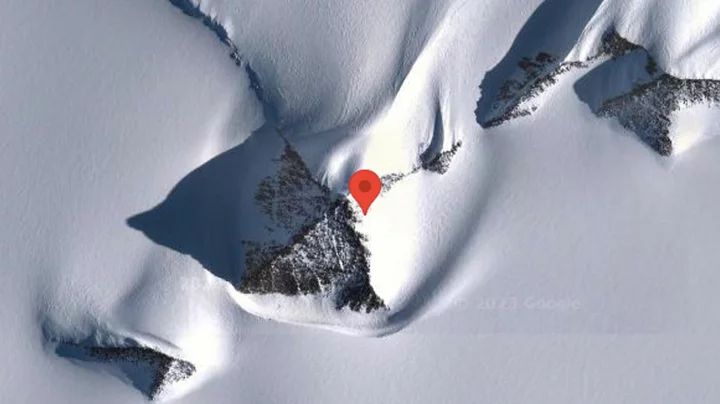

Mysterious 'pyramid' discovered in Antarctica beneath the ice
Conspiracy theorists have been turning their attention to Antarctica more than you’d expect over recent years. First, there was the case of the “bleeding waterfalls”, which remains one of the strangest natural phenomena you're likely to see, and there’s also the mystery of a so-called “pyramid” which has been found on the continent. Only, it’s not a pyramid at all – in fact, it’s a mountain. The Ellsworth Mountains are the highest mountain range in Antarctica and stretch 400km and the mountain in question was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition of 1910-1913 It was called “The Pyramid” to keep the true nature of the discovery hidden from others at the time. Over the last hundred years, however, people have been speculating about the true nature of the location (even though it’s very much a mountain, poking up out of the ice) and now a second interesting geographical feature has bee discovered and got them talking all over again. The location in question is found at the coordinates 79°58’39.25?S 81°57’32.21?W, which has been a much-searched spot on Google Earth. Speaking to IFL Science, geologist at the German Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam, Dr Mitch Darcy, said: “The pyramid-shaped structures are located in the Ellsworth Mountains, which is a range more than 400 km long, so it’s no surprise there are rocky peaks cropping out above the ice. The peaks are clearly composed of rock, and it’s a coincidence that this particular peak has that shape. “It’s not a complicated shape, so it’s not a special coincidence either. By definition, it is a nunatak, which is simply a peak of rock sticking out above a glacier or an ice sheet. This one has the shape of a pyramid, but that doesn’t make it a human construction.” So, the new location is just that – a mountain poking out the top of the ice in Antarctica, and not a mysterious pyramid at all. Antarctica has been the subject of more than its fair share of speculation recently, after conspiracy theorist Eric Hecker described the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station by the south pole as an “air traffic control” hub for aliens earlier this year. Hecker claimed that in 2010 Raytheon, the US aerospace and defence conglomerate chose him to be a contractor on the research centre operated by the United States National Science Foundation. There was “much more” to the station that first met the eye, according to Hecker. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-19 19:17
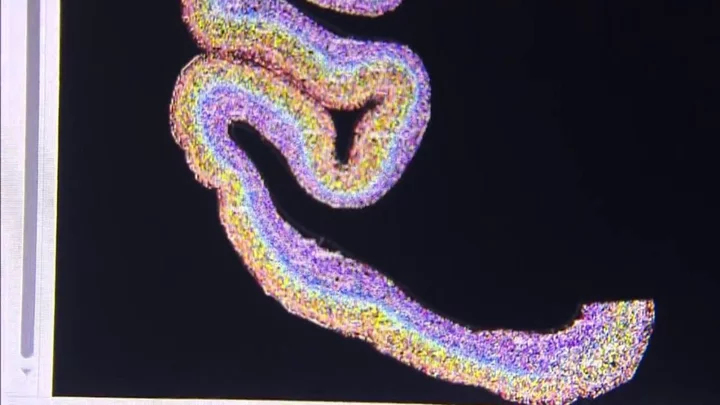
Strange 'mathematical pattern' found in the human bodies
The human body is a marvel of science and researchers have discovered a strange reoccurring mathematical pattern within its cells. Our bodies are made up of a massive variety of individual cells with countless different functions, from neurons in our nervous system to the oxygen carriers that all work in harmony to keep us alive. Experts from scientific research institutions in Germany, Canada, Spain, and the US have worked together on a study to determine just how many cells of each type there are in the human body and the results are staggering. They found that most adult males possess around 36 trillion cells, while adult females have in the region of 28 trillion cells. For a 10-year-old child, they have around 17 trillion. Interestingly though, scientists discovered that, regardless of the total number of cells, if they are grouped according to their function, the proportions for each individual remain the same. The researchers explained in their findings: “These patterns are suggestive of a whole-organism trade-off between cell size and count and imply the existence of cell-size homeostasis across cell types.” Scientists believe there is a natural balancing act at play between different cell types with new cells being produced to maintain the balance. The body produces fewer larger cells (such as muscle fibres) and more smaller cells (like blood cells). It is hoped that future studies will be able to uncover exactly how this happens and how bodies seem to naturally regulate cells. They explained that all cells are perfectly sized for their roles and any deviation from their scale can indicate the presence of disease. Experts have made their data, analysis and results public in the hopes that future studies into biology will be able to utilise their research. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-19 18:58

Scientists have discovered a new fly that fails its one job
Scientist have discovered a fly that... can't fly. In December 2021, the John Midgley and Burgert Muller from the Diversity of Pollinating Diptera in South African Biodiversity Hotspots project went to Lesotho, the only country in the world that has its entire territory located at an altitude of 1,000 metres and higher to see what they could find. At the Afriski mountain resort, they found 51 male specimens of Atherimorpha latipennis (a species discovered in 1956 but whose female had never been described) and a for the first time a female belonging to the same species which couldn't get off the ground. “It’s not unheard of for only the female of a species to be flightless,” says Midgley. “But there were no examples in this fly’s family, let alone its genus.” Martin Hauser, a senior dipterologist at the California Department of Food and Agriculture, who was not involved in the research, told the Guardian: “Active flight has only originated four times in the last three billion years, so it’s always interesting when a species loses the ability to fly. It isn’t super surprising to find flightless species. But it is remarkable when the first case of flightlessness is reported in a family.” Scientists could only make educated guesses about why the female had lost the ability to fly. Despite it being much faster than walking, allowing flies to escape predators. “flight is also costly,” said Midgley. “You have to grow wings, and it uses a lot more energy than walking.” “For the males it is worth flying around and being able to search a larger area for females,” said Hauser. “Even if, while flying, they are exposed to birds and other predators, and risk being blown off the mountain and ending up in a hot valley with no females.” Meanwhile, there are other species that can't fly like ostriches, kiwi and emus. It is thought they evolved to lose flight after the dinosaurs became extinct because there were no predators big enough to hunt them. Fly - you had one job... Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-18 19:28
