
New York Forecast to Get More Snow This Winter: Weather Watch
The snow drought could be over for New York and the northeastern US this coming winter, according to
2023-10-05 21:51

Hyundai, Kia to adopt Tesla EV-charging standard from 2024 in US
SEOUL (Reuters) -Hyundai Motor and Kia Corp said on Thursday that they had decided to adopt Tesla Inc's electric vehicle
2023-10-05 21:51

Nintendo Download: An Electrifying Enigma
REDMOND, Wash.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Oct 5, 2023--
2023-10-05 21:20
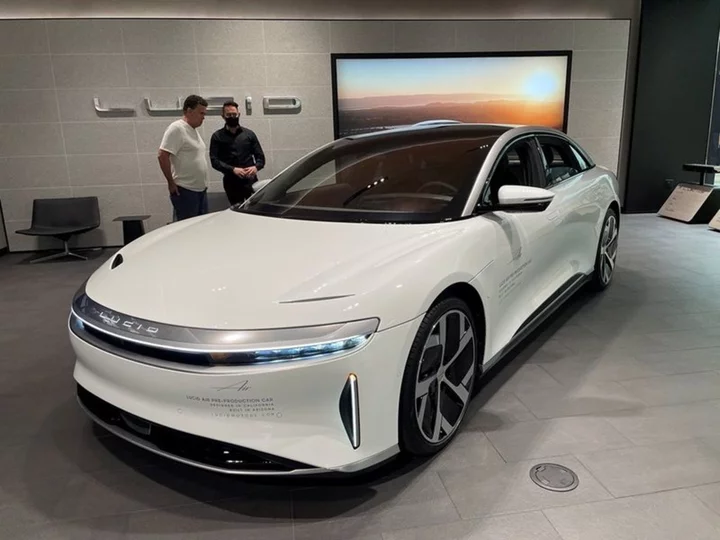

Lucid launches cheaper Air Pure electric sedan to revive demand
(Reuters) -Luxury electric-vehicle maker Lucid Group on Thursday launched a cheaper, rear-wheel drive version of the Air Pure sedan starting
2023-10-05 21:19

Scientists make creepy discovery about ancient cannibal rituals
A stark new discovery has revealed that cannibalism was a common practice in Europe to commemorate the dead 15,000 years ago. Research from London’s Natural History Museum (NHM) found human remains at a famed Paleolithic site in Cheddar Gorge that appeared to have bite marks across 100 of the bones. Scientists believe this is sufficient evidence of cannibalism in the Magdalenian group. "We interpret the archaeological evidence that cannibalism was practised on multiple occasions across northwest Europe over a short period of time as an indication that such behaviour was part of a funerary behaviour among Magdalenian groups, and not simply practised out of necessity," Dr Silvia Bello, paleoanthropologist and principal researcher said in a statement. Postdoctoral researcher William Marsh went on to say that the study contextualised the area by reviewing all sites "attributed to the Magdalenian culture." "During the terminal time period of the Palaeolithic, you actually see a turnover in both genetic ancestry and funerary behaviour, indicative of population replacement as Epigravettian groups migrated northwards," he said, as per IFL Science. "We believe that the change in funerary behaviour identified here is an example of demic diffusion where essentially one population comes in and replaces another population and that brings about a change in behaviour." Fast forward to 2023, and now people are having their bodies frozen in hopes they can "wake up" in the future. Cryonics "is the practice of preserving humans and animals at cryogenic temperatures in the hope that future science can restore them to a healthy living condition as well as rejuvenate them," according to the National Library of Medicine. "At present cryonics can only be performed after pronouncement of legal death of the cryonics subject." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-05 21:18
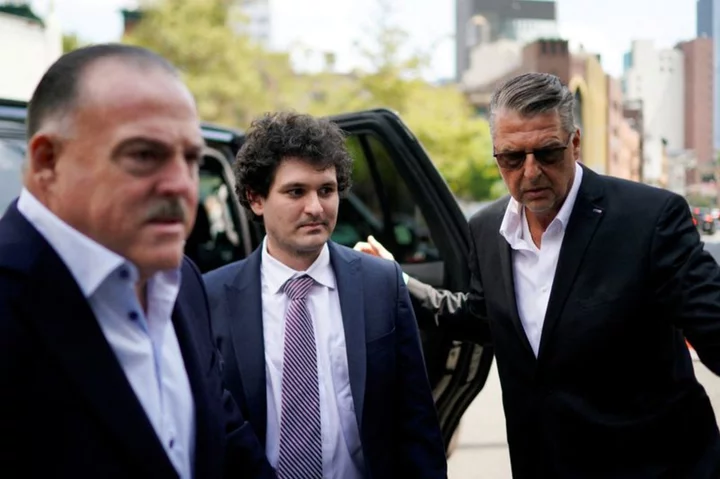

FTX customers are still grappling with crypto platform's collapse
By Elizabeth Howcroft and Medha Singh LONDON For Lee Rees, 43, FTX was one of a handful of
2023-10-05 20:51
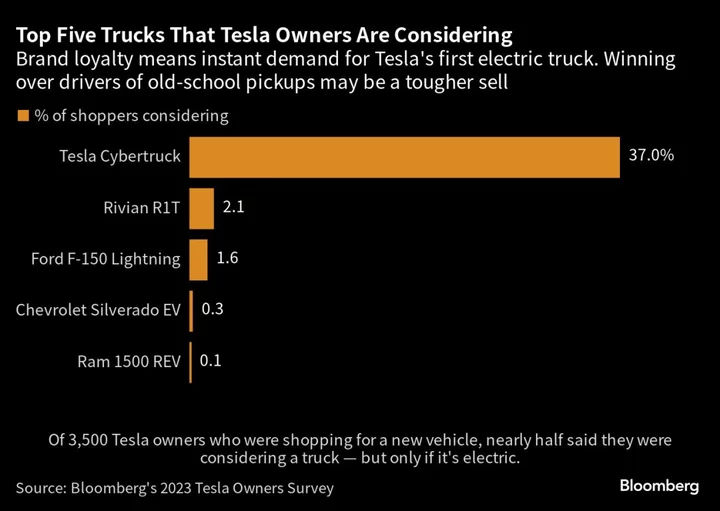
Where Is Tesla’s EV Competition?
After a decade of being trounced by Tesla Inc., this was supposed to be the year that traditional
2023-10-05 20:27

UAE Energy Giant Awards $17 Billion Gas Expansion Contracts
The biggest oil producer in the United Arab Emirates awarded contracts worth almost $17 billion to develop an
2023-10-05 20:19
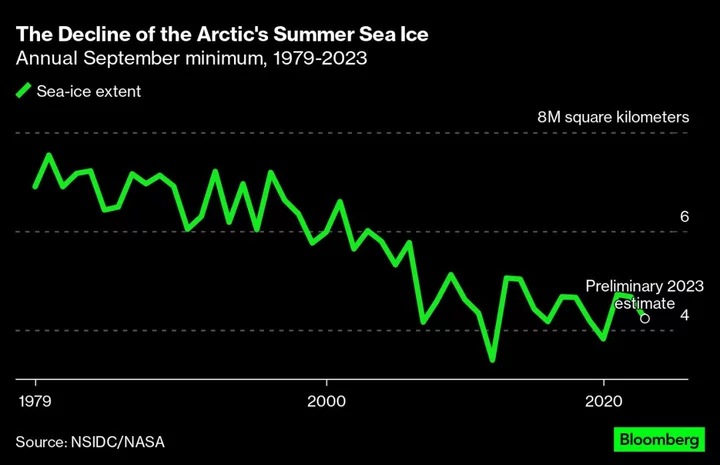
Baby Polar Bears Can’t Get Enough Milk When Sea Ice Disappears
Polar bears may be struggling to nourish their young as melting sea ice forces some populations to fast
2023-10-05 19:48
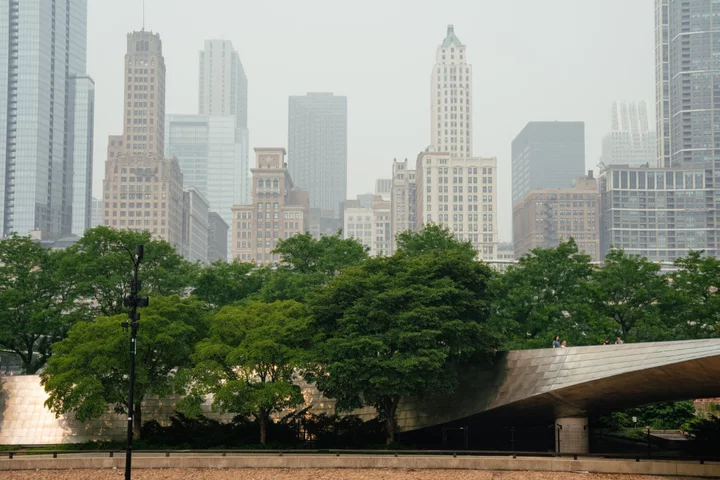

Chicago Seeks to Nix Rust Belt Label With $1 Billion Climate Bid
Eager to scrap its Rust Belt reputation, a new US Midwest coalition is seeking $1 billion in federal
2023-10-05 19:46
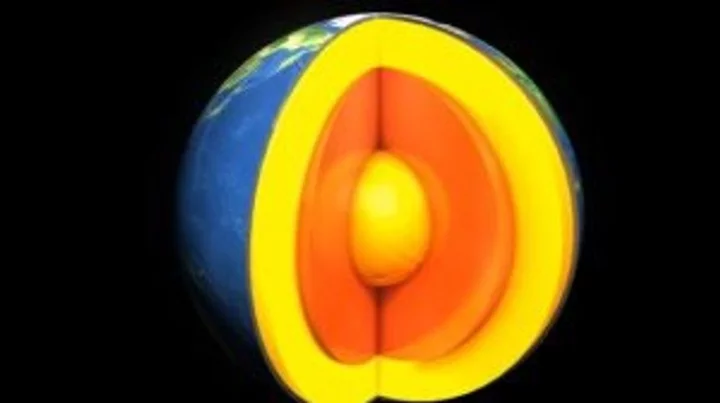

Scientists shed surprising new light on the Earth's 'butter-like' inner core
For centuries we’ve been told that the Moon is made of cheese but now, it turns out, the Earth is more like butter. Or, at least, its inner core is. A new study led by experts at the University of Texas (UT) and collaborators in China found that iron atoms at the very centre of our world move around much more than previously thought, and the implications could be huge. Scientists have long sought to dissect the insides of our planet but it isn’t easy, given that we have no way of directly exploring its core. The deepest hole humans have ever dug – branded the "entrance to hell" – extended an impressive 12,263m (40,230ft) down, but even that doesn’t come close to breaking through the crust to the layers beneath. Still, thanks to techniques like seismic tomography – which analyses how waves of energy travel through different materials during earthquakes – we’ve been able to map out the world’s interior. Now, researchers have used lab experiments and AI algorithms to shed a striking new light on the heart of the planet. "Seismologists have found that the centre of the Earth, called the inner core, is surprisingly soft, kind of like how butter is soft in your kitchen," Youjun Zhang, a Sichuan University professor who co-led the investigation, said in a statement shared with Phys.org. "The big discovery that we've found is that solid iron becomes surprisingly soft deep inside the Earth because its atoms can move much more than we ever imagined. This increased movement makes the inner core less rigid, weaker against shear forces." The findings are significant because they could help explain the role that the inner core plays in generating the world’s magnetic field. They could also help us understand a number of the inner core’s key properties, which have long flummoxed experts. "Now, we know about the fundamental mechanism that will help us with understanding the dynamic processes and evolution of the Earth's inner core," Jung-Fu Lin, one of the study's lead authors, explained. Given that it is impossible for scientists to directly extract specimens from the inner core, Lin and his colleagues recreated it in miniature. They took a small iron plate, shot it with a fast-moving projectile, and collected the resulting temperature, pressure and velocity data, which they then fed into an AI computer model. Using this machine learning system, they were able to scale up the sample iron atoms configuration to mimic the atomic environment within the inner core. At this beefed-up scale, the researchers observed groups of atoms moving about while still maintaining their overall structure. Inner Core iron atom motion model University of Texas This movement could explain why seismic measurements of the inner core reveal an environment that's softer and more malleable than would be expected at such pressures, Prof Zhang explained. Around half of the energy that goes into generating the Earth's magnetic field can be attributed to the inner core, with the rest coming from the outer core, according to the UT team. Thanks to Zhang, Lin and their colleagues, we now have a clearer understanding of the inner core’s machinations at an atomic level, which could help inform how energy and heat are generated at the heart of the planet. This could also shed light on how the inner and outer core work together to generate the Earth’s magnetic field – a key ingredient in making a planet habitable. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-05 19:22
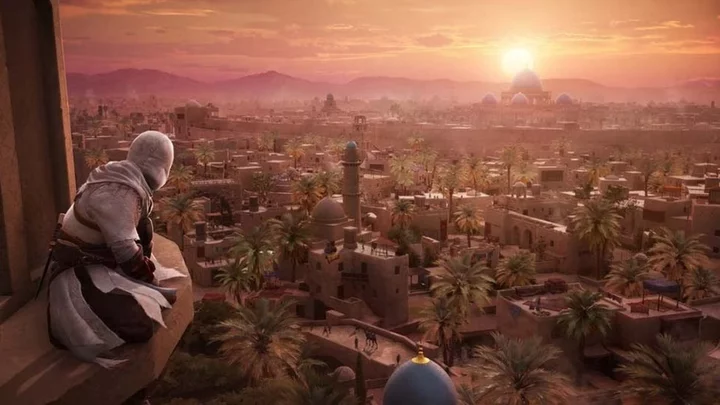

Assassin's Creed Mirage: Why Arabic is at the heart of the new game
The makers of the latest in the stealth action series have put Arabic front and centre of the project.
2023-10-05 19:16
