
US Treasury unit proposes stepping up scrutiny of crypto mixers
By Hannah Lang (Reuters) -The U.S. Treasury Department’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) on Thursday proposed increasing transparency around cryptocurrency
2023-10-20 03:55
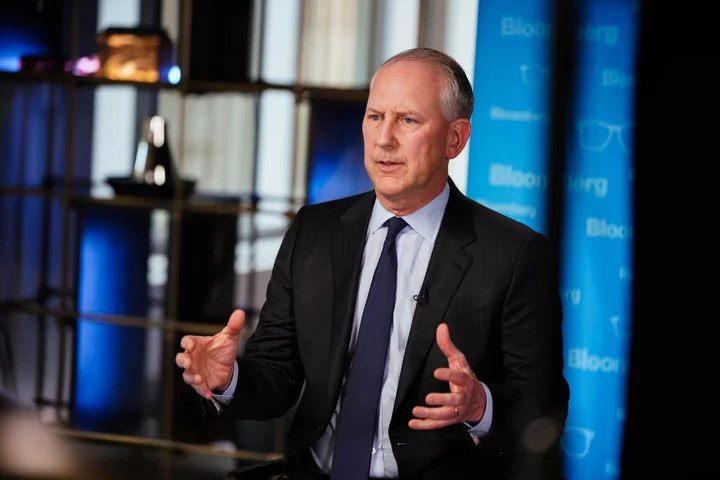

AIG’s CEO Sees Pandemic, Wars and Climate Change Among Biggest Risks
American International Group Inc. Chief Executive Officer Peter Zaffino said the biggest challenge to the insurance sector over
2023-10-20 02:58

Cities: Skylines 2 Recommended Specs
Players are curious about the city-builder simulation known as Cities: Skylines 2.
2023-10-20 02:48

Here's When Call of Duty Games Are Likely Coming to Xbox Game Pass
Call of Duty Games are likely coming to Xbox Game Pass in 2024 as Microsoft works to bring Modern Warfare 3 and more CoD titles to the service in the future.
2023-10-20 02:23

Scientists receive powerful ‘fast radio burst’ from the depths of the universe
The Earth has been hit by a powerful blast of energy from the very depths of the universe. The fast radio burst is the most distant of its kind of ever seen, coming from so far away that it has travelled eight billion years to get to Earth. It is also astonishingly powerful, one of the most energetic of its kind ever seen. In less than a second, it released the same energy that comes out of the Sun in more than 30 years. Fast radio bursts are intense, short bursts of energy that come from unknown but extreme activity in space. Scientists are still unsure of how they are formed, but explanations have included everything from extraterrestrial technology to neutron stars. The newly discovered burst appears to come from a small group of merging galaxies, scientists say, which helps support current theories about where they come from. But the intensity of the burst is harder to explain, which challenges our understanding of how they are actually emitted. “While we still don’t know what causes these massive bursts of energy, the paper confirms that fast radio bursts are common events in the cosmos and that we will be able to use them to detect matter between galaxies, and better understand the structure of the Universe,” said Ryan Shannon, from the Swinburne University of Technology. The blasts could be useful ways of answering some of the deepest questions about our cosmos, such as how much it actually weighs. At the moment, attempts to answer that have led to confusing results. “If we count up the amount of normal matter in the Universe — the atoms that we are all made of — we find that more than half of what should be there today is missing,” said Professor Shannon. “We think that the missing matter is hiding in the space between galaxies, but it may just be so hot and diffuse that it’s impossible to see using normal techniques. “Fast radio bursts sense this ionised material. Even in space that is nearly perfectly empty they can ‘see’ all the electrons, and that allows us to measure how much stuff is between the galaxies.” The blast was spotted last year, using a telescope in Japan. Researchers then used other telescopes to verify the find and examine it in more detail. “Using ASKAP’s array of dishes, we were able to determine precisely where the burst came from,” said Stuart Ryder, the first author on the paper. “Then we used the European Southern Observatory (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile to search for the source galaxy, finding it to be older and further away than any other FRB source found to date, and likely within a small group of merging galaxies.” The findings are reported in a new paper, ‘A luminous fast radio burst that probes the Universe at redshift 1’, published in the journal Science. Read More Scientists unveil radical new ‘missing law’ to explain the universe India’s Modi declares goal to land human on Moon by 2040 Researchers reveal source of largest ever Mars quake
2023-10-20 02:23
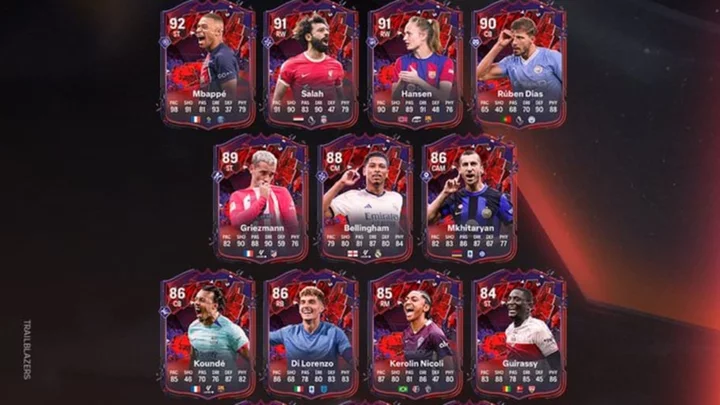
FC 24 Trailblazer Interceptor Evolution: How to Complete, Best Players to Use
FC 24 Trailblazer Interceptor Evolution program guide including how to complete each level, the full list of upgrades, the best players to use and when the program expires.
2023-10-20 02:17

COP28 Countdown Heats Up as Countries Spar Over Loss and Damage
COP28 is just six weeks away and countries are already trading blows over what is likely to be
2023-10-20 02:15
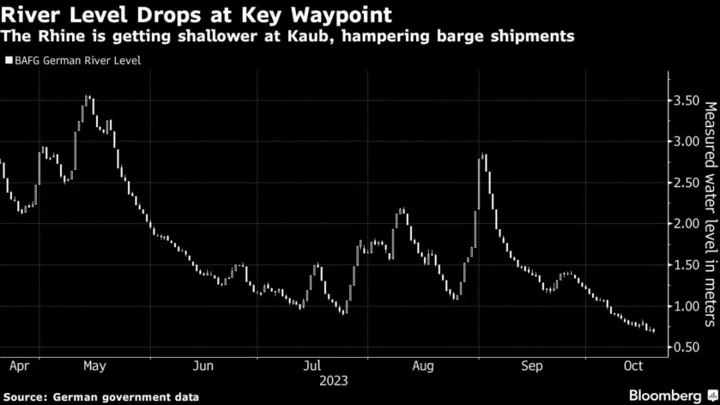
The River Rhine Gets Shallow Again in Fresh Climate Blow
The cost of shipping fuel along the Rhine river has surged as low water levels curb barges’ carrying
2023-10-20 00:56
Solar energy set to eclipse fossil fuels as world passes ‘tipping point’, study reveals
Solar energy has reached an “irreversible tipping point” that will see it become the world’s main source of energy by 2050, according to a new study. Researchers at the University of Exeter and University College London analysed recent technological and economic advances to determine that the transition to clean energy is not just reachable, but inevitable. “The recent progress of renewables means that fossil fuel-dominated projections are no longer realistic,” said Femke Nijsse from the University of Exeter. “Using three models that track positive feedbacks, we project that solar PV will dominate the global energy mix by the middle of this century.” Barriers may still arise to hamper this positive trend, the researchers noted, including political resistance from anti-environmentalists and the lack of financing for solar power in developing countries. “Solar energy is the most widely available energy resource on Earth, and its economic attractiveness is improving fast in a cycle of increasing investments,” the researchers wrote in a study detailing their findings. “We find that, due to technological trajectories set in motion by past policy, a global irreversible solar tipping point may have passed where solar energy gradually comes to dominate global electricity markets, without any further climate policies.” The study, titled ‘The momentum of the solar energy transition’, was published in the journal Nature Communications. The latest research comes less than a month after a Berlin-based research institute calculated that fossil fuel-generated power will no longer be economically viable within the next 30 years due to the plummeting costs of solar, batteries and other renewable technologies. The Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC) found that the transition to renewable energy was “cheaper than expected” and could make fossil fuels obsolete by 2050. “This is an extremely optimistic scenario – but it illustrates that the future is open,” MCC researcher Felix Creutzig noted. “Climate science, which provides policymakers with guidance in its scenario models, must reflect technical progress as closely as possible.” The UK saw a record-breaking year for renewable energy last year, and is on track to do the same in 2023 following the installation of new solar and wind plants. Wind, solar, biomass and hydro power generated 40 per cent of the country’s electricity in 2022, according to figures compiled by Imperial College London, up 5 per cent from the year before. Read More Fossil fuels ‘becoming obsolete’ as solar panel prices plummet Solar panel breakthrough could supercharge ‘miracle material’ production ‘Game-changing’ facial recognition technology catches prolific shoplifters WhatsApp update will change how you log in forever Amazon trials humanoid robots to see if they can help staff warehouses
2023-10-20 00:49

EU asks Meta for more details on efforts to stop illegal and inaccurate content on Israel-Hamas war
The European Union has told Meta it has a week to explain in greater detail how it is fighting the spread of illegal content and disinformation on its Facebook and Instagram platforms following the attacks across Israel by Hamas.
2023-10-20 00:21

US FCC votes to advance plan to reinstate net neutrality rules
WASHINGTON The U.S. Federal Communications Commission voted Thursday to advance a proposal to reinstate landmark net neutrality rules
2023-10-19 23:47

New York AG accuses crypto firms of deceiving investors in $1 billion fraud
On Thursday, New York's attorney general filed a lawsuit against three digital asset firms that were caught up in the collapse of Bankman-Fried's empire last fall — Gemini Trust, Genesis Global Capital and Digital Currency Group, parent company of Genesis.
2023-10-19 23:29
