
AI breakthrough could help us build solar panels out of ‘miracle material’, scientists say
Artificial intelligence is helping engineers build solar panels out of a “miracle material”. Scientists have long been excited about the possibility of new perovskite tandem solar cells, which could help bring the vastly improved efficiency of perovskite to mass production. They have an efficiency of more than 33 per cent, dramatically higher than conventional silicon solar cells. Those tandem solar cells come with a host of other benefits, too. They rely on inexpensive raw materials and can be made relatively easily. Engineers have faced a problem, however, in making them cheaply and at scale. To make them efficient, manufacturers need to make a very thin, high-grade layer of perovskite. Doing that is difficult. It relies on a complex process that varies significantly, seemingly with little explanation. Trying to improve that process has often relied on a gradual process of trying out new possibilities through trial and error. Now scientists have successfully built a new system that uses artificial intelligence to try and work out how to build those layers better. Instead of picking through video recordings to work out how different layers work, researchers were able to train a computer system to spot the hidden signs of good and bad coatings. After the system was built, it was able to be used better understand how to change the production to make it more efficient, researchers said. “These are extremely exciting results,” said Ulrich W Paetzold, a researcher from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, who worked on the new study. “Thanks to the combined use of AI, we have a solid clue and know which parameters need to be changed in the first place to improve production. “Now we are able to conduct our experiments in a more targeted way and are no longer forced to look blindfolded for the needle in a haystack. This is a blueprint for follow-up research that also applies to many other aspects of energy research and materials science.” An article describing the breakthrough, ‘Discovering Process Dynamics for Scalable Perovskite Solar Cell Manufacturing with Explainable AI’, is published in Advanced Materials. Read More Tiny solar-powered van unveiled in Japan Solar panel world record smashed with ‘miracle material’ ‘We let you down’: Peloton apologises for Thanksgiving ride
2023-11-25 01:16

Sunak Will Pledge UK Support for New Climate Damage Fund at COP28
The UK plans to announce its support for a new fund that helps vulnerable countries cope with the
2023-11-25 00:57

Apple’s China Demand Remains Firm Heading Into the Holidays. There Is No ‘Growth Demise’.
The latest data on iPhone demand in China should reassure Apple bulls it can keep climbing, according to Wedbush’s Dan Ives.
2023-11-25 00:29

World's largest iceberg breaks free, heads toward Southern Ocean
(Adds additional reporting credit) By Gloria Dickie -The world's largest iceberg is on the move for the first time in
2023-11-24 23:59
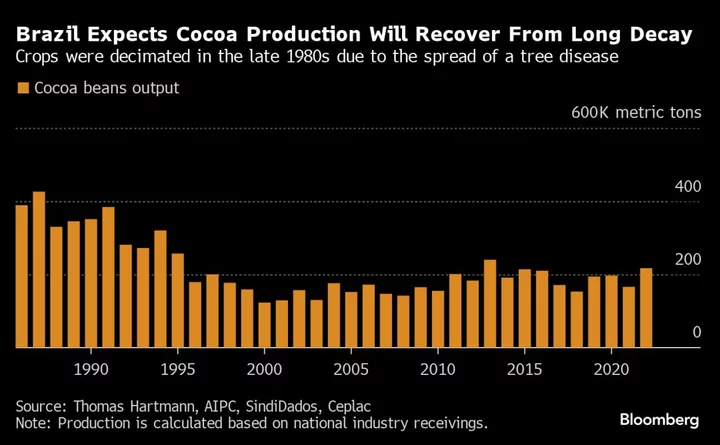
Cocoa Farming Lures New Money as Brazil Is Set to Revive Exports
Cocoa farmers in Brazil are getting ready for a dramatic comeback. Once a prominent global supplier, the country
2023-11-24 23:58
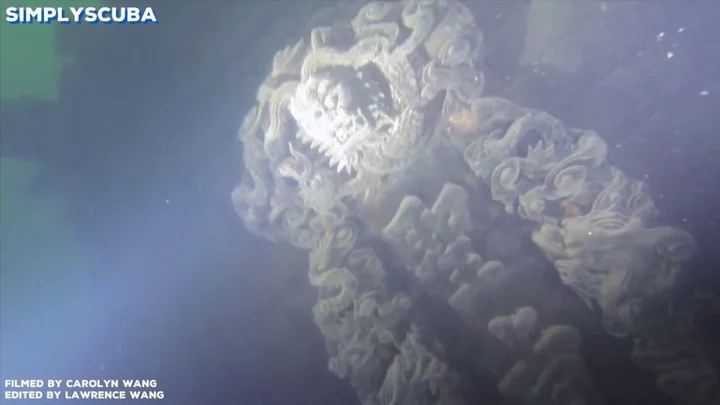

Ancient Chinese city found perfectly preserved at the bottom of a lake
Submerged beneath a manmade lake in China lies a forgotten city, dubbed by experts as “China’s Atlantis”. The underwater city, known as the Lion City or Shi Cheng, is hidden 40 metres beneath the surface of Qiandao Lake in eastern China. In 2001, officials discovered – or rediscovered – that the metropolis had been perfectly preserved after years underwater, and by 2017 had opened it up as a diving site for tourists. But what is the history of the Lion City, and how did it end up underwater? Shi Cheng is thought to have been built during the Eastern Han Dynasty between 25AD and 200AD. It was once a political and economic hub in the eastern province of Zhejiang, with a regional seat of power located in the city. The city walls, believed to date back to the 16th century, had five entrance gates, as opposed to the traditional four in old Chinese cities, and its wide streets contain 265 archways featuring stonework of dragons, phoenixes and (you guessed it) lions. However, in 1959, the Chinese government decided to build a hydroelectric power plant in the area and, somewhat shockingly, decided to flood the city to do it. This didn’t just amount to getting rid of a historical artefact. More than 300,000 people needed to be rehoused for the project, which ultimately birthed Qiandao Lake. A surprising side effect to this was that the city remains as a time capsule to the period when it was flooded. Since the water used to submerge it did not contain anything corrosive, and was not conducive to marine life, the remains are in perfect condition. And even though it was still functioning as a city until the mid-20th century, the Lion City has still not been completely mapped out. Now, divers are slowly working through each building, structure, archway, road and house to eventually put together a full picture of what it would have looked like. Until then, it will remain at least party shrouded in mystery, as China’s very own Atlantis. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-24 23:51

Kinnate Biopharma, Madrigal Pharma, and More Stocks See Action From Activist Investors
OrbiMed Advisors is part of a partnership interested in acquiring all of Kinnate Biopharma. Baker Brothers increased an investment in Madrigal Pharmaceuticals.
2023-11-24 23:22

The Microsoft Black Friday Ad: Save Big on Surface and Xbox
If you've been eyeing a Surface device, Black Friday is a great time to save
2023-11-24 23:20

Snag a PS5 Bundle Deal for Black Friday
Some deals are harder to come by, and that’s true for the PlayStation 5 games
2023-11-24 23:18

U.N. meeting debates aviation emissions goal through cleaner fuels
By Allison Lampert (Reuters) -Global aviation officials on Friday sought to agree an interim target for cutting carbon emissions from
2023-11-24 22:59
Scientists discover that bacteria has 'memories' that pass on to future generations
Scientists have made an astonishing discovery that suggests bacteria contain memories to be passed on to future generations. Researchers at the University of Texas and the University of Delaware found that despite having no brain or nervous system, certain bacteria may be able to form memories and remember certain behaviours depending on the available cellular iron. When iron levels are low, bacteria can hunt for local iron in their environment, prompting scientists to believe its memory has evolved, according to Science Alert. "Bacteria don’t have brains, but they can gather information from their environment, and if they have encountered that environment frequently, they can store that information and quickly access it later for their benefit," Souvik Bhattacharyya, the lead author of the recent study said. "We show [...] that a prior experience of swarming is remembered when Escherichia coli encounters a new surface, improving its future swarming efficiency," Souvik explained. "An iron-based memory might offer the advantage of providing a hub connecting various stress responses such as antibiotic survival and biofilms." The 'memories' lasted for around four generations, before generally coming to an end by the seventh. "Before there was oxygen in the Earth’s atmosphere, early cellular life was utilizing iron for a lot of cellular processes. Iron is not only critical in the origin of life on Earth, but also in the evolution of life,” the study author went on to explain. "It makes sense that cells would utilize it in this way." How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-24 22:21

iRobot Stock Jumps on Report Amazon Deal Set to Win EU Approval
Amazon's $1.4 billion deal to buy smart vacuum cleaner company iRobot is set to win full EU antitrust approval, according to a report.
2023-11-24 21:56
