
Several US regulators seek information from Kazakh fintech Freedom
(Reuters) -Several U.S. regulators have requested Kazakhstan-based Freedom Holding for information, a company spokesperson told Reuters on Friday, adding that
2023-10-07 00:57
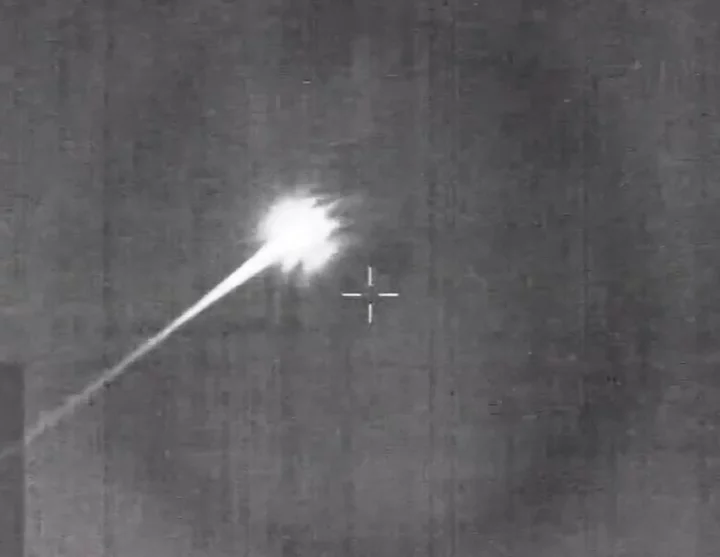

Pieces of distant, ancient asteroid arrive on Earth from Nasa spacecraft, after travelling billions of miles
A piece of asteroid has arrived on Earth from the other side of the solar system, in a major success for Nasa’s Osiris-Rex mission. The spacecraft has spent years flying to Asteroid Bennu, gathering up a piece of it, and bringing it back home so that it can be studied by researchers. It brings an end to a mission that took seven years, saw it travel 4 billion miles, and cost more than a billion dollars. Scientists hope that study can help reveal how planets formed and evolved, and might shed light on how life itself began. Since Bennu is around 4.5 billion years old, the sample is almost like a look back into the solar system during its early years and Nasa has referred to it as a “time capsule”. Asteroid Bennu is also notable as Nasa’s “most dangerous asteroid”, according to a scale used to measure how much of a hazard a given object poses. It is the first time that Nasa has brought back a piece of an asteroid, and the first time since 2020. It is also the biggest ever to be gathered, at around 250 grams. Nasa sent a team on board helicopters to gather the sample canister, extracting it to ensure that it did not become contaminated by the environment. Since the sample was directly from the asteroid, it will not have any trace of material from the Earth on it, unlike those that fall to Earth. That sample will be distributed between 200 people at 38 institutions across the world, including those in the UK. The Osiris-Rex mission left Earth in September 2016, and arrived at the asteroid in October 2018. It gathered samples in October 2020, and then left the asteroid in April 2021. Since then, both the sample and the spacecraft have been returning back from the other side of the solar system to Earth. The spacecraft then dropped off the sample to return home, while Osiris-Rex will carry on to study another asteroid called Apophis, where it will arrive in 2029. Apophis is also notable for its danger: at times, it has challenged Bennu at the top of the league table of most dangerous objects. But recent research has suggested that Apophis poses less of a danger. Ashley King, UKRI future leaders fellow, Natural History Museum, said: “Osiris-Rex spent over two years studying asteroid Bennu, finding evidence for organics and minerals chemically altered by water. “These are crucial ingredients for understanding the formation of planets like Earth, so we’re delighted to be among the first researchers to study samples returned from Bennu. ‘We think the Bennu samples might be similar in composition to the recent Winchcombe meteorite fall, but largely uncontaminated by the terrestrial environment and even more pristine.” Dr Sarah Crowther, research fellow in the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences at the University of Manchester, said: “It is a real honour to be selected to be part of the Osiris-Rex sample analysis team, working with some of the best scientists around the world. “We’re excited to receive samples in the coming weeks and months, and to begin analysing them and see what secrets asteroid Bennu holds. “A lot of our research focuses on meteorites and we can learn a lot about the history of the solar system from them. “Meteorites get hot coming through Earth’s atmosphere and can sit on Earth for many years before they are found, so the local environment and weather can alter or even erase important information about their composition and history. “Sample return missions like Osiris-Rex are vitally important because the returned samples are pristine, we know exactly w Read More Pieces of a distant asteroid are about to fall to Earth Nasa to return largest asteroid sample ever as UK helps with research Astronomers find abundance of Milky Way-like galaxies in early universe Pieces of a distant asteroid are about to fall to Earth Nasa to return largest asteroid sample ever as UK helps with research Astronomers find abundance of Milky Way-like galaxies in early universe
2023-09-24 23:26

Wemade Celebrates Second Anniversary of MIR4 Global Service with Special Events!
SEOUL, South Korea--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 22, 2023--
2023-08-22 21:22

Samoa media guide
An overview of the media in Samoa, including links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-07-11 20:53
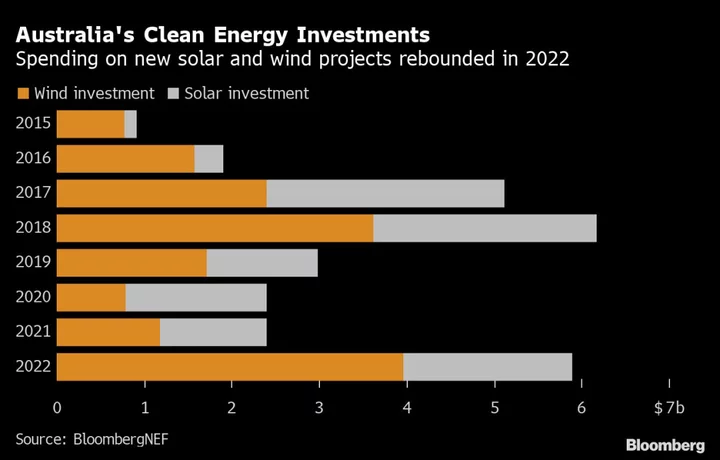
Australia Sees Power Gaps Over Next Decade as 62% of Coal Operations Shut Down
Australia’s grid operator sees risks of energy shortfalls over the next 10 years as the nation retires 62%
2023-08-31 07:53

ATLAS Space Operations Welcomes John Williams as New Chief Executive Officer
TRAVERSE CITY, Mich.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 5, 2023--
2023-07-05 17:23

Australia says tougher laws needed on artificial intelligence
SYDNEY Australia said on Thursday it planned to regulate artificial intelligence (AI) including a potential ban on deep
2023-06-01 09:51

Uber increasingly considering buybacks as cash flow ramps up - CEO
Uber Technologies is considering buybacks and dividends to shareholders as its cash flow ramps up, CEO Dara Khosrowshahi
2023-09-08 03:57
Twitter 'X' renaming gathers the internet to warm itself around the garbage fire
Elon Musk rebranded Twitter as "X" and the internet reacted with jokes and befuddlement. The
2023-07-24 22:53
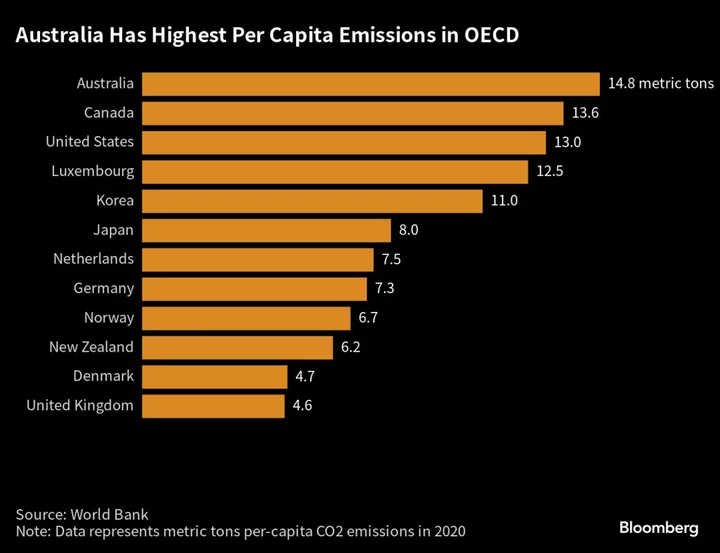
Investors With $8 Trillion Target Australia Over Climate Change
A UN-backed investor program designed to pressure Australia to accelerate decarbonization plans will add 18 new money managers
2023-09-01 04:26
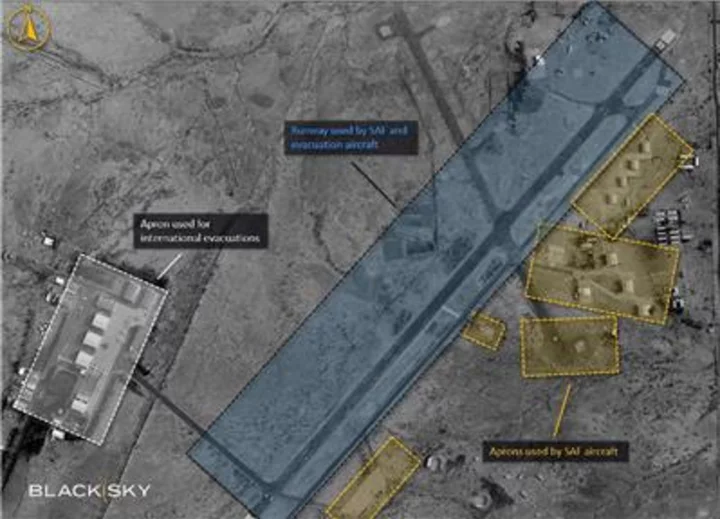
BlackSky Imagery Highlights Scale of Operational Complexity of International Evacuation During Early Days of 2023 Sudan Conflict
HERNDON, Va.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 24, 2023--
2023-08-24 20:46
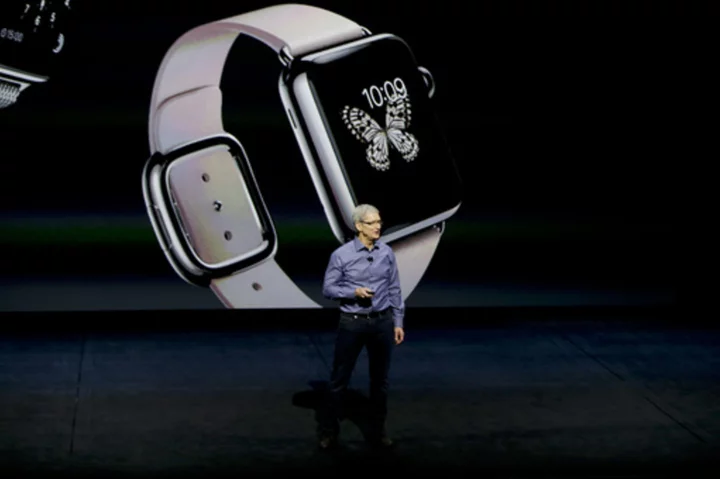

Apple is expected to unveil a sleek, pricey headset. Is it the device VR has been looking for?
Apple appears poised to unveil a long-rumored headset that will place its users between the virtual and real world
2023-06-04 20:51
You Might Like...
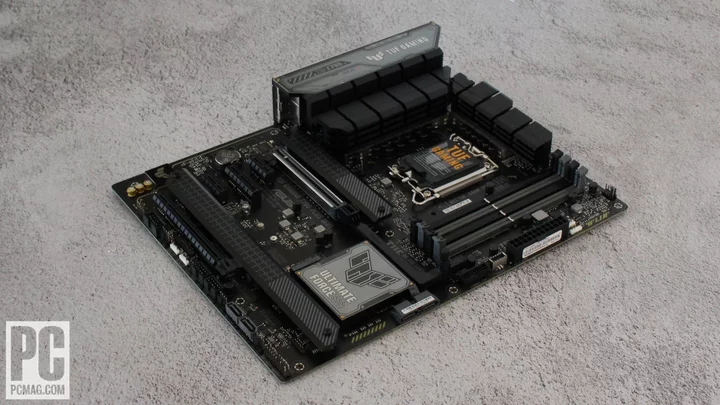

Asus TUF Gaming Z790-Plus Wi-Fi Review

'Browse With Bing' Disabled on ChatGPT Plus Because It Bypassed Paywalls

California’s Newsom Says State Needs Infrastructure Boom Bigger Than Any in Decades

'Sister Wives' star Meri Brown sparks dating rumors over cryptic post about 'best friend' Blair M Struble

Canada's Bell deepens news industry gloom with 1,300 job cuts

Amazon expands pay-by-palm service in US grocery stores

Google monopoly trial: Is the US losing the fight against Big Tech?

Reddit on New Pricing Plan: Company ‘Needs to Be Fairly Paid’
