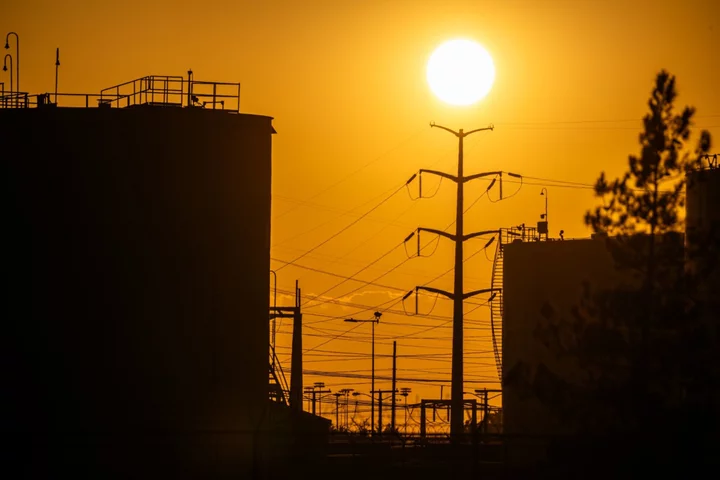

Quarter of US Population Faces Extreme Heat This Week
Nearly 25% of the US population is facing high, wilting temperatures that show no sign of abating anytime
2023-07-14 00:51

Fortnite x Futurama Bender, Fry, and Leela Skins: All Items, Price
Futurama x Fortnite Bender, Fry, and Leela skins, along with matching cosmetics, are now available to purchase for 2,800 V-Bucks in the Item Shop.
2023-07-27 00:20

Presenting the Razer Blade 16 x Automobili Lamborghini Edition – Supercar Excellence Meets Gaming Dominance
IRVINE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 21, 2023--
2023-09-22 02:24

Internet accuses Adin Ross of copying Kai Cenat and Andrew Tate as he announces 'jail' warehouse stream
'Damm got to steal other people’s ideas because he can’t come up with his own,' one social media user wrote
2023-09-12 19:59

Life After Stadia: How to Play Games on Your Chromebook
You would be forgiven for thinking your Chromebook can't handle the rigors of PC gaming.
2023-05-20 06:22
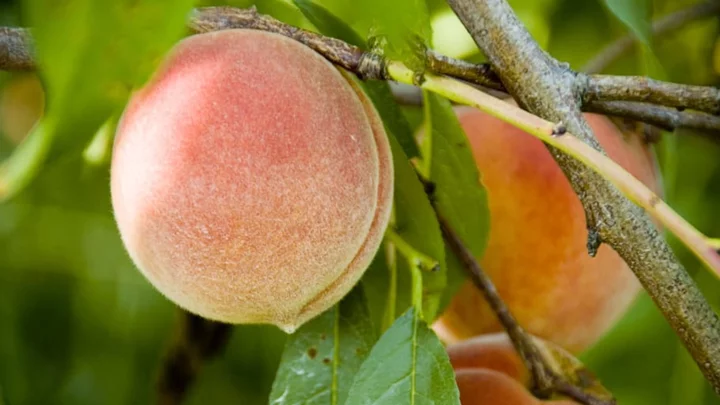

Why Are Peaches Fuzzy?
Whether you enjoy the velvety skin on peaches or peel it off, you may wonder why they developed fuzz in the first place.
2023-06-09 22:24

Is IShowSpeed possessed? Kai Cenat warns YouTuber as he sits in most haunted chair: 'You stupid a**'
Explore the details of what transpired in the video, the whereabouts of these two internet personalities, and the reasons behind Speed's 'possession'
2023-07-04 14:57

GPR Appoints Dr. Ingo Stuermer to Advisory Board Following Recent Series A Funding Announcement
SOMERVILLE, Mass.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 1, 2023--
2023-06-01 22:46
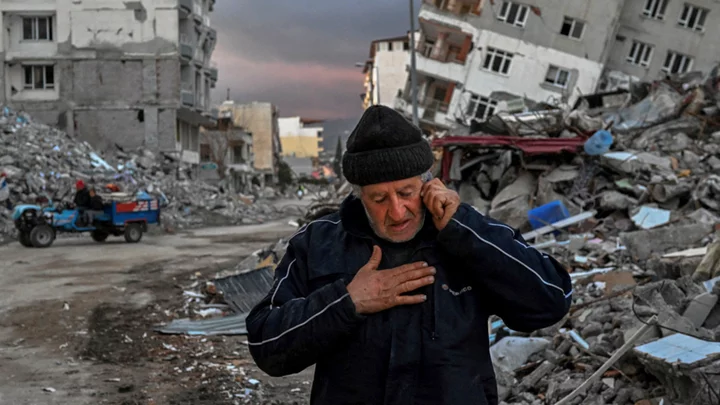

Google alert failed to warn people of Turkey earthquake
The tech giant claims millions of people were sent a warning before the deadly earthquake earlier this year.
2023-07-28 00:20
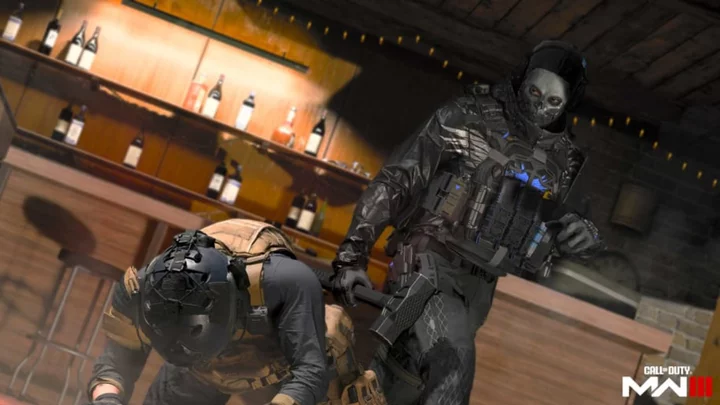

What's the Average K/D in MW3?
The average K/D in MW3 right now is a 1.0 K/D, meaning for every kill you get, you also record a death. Here's how to check your K/D in MW3.
2023-11-16 02:21

Scientists invent electronic skin that gives amputees sense of touch
Scientists have invented a type of electronic skin that can “talk directly to the brain”, allowing amputees to feel a human-like sense of touch through prosthetic limbs. The ground-breaking artificial skin is embedded with sensors for temperature, pressure and strain, which are converted into electrical signals – similar to how nerve impulses communicate with the brain. The wearable electronic circuit, known as a monolithic e-skin, was developed by a team from Stanford University, who detailed their breakthrough in a study published in the journal Science. Stanford University’s Zhenan Bao, who was a senior author of the study, told The Independent that the next-generation technology could also be used to feel objects and sensations while controlling a robotic limb remotely. “We’ve been working on a monolithic e-skin for some time,” Professor Bao said. “The hurdle was not so much finding mechanisms to mimic the remarkable sensory abilities of human touch, but bringing them together using only skin-like materials.” Weichen Wang, a doctoral candidate in Bao’s lab, added: “Much of that challenge came down to advancing the skin-like electronic materials so that they can be incorporated into integrated circuits with sufficient complexity to generate nerve-like pulse trains and low enough operating voltage to be used safely on the human body.” A prototype of the e-skin, which is about the thickness of a piece of paper, is the first to combine all the desired electrical and mechanical features of human skin in a soft and durable form. The team now plans to increase the scalability of the technology and develop an implantable chip to allow wireless communication through the body’s peripheral nerve. Other recent research into electronic skin has focussed on robotics, aiming to provide robots with sensory feedback and physical self-awareness. A team from the University of Edinburgh unveiled a device earlier this year that offered perceptive senses “similar to those of people and animals”. A separate study in 2023 from engineers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) outlined a type of artificial skin capable of sensing toxic chemicals, which could allow robots to detect anything from pollution in rivers to nerve agents and biohazards. Read More AI robots figure out how to play football in shambolic footage Scientists develop device that allows amputees to feel warmth in phantom hand Charting the controversial rise of the world’s most popular app Montana TikTok ban ‘unconstitutional’ and ‘impossible to enforce’
2023-05-19 02:26
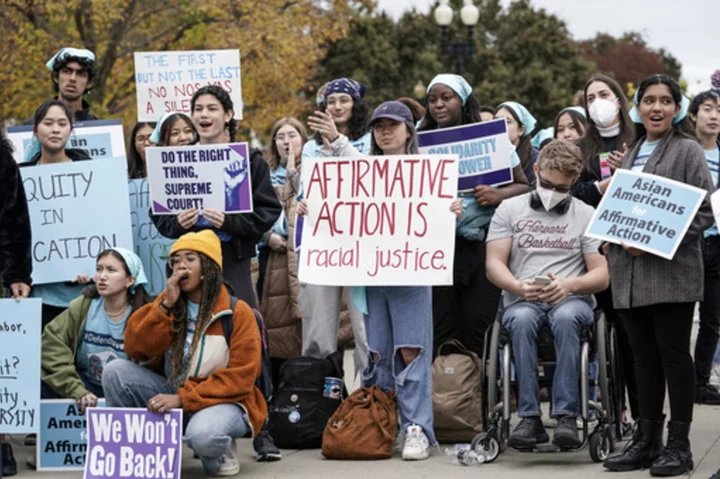
Most in U.S. say don't ban race in college admissions but that role should be small: AP-NORC poll
As the Supreme Court decides the fate of affirmative action, most people in the U.S. say the court should allow consideration of race as part of the admissions process
2023-05-30 12:54
You Might Like...

Scientists discover why a huge gravity hole has opened in the Indian ocean

Pay once for 20TB of cloud storage for life, and save 93%

Stellantis resets China strategy with $1.6 billion stake in EV firm Leapmotor

Starfield becomes Bethesda's biggest game launch of all time

How to do the Remini AI headshots on TikTok

China's electric vehicle giant BYD sees Q3 net profit as much as doubling
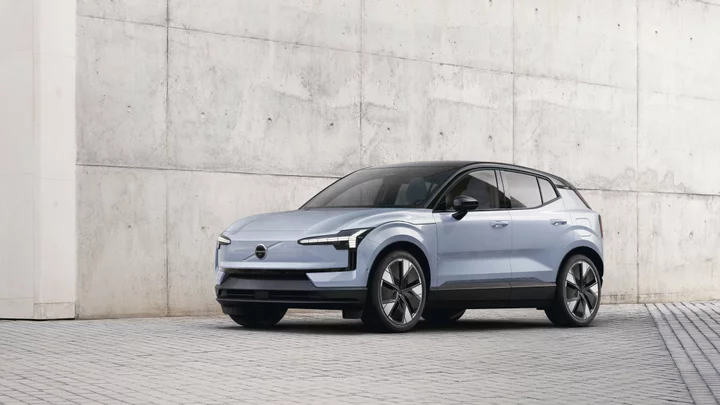

$35K Volvo EX30 Is a High-Tech, Sophisticated EV for Urban Drivers

FEV and dSPACE cooperate in worldwide integration of power HIL test benches
