
Winklevoss claims fuel US probe of DCG crypto business - Bloomberg News
Several U.S. agencies are investigating allegations of fraud leveled by billionaire Cameron Winklevoss against Digital Currency Group (DCG)
2023-09-08 04:47

Final Fantasy 16 faces ban from Saudi Arabia
'Final Fantasy 16' won't be released in Saudi Arabia unless modifications are made.
2023-05-09 20:19

Roblox misses quarterly bookings estimates on lower spending, shares tumble
(Reuters) -Gaming platform Roblox missed estimates for second-quarter bookings on Wednesday as waning demand for its online games and intensifying
2023-08-09 20:55

X now lets Premium subscribers hide likes and verify their real IDs
X, the platform formerly known as Twitter, got some new features this week. They are,
2023-09-16 04:27

Google in last ditch effort to overturn $2.6 billion EU antitrust fine
By Foo Yun Chee LUXEMBOURG Alphabet's Google on Tuesday made a last ditch effort at Europe's top court
2023-09-19 17:59

SimScale Strengthens Presence in Asia through Strategic Partnership with KKE Japan
MUNICH & TOKYO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 26, 2023--
2023-06-26 13:16

Four things to expect from GTA 6's first trailer
The hotly anticipated new trailer for the next Grand Theft Auto game is nearly upon us, and gamers are on tenterhooks. It has been more than 10 years since the last instalment of the world’s most popular video game, and the makers, Rockstar Games have been dropping cryptic hints about the next one over the next few months. Some fans have even reportedly quit smoking so they definitely live until the eventual release date. Safe to say, some people are unhealthily obsessed. With the trailer set to drop in early December, here are six things to expect. The location Previous Rockstar Games trailers have featured a highlight reel revealing the location of the game, and giving fans an idea of the new world they’ll be tearing up. Liberty City, Vice City, and Los Santos, the previous game locations, are as iconic to GTA players as any of its playable characters, so this is likely to be an important one. Moreover, Rockstar spends a huge amount of time and effort on world design, it’s a key part of the franchise. Any trailer will surely feature this heavily. The big question is: where will it be? A data leak last September suggested that it will be in a revamped version of Vice City – but whether that's the only location is anyone's guess. Some cars Everyone loves cruising around GTA game worlds in classic cars blasting music and occasionally stopping to commit some virtual crimes, right? Social media users certainly hope that cars – and other vehicles – will play a part in the upcoming trailer. One person commented on Reddit: “I know the game will take place in the modern era, but I really hope we'll see classic/old-school cars as well, like in GTA 5. “Something like a Chevrolet Bel Air or a Ford F-100 or basically anything from the 50s to the 80s. If 90% of the cars are going to be modern and electric, I will be pretty disappointed, not gonna lie.” How it will deal with the popularity of GTA Online The massive success of GTA Online, where players play against one another in a virtual world, will cause some headaches for people designing the trailer – and the next game in general. Will it give people the chance to continue their online adventures in the last game into the new one? Some gamers have spent untold amounts of money – and days of their life – on their GTA multiplayer profiles, so this will be a big concern for them. Other bits from the recent leak While official information about the game has been sparse, a massive data leak last September gave fans a sneak peak. About 90 videos from an in-development version of the game appeared on a forum, showing that the game might feature the series’ first playable female protagonist. The character, called Lucia, was clad in a pink outfit, and appeared to be robbing someone at gunpoint. It wouldn’t be unreasonable to expect that she will feature somewhere in the upcoming trailer. Fans on social media also speculated that the makers of the trailer will include various other, more random, aspects – one person suggested rollerblades, for example. Another person said they wanted to see a “police shootout”, which sounds a little more in-keeping with the franchise. Whatever the trailer brings, it will have gamers across the land incredibly excited.Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-29 03:29

11 Fictional Bands Who Scored Very Real Hit Songs
The Monkees may not have been a "real" band, but their chart-topping legacy speaks for itself.
2023-08-19 05:19

Chipotle restaurant hit with bad reviews after claims employee seduced women's husbands
A Florida branch of the Chipotle restaurant chain has been hit with a wave of negative reviews after claims an employee seduced multiple women’s husbands. An employee appearing to go by the name Lucy has apparently caused a stir after being named in several negative Yelp reviews of a Fort Myers, Florida, Chipotle restaurant. The reviewers all claim that Lucy has a tendency to seduce husbands and sleep with them and the scathing reviews were shared online. Twitter user @fiveeightshorty shared a screenshot of the Yelp reviews, writing: “Apparently there's some controversy at my local Chipotle.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Three separate one-star reviews posted one month ago all mentioned the employee Lucy by name and insinuated she sleeps with married customers. One of the reviews read: “Stay far away. Lucy the GM or whatever position she is in-- she likes to sleep with married men AKA her customers.” Another reviewer also added, “The guac sucks too!!”, at the end of their review about Lucy’s alleged activities. The tweet has been viewed almost 12 million times and led to a whole host of jokes. One person wrote: “Let her cook!!” Another said: “Sounds like Lucy is great with customer service to me.” “Sounds like Lucy's guac brings all the boys to the Chipotle,” someone else wrote. Since the review went viral, the Yelp page has been flooded with some hilarious (likely fake) five-star reviews. One review said: “Lucy went above and beyond when handling my burrito. Will be visiting this location much more frequently.” indy100 has contacted Chipotle for comment. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-25 22:57

TikTok CEO says 'we will prevail' against Montana ban
TikTok CEO Shou Chew vowed Tuesday that his company's legal battle against Montana will succeed, after the state passed a law that would ban the app from personal devices starting in January.
2023-05-24 01:19

Super Mario RPG Best Bonus Stats
Players wonder which bonus stats are best for each character in Super Mario RPG. We've got the answers here!
2023-11-21 08:57

Flexiv and Cardinal Machine Join Forces to Combat Labor Shortages With Adaptive Robots
SAN JOSE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 11, 2023--
2023-05-11 21:24
You Might Like...
Humans could be controlled by robots, AI firm’s founder warns

Former Twitter employee says working for Elon Musk was ‘hardest experience of her life’
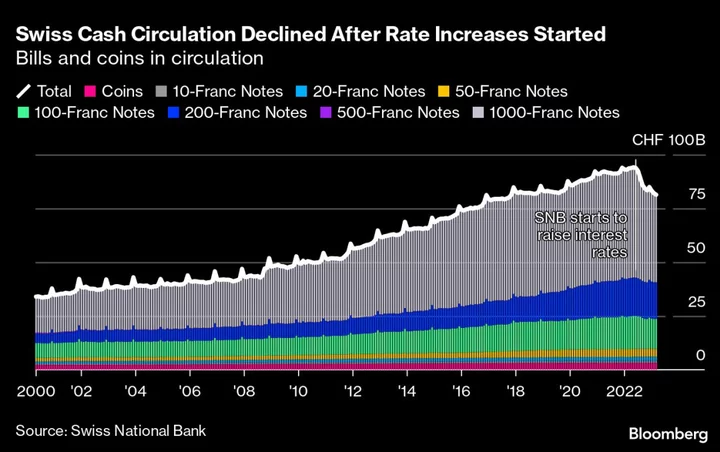
Swiss Fall Out of Love With Cash Amid Soul Searching About Money

Is Texas Chainsaw Massacre on Xbox Game Pass?

Venezuela: 'I'm paid to tweet state propaganda'

Dutch Ask TikTok for Access to Data as EU Scrutinizes Big Tech

The solution to Twitter's downfall isn't five Twitter clones

10 Facts About ‘My Brilliant Friend’
