
OpenAI just revealed DALL-E 3, it's newest image generator
OpenAI, the parent company of ChatGPT, has given its first official public preview of DALL-E
2023-09-21 03:50
Print your own temporary tattoos with this $230 gadget
TL;DR: As of May 15, you can grab the Prinker M temporary tattoo printer for
2023-05-15 17:50

Apex Legends Revenant Prestige Skin Leaked
New leaks claim an Apex Legends Revenant Prestige skin is coming to the Mythic Store, available for 150 Heirloom Shards, sometime in Season 18.
2023-08-15 00:53
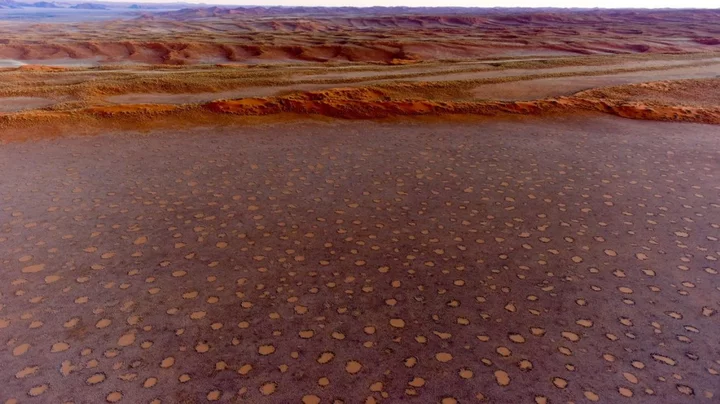

Mysterious 'fairy circles' are spreading across the world and scientists don't know why
A natural phenomenon consisting of polka-dot-style formations has been cropping up around the world, and scientists are baffled as to why. The circular-shaped patches of ground have been seen in deserts in Australia and Namibia but now experts believe they are more widespread than originally thought. Known as “fairy circles”, there are now 263 known sites across the globe where they can be found, according to new research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). They have been documented in 15 countries, across three continents, including the Sahel region of Africa, Madagascar, and in Middle-West Asia. And yet, despite the spread of these anomalies, scientists are still none the wiser about how they actually form. A team led by environmental scientist Emilio Guirado, of the University of Alicante in Spain, explained in their paper on the "intriguing" phenomenon: “We conducted a global and systematic assessment of fairy circle-like vegetation patterns and discovered hundreds of [fairy-circle]-like locations on three continents. “Our study provides insights into the ecology and biogeography of these fascinating vegetation patterns and the first atlas of their global distribution.” The mysterious circles appear in desert regions and can be as wide as 12 metres (39 feet) in diameter. They are almost always spaced out and rarely connect or overlap with one another. Several theories have been put forward as to what causes them, including, tiny insects, termites, and plant toxins. But, none have been accompanied by any significant evidence and some have been debunked completely. One significant factor limiting their study is they are often found in places that are difficult to access and are inhospitable. Locating the 263 different sites of “fairy circles” involved analysing high-resolution satellite imagery. Guirado and his team wrote in their paper: “[The sites] include those already identified in Namibia and Western Australia, as well as areas never described before, including the Sahel, Western Sahara, Horn of Africa, Madagascar, Southwest Asia, or Central and Southwest Australia. “By doing so, our study provides a global atlas of areas showing FC-like vegetation patterns and expands the known existence of this vegetation type to new countries and continents.” The team hopes that locating new sites will enable them to find common traits that may point towards their cause. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-26 20:18

Students: Slide into Summer Break Without Risking the Summer Slide
LOS ANGELES--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 22, 2023--
2023-06-22 22:53

Lies of P Pre-Load Times
Lies of P will arrive on Sept. 19, but when can players pre-load the game?
2023-09-06 03:25

Martin Odegaard FIFA 23: How to Complete the Premium FUTTIES SBC
Martin Odegaard FIFA 23 Premium FUTTIES SBC is now live requiring two segments to complete. Here's how to complete the SBC and if it's worth it.
2023-08-29 01:58

Bulgari apologizes to China for listing Taiwan as a country after online backlash
Italian luxury brand Bulgari is the latest international brand to apologize to China after listing Taiwan as a country on its website
2023-07-12 18:17
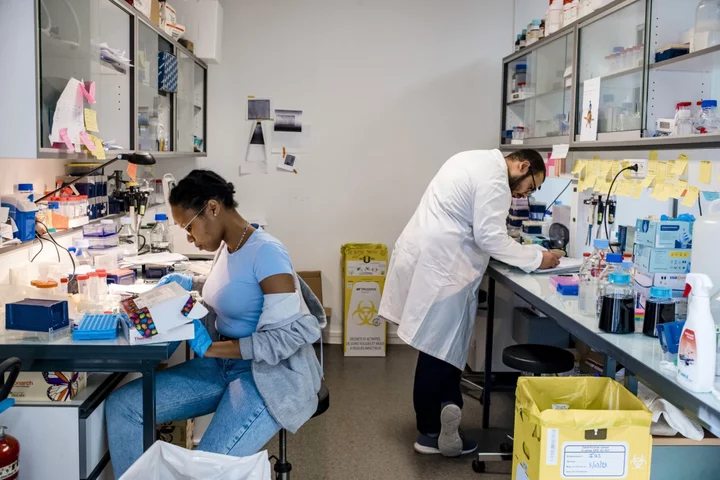

The Scientist Who Sounded the Alarm on 50,000-Year-Old Viruses
A fortnight camping on the mosquito-ridden, muddy banks of the Kolyma River in Russia may not sound like
2023-10-09 17:28

The best Apple deals from day two of Prime Day: AirPods, iPads, MacBooks, and more
You don't have to be a diehard Apple fan to know that aside from its
2023-07-13 01:23

Who is Amouranth dating? A look at Twitch streamer's ex-boyfriends
Amouranth has never been public with any of her relationships
2023-05-21 14:52

Ex-Apple designer Ive, OpenAI's Altman discuss AI hardware -The Information
Apple's former design chief, Jony Ive, and OpenAI CEO Sam Altman have been discussing building a new artificial
2023-09-27 11:28
You Might Like...

Analysis-Germany to face EU ire over Huawei supplies ahead of China talks

Australia’s Albanese May Face Anti-Nuclear Push at Pacific Talks

Update your Mac, iPhone and iPad right now to fix critical security hole

Jane Street, Jump Pull Back Crypto Trading Over US Regulatory Uncertainty

To Tame Inflation, Gen Z Is Turning to Cash

How BlackRock May Clear the Way for Spot-Bitcoin ETFs
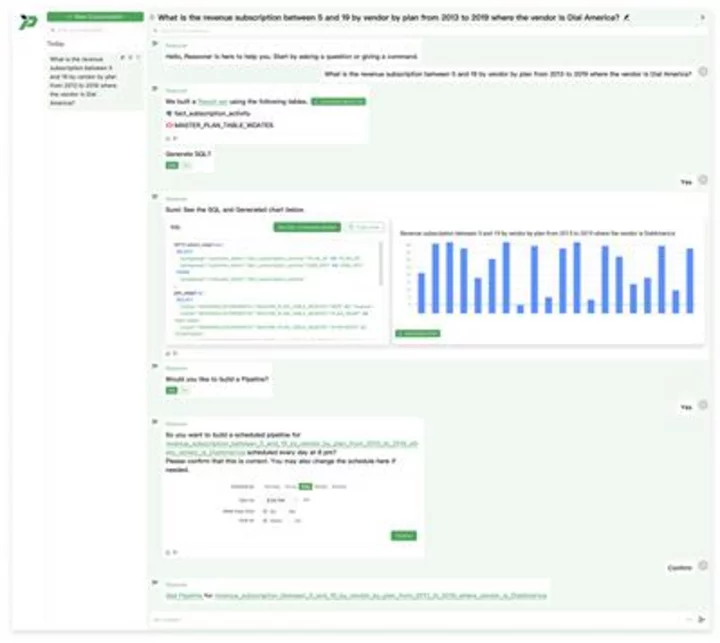
Promethium Brings the Power of Generative AI to the Data Fabric

Personalized Learning – It’s What Teachers Want
