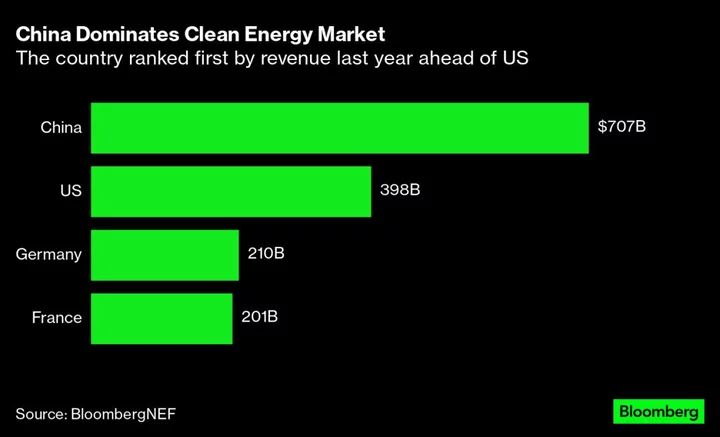
The biggest US companies are badly trailing their Chinese counterparts when it comes to generating income from solar, wind, nuclear and other types of renewable energy.
Companies that make up the S&P 500 produce just 3.4% of their revenue from clean-energy sources, which is roughly half what companies on the Shanghai Composite Index earn, according to BloombergNEF.
With corporations struggling to make the transition to net-zero emissions, analysts at BNEF looked under the hood of more than 8,000 companies to determine how much of their revenue is attributable to clean energy.
“Shifting business models toward greener activities is about more than being virtuous for the sake of the planet,” says BNEF’s Michael Daly. “There’s a huge financial opportunity for companies that help drive the energy transition.”
Read More: The Trillions Forgotten in the Energy Transition
Chinese companies such as solar leaders LONGi Green Energy Technology Co. and Tongwei Co. are benefiting from the nation’s dominant position in the clean energy supply chain. In fact, the largest number of clean energy equity investment opportunities are in the Asia-Pacific region, according to BNEF.
The APAC region has more than 680 companies that draw more than half their revenue from clean energy, which includes renewable and nuclear power, electrified transport, biofuels, hydrogen and carbon capture, BNEF estimates. That compares with closer to 410 companies in the US and roughly 430 in Europe, the Middle East and Africa combined.
The opacity of company reports makes uncovering clean energy exposures a major challenge, Daly says. For instance, most large oil and gas companies don’t break out clean-energy revenue as a standalone category. And some, such as fossil fuel giants Exxon Mobil Corp. and Marathon Petroleum Corp., provide no information whatsoever about any proceeds from clean energy activities.
Unsurprisingly, almost all renewable energy manufacturers and developers derive most of their revenue from clean energy, which earns them an A1 rating from BNEF, led by companies including Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. of China and Denmark’s Vestas Wind Systems A/S. By comparison, 45% of electric utilities tracked by the research firm are rated A1.
Electricitie de France SA generated almost 70% of its revenue last year from nuclear power, with additional income from hydro, wind and solar sources, according to BNEF. Italy’s Enel SpA has a more balanced set of clean power generation revenue and ranks just behind EDF and Sweden’s Vattenfall AB among the world’s largest utilities with the highest clean-energy exposure.
In the automotive sector, Tesla Inc. and BYD Co. are the clear leaders, far ahead of traditional carmakers such as BMW AG and Ford Motor Co., according to BNEF.
Looking forward, Daly says “we expect the latter group—traditional carmakers—to raise its electric-vehicle exposure, as more models are released and new policies supporting the EV rollout are introduced.”