
Banks in EU Get World’s First ESG Add-On to Capital Rules
In a global first, Europe’s main bank regulator is revising the framework that sets capital requirements so that
2023-10-12 23:22

Scientists reveal plan to use lasers to build roads on the moon
We could shoot lasers at the lunar soil to help us live on the Moon, scientists have proposed. By melting the lunar soil into a more solid, layered substance, we might be able to build paved roads and landing pads on the Moon’s surface, a new study suggests. Many space agencies including Nasa have plans to establish semi-permanent bases on the Moon, which would both allow us to better study it but also serve as a stop off on the way to Mars and elsewhere in the solar system. The Moon’s surface is a tough place t land and live, however. The dust of the soil tends to get kicked up by landers – and the low gravity means that it floats around after it is disturbed, potentially finding its way into equipment. As such, future Moon colonies may require robust roads and landing pads to allow for us to travel both to and around the Moon. But it is unlikely we would be able to transport materials to build them, given the cost of doing so, leading scientists to look at what is available there already. In the new study, scientists examined whether lunar soil could be turned into something more substantial by using lasers. And they had some success, finding that lunar dust can be melted down into a solid substance. They used a variety of different sized and types of lasers to see what they would produce. The best used a 45 millimetre diameter laser beam to make hollow triangular shapes that were about 250 millimetres in size. Those pieces could be locked together to create solid surfaces that could be placed across the Moon’s surface, they suggest, and then used as roads and landing pads. On the Moon, the same approach would require a lens of around 2.37 metres squared, which would have to be transported from Earth. That could then be used to concentrate sunlight, rather than using a laser, and so allow the material to be created with relatively small equipment. The plan is reported in a new journal article, ‘Laser melting manufacturing of large elements of lunar regolith simulant for paving on the Moon’, published in Scientific Reports. Read More Nasa opens up pieces of a distant asteroid transported back to Earth Earth hit by a huge solar storm that would devastate civilisation, trees show Incels using TikTok to spread ‘hateful beliefs’, research suggests
2023-10-12 23:21

EU to Push ‘Made in Europe’ Tag in Green Industry, Sefcovic Says
The European Union will be much more “assertive” in touting a “made in Europe” approach to ensure that
2023-10-12 23:18

FC 24 Title Update 3: Full List of Gameplay Changes
Full list of gameplay changes and Ultimate Team updates in EA Sports FC 24 Title Update 3 including major bug fixes.
2023-10-12 22:54

Why Exxon’s One-Time Adversary Unanimously Backed Mega Deal
When a then little-known fund defeated Exxon Mobil Corp. in a climate-charged activist battle in 2021, snagging three
2023-10-12 22:45

PlayStation announces plan to launch cloud streaming access
Hideaki Nishino has revealed details of the PlayStation cloud streaming launch.
2023-10-12 22:29
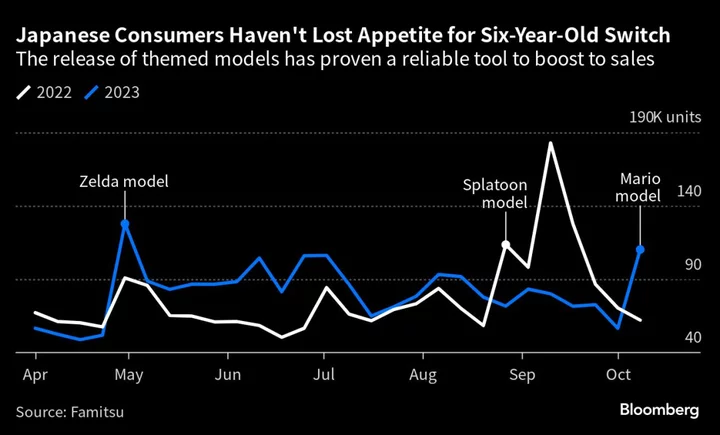
Mario-Themed Switch Console Proves a Hit for Nintendo in Japan
Nintendo Co.’s Switch sales doubled in Japan on the release of a Super Mario edition of the console,
2023-10-12 22:29

Scientists unearth a secret hidden within the Mona Lisa
The Mona Lisa has been the subject of awe and fascination for centuries, with experts from around the world desperate to solve the mystery behind her iconic, enigmatic smile. Now, thanks to X-ray technology, scientists have begun to uncover the secrets of Leonardo da Vinci’s legendary portrait, and explain how he was able to create something so mind-bending with just a few strokes of a brush. The research, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on Wednesday, suggests that the Italian Renaissance master may have been in a particularly inventive mood when set about crafting the piece in the early 16th century. "He was someone who loved to experiment, and each of his paintings is completely different technically," Victor Gonzalez, the study's lead author, told the Associated Press.. Gonzalez, who has studied the chemical compositions of dozens of works by Leonardo and other artists, discovered that there was something special about the paint used for the Mona Lisa. Specifically, the researchers found a rare compound, called plumbonacrite, in Leonardo's first layer of paint. The discovery confirmed that Leonardo most likely used lead oxide powder to thicken and help dry his paint as he began working on the portrait. He is thought to have dried the powder, which has an orange colour, in linseed or walnut oil by heating the mixture to make a thicker, faster-drying paste. "What you will obtain is an oil that has a very nice golden colour," Gonzalez said. "It flows more like honey." Carmen Bambach, a specialist in Italian art and curator at New York's Metropolitan Museum of Art, who was not involved in the study, called the research "very exciting". She emphasised that any scientifically proven new insights into Leonardo's painting techniques are "extremely important news for the art world and our larger global society." Finding plumbonacrite in the Mona Lisa attests "to Leonardo's spirit of passionate and constant experimentation as a painter—it is what renders him timeless and modern," Bambach said. The paint fragment Gonzalez and his team analysed for their study was taken from the base layer of the painting and was barely visible to the naked eye. It was no larger than the diameter of a human hair, and came from the top right-hand edge of the picture that now takes pride of place in Paris’s Louvre Museum. The scientists peered into the sample’s atomic structure using X-rays in a synchrotron – a large machine that accelerates particles to almost the speed of light. This allowed them to unravel the speck's chemical makeup and detect the plumbonacrite. The compound is a byproduct of lead oxide, allowing the researchers to say with more certainty that Leonardo likely used the powder in his paint recipe. "Plumbonacrite is really a fingerprint of his recipe," Gonzalez said. "It's the first time we can actually chemically confirm it." After Leonardo, Dutch master Rembrandt may have used a similar recipe when he was painting in the 17th century; Gonzalez and other researchers have previously found plumbonacrite in his work, too. "It tells us also that those recipes were passed on for centuries," Gonzalez said. "It was a very good recipe." Still, the ‘Mona Lisa’—said by the Louvre to be a portrait of Lisa Gherardini, the wife of a Florentine silk merchant—and other works by Leonardo still have other secrets to tell. "There are plenty, plenty more things to discover, for sure,” Gonzalez said. “We are barely scratching the surface.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-12 22:25

Caroline Ellison faces cross-examination at Sam Bankman-Fried's trial
By Jody Godoy NEW YORK (Reuters) -Sam Bankman-Fried's confidant Caroline Ellison took the stand again at the FTX founder's trial
2023-10-12 21:59
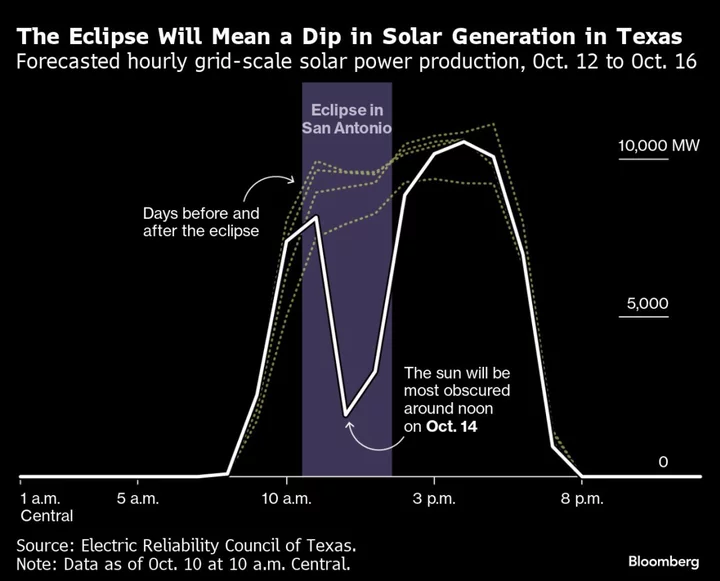
‘Ring of Fire’ Eclipse This Weekend Will Send US Solar Power Plunging
US grid operators are set to face their largest controlled experiment for dealing with big swings in renewable
2023-10-12 21:53

Play for All - Logitech G Introduces Adaptive Gaming Kit for Access™ Controller for the PS5 Console
LAUSANNE, Switzerland & SAN JOSE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Oct 12, 2023--
2023-10-12 21:48
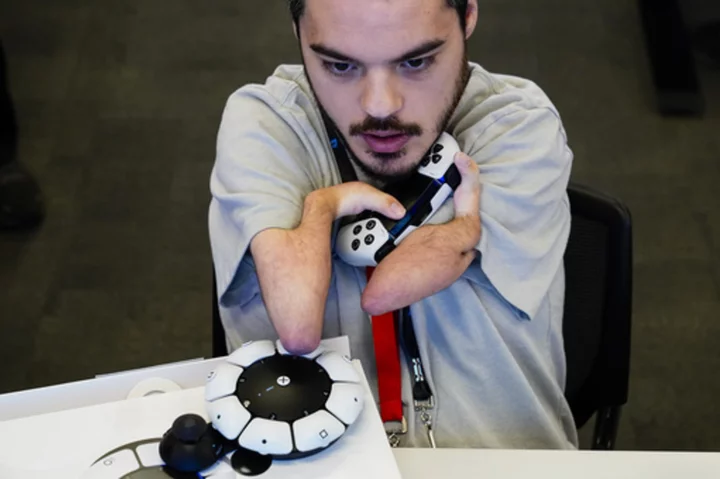

Sony's Access controller for the PlayStation aims to make gaming easier for people with disabilities
Playing video games has long been a challenge for many people with disabilities, since the traditional controllers for the PlayStation, Xbox or Nintendo can be difficult or for many people with disabilities, since the traditional controllers even impossible to maneuver when a person has limited mobility
2023-10-12 21:27
You Might Like...

NordVPN Partners With Mamenta to Streamline Global Digital Downloads

Applied Materials Gives Strong Forecast as Chip Slump Eases

Warzone Mobile Changes Expected Release Date on App Store

Hundreds of Fires Are Out of Control in Canada’s Worst-Ever Season

Refurbished Lenovo ThinkPad and a lifetime of MS Office: Just $359.98

SOUTHTEC 2023 Programming Features Tooling U-SME Workforce Day, CESMII SMART Manufacturing Experience and Manufacturing USA’s Modern Makers

Mizkif slams Twitch after Alinity’s twerk ban; pro gamer bombarded with streaming offers

DSP Concepts Provides Voice Control Optimizing Technology for the KT Genie TV All-in-One Soundbar
