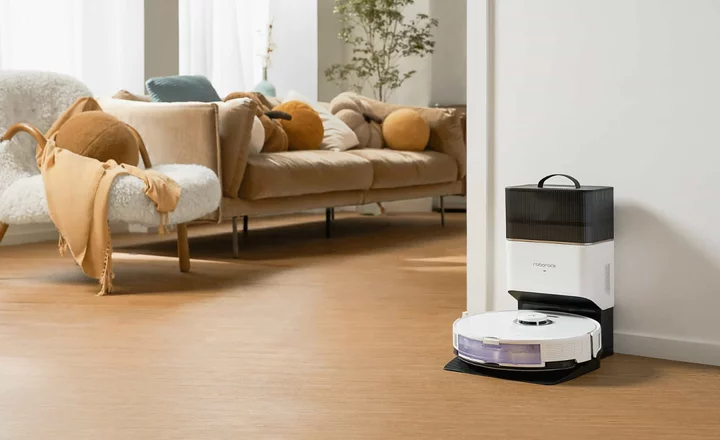

Roborock's S8 series vacuums haven't even been out for 2 months, but they're already on sale
SAVE UP TO 23%: As of June 6, the new Roborock S8 and Roborock S8+
2023-06-07 00:16

Dahua Revolutionizes Fire Safety Inspection in Power Station
HANGZHOU, China--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 1, 2023--
2023-09-01 20:24
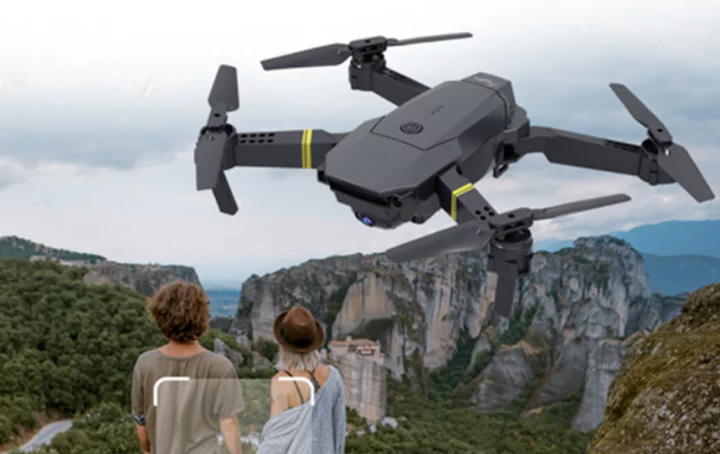

Get two beginner-friendly 4K drones for $109.97
TL;DR: As of September 23, you can get two beginner-friendly 4K camera drones for just
2023-09-23 17:54

Joe Rogan once opened up about Logan Paul's controversial forest vlog: 'He realized that he f***ed up'
'The Joe Rogan Experience' covers a wide range of topics and has grown to become one of the world's most popular podcasts
2023-07-23 14:29

Canada to start planning how it will make internet giants pay for news
OTTAWA The Canadian regulator responsible for implementing the country's online news law on Thursday said it will start
2023-08-25 00:46

Valorant Deadlock Recruitment Event End Date
The Valorant Deadlock Recruitment Event ends on July 25, 2023, giving players just 28 days to unlock Deadlock by collecting 200,000 XP.
2023-06-29 02:20
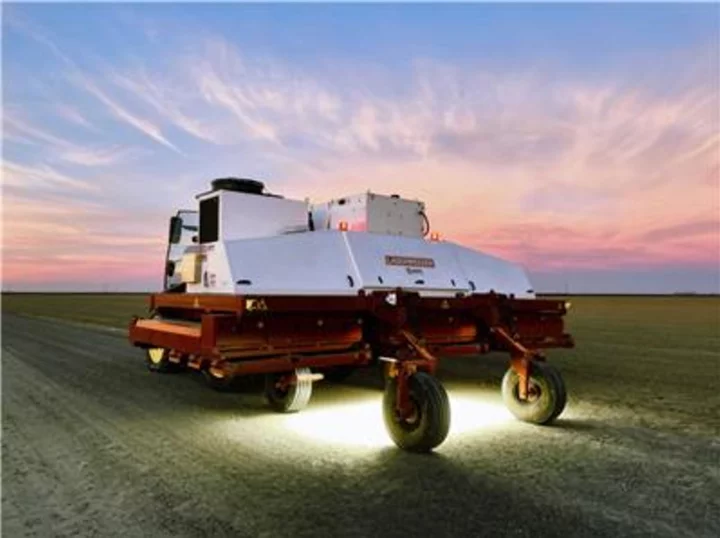

Carbon Robotics’ LaserWeeder™ Selected as “Best AI-based Solution for Agriculture” In 2023 AI Breakthrough Awards
SEATTLE--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 21, 2023--
2023-06-21 21:18
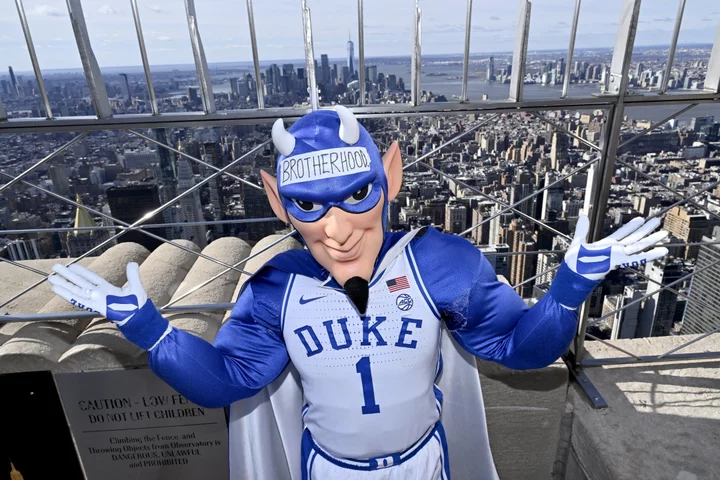

Where to watch Northwestern vs Duke livestream
Duke and Northwestern have formed a bit of a rivalry over the past six seasons
2023-09-16 16:56

Amazon, Meta Among Firms to Unveil AI Safeguards After Biden’s Warning
Seven leading artificial intelligence firms will debut new voluntary safeguards designed to minimize abuse of and bias within
2023-07-21 20:29

OpenAI researchers warned of powerful AI discovery before CEO fired
OpenAI researchers warned about a potentially dangerous artificial intelligence discovery ahead of CEO Sam Altman being ousted from the company, according to reports. Several staff members of the AI firm wrote a letter to the board of directors detailing the algorithm, two people familiar with the matter told Reuters. The disclosure was reportedly a key development in the build up to Mr Altman’s dismissal. Prior to his return late Tuesday, more than 700 employees had threatened to quit and join backer Microsoft in solidarity with their fired leader. The sources cited the letter as one factor among a longer list of grievances by the board leading to Altman’s firing, among which were concerns over commercialising advances before understanding the consequences. The staff who wrote the letter did not respond to requests for comment and Reuters was unable to review a copy of the letter. OpenAI declined to comment on the letter but acknowledged in an internal message to staffers a project called Q* and a letter to the board before the weekend’s events, one of the people said. An OpenAI spokesperson said that the message, sent by long-time executive Mira Murati, alerted staff to certain media stories without commenting on their accuracy. Some at OpenAI believe Q* (pronounced Q-Star) could be a breakthrough in the startup’s search for what’s known as artificial general intelligence (AGI), one of the people told Reuters. OpenAI defines AGI as autonomous systems that surpass humans in most economically valuable tasks. Given vast computing resources, the new model was able to solve certain mathematical problems, the person said on condition of anonymity because the individual was not authorised to speak on behalf of the company. Though only performing maths on the level of grade-school students, acing such tests made researchers very optimistic about Q*’s future success, the source said. Reuters could not independently verify the capabilities of Q* claimed by the researchers. Researchers consider maths to be a frontier of generative AI development. Currently, generative AI is good at writing and language translation by statistically predicting the next word, and answers to the same question can vary widely. But conquering the ability to do mathematics where there is only one right answer implies AI would have greater reasoning capabilities resembling human intelligence. This could be applied to novel scientific research, for instance, AI researchers believe. Unlike a calculator that can solve a limited number of operations, AGI can generalize, learn and comprehend. In their letter to the board, researchers flagged AI’s prowess and potential danger, the sources said without specifying the exact safety concerns noted in the letter. There has long been discussion among computer scientists about the danger posed by highly intelligent machines, for instance if they might decide that the destruction of humanity was in their interest. Researchers have also flagged work by an “AI scientist” team, the existence of which multiple sources confirmed. The group, formed by combining earlier “Code Gen” and “Math Gen” teams, was exploring how to optimise existing AI models to improve their reasoning and eventually perform scientific work, one of the people said. Altman led efforts to make ChatGPT one of the fastest growing software applications in history and drew investment – and computing resources – necessary from Microsoft to get closer to AGI. In addition to announcing a slew of new tools in a demonstration this month, Altman last week teased at a summit of world leaders in San Francisco that he believed major advances were in sight. “Four times now in the history of OpenAI, the most recent time was just in the last couple weeks, I’ve gotten to be in the room, when we sort of push the veil of ignorance back and the frontier of discovery forward, and getting to do that is the professional honor of a lifetime,” he said at the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation summit, a day before he was fired by OpenAI’s board. Additional reporting from agencies. Read More 10 ways AI will change the world – from curing cancer to wiping out humanity YouTube reveals bizarre AI music experiments AI-generated faces are starting to look more real than actual ones One of the world’s most hyped tech products just launched – and made a big mistake
2023-11-23 18:24

Google makes emergency request to block Texas antitrust lawsuit move
By Diane Bartz WASHINGTON Google asked a U.S. appeals court in New York on Tuesday to pause a
2023-08-09 04:50

Alibaba Saw Singles Day Sales Growth, but Don’t Call It a Win for China’s Economy
Chinese e-commerce giants may have eked out another year of sales growth on Singles Day, but the data isn't all encouraging.
2023-11-13 21:45
You Might Like...

xQc criticizes Twitch's new policy: 'Definitely not going to go to Twitch anymore’

EU Looks to Boost Efforts to Store Captured Carbon Underground

This new LG Gram laptop is on sale for $800
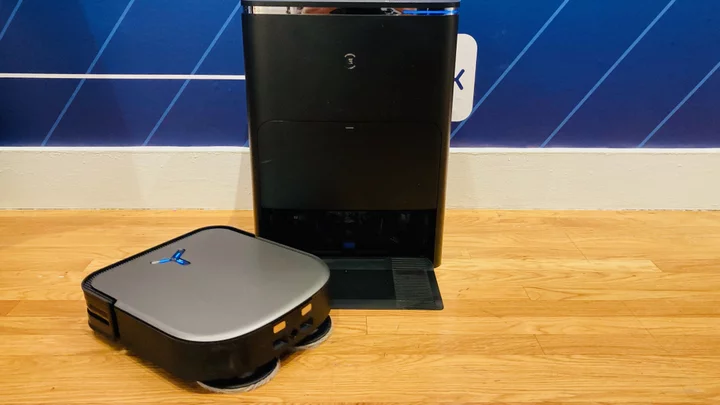

Is this the most advanced robot vacuum in the world? Meet the X2 Omni from Ecovacs
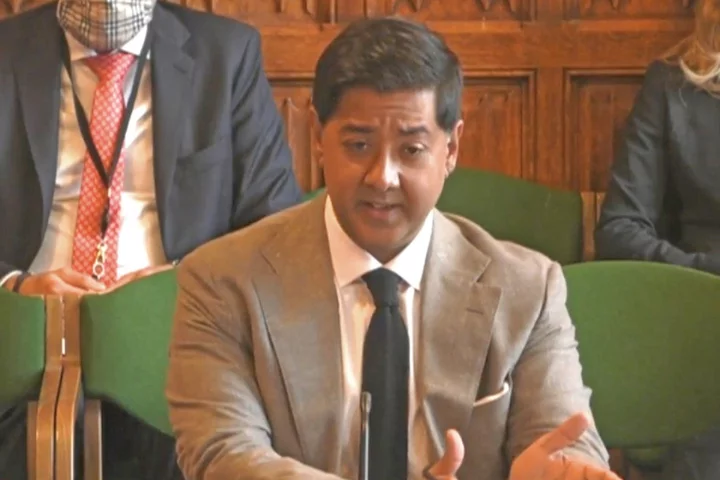

Queen assassin case exposes ‘fundamental flaws’ in AI – safety campaigner

Germany's biggest newspaper is cutting 20% of jobs as it prepares for an AI-powered digital future
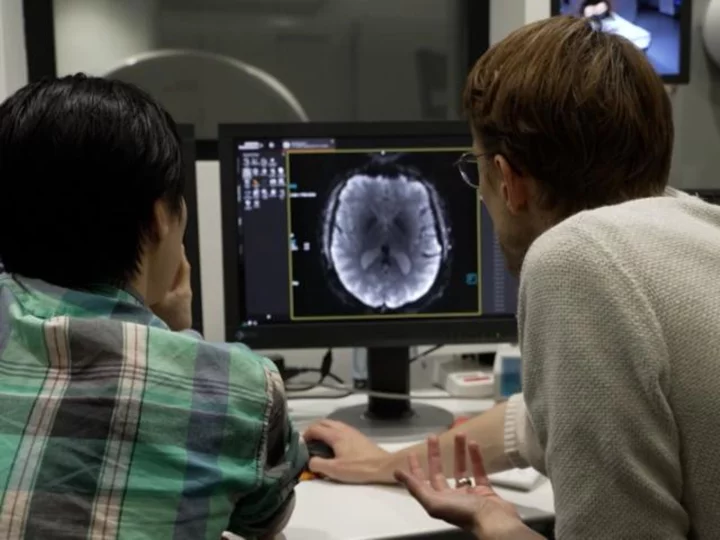
How the technology behind ChatGPT could make mind-reading a reality

Top US Chip Gearmaker Accuses China Rival of 14-Month Spy Spree
