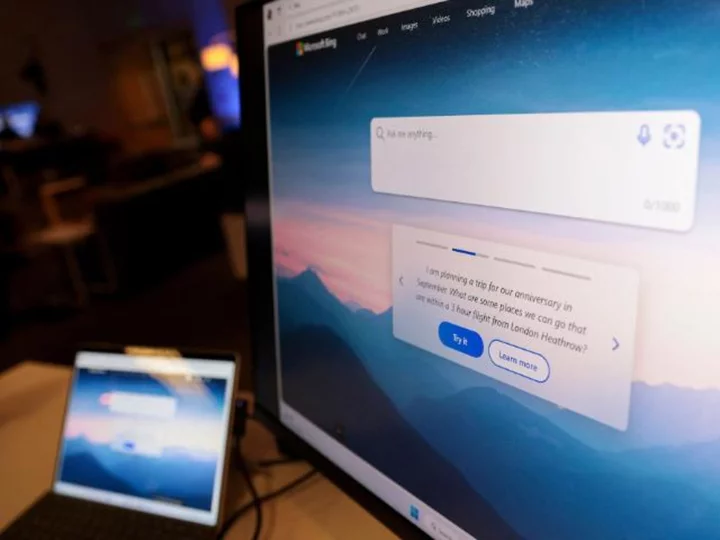
Microsoft leaps into the AI regulation debate, calling for a new US agency and executive order
Microsoft joined a sprawling global debate on the regulation of artificial intelligence Thursday, echoing calls for a new federal agency to control the technology's development and urging the Biden administration to approve new restrictions on how the US government uses AI tools.
2023-05-26 00:46

Australian regulator calls for new competition laws for digital platforms
(Reuters) -Australia's competition watchdog said on Monday new competition laws were required in response to the rapid expansion of digital
2023-11-27 09:17

AVEVA Recognized as a Leader in the IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Process Manufacturing Execution System 2023 Vendor Assessment
LONDON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 1, 2023--
2023-06-01 15:26

The Best Web Hosting Services for 2023
Web hosting is crucial for business owners and digital creators; it's not something you can
2023-06-02 06:57

Are Paige Spiranac and Trevor Lawrence related? Here's why golf influencer got offended by NFL player comparison
Paige Spiranac is no stranger to social media trolls, but fans' comments comparing her to Trevor Lawrence is something she 'can't unsee'
2023-08-04 15:50
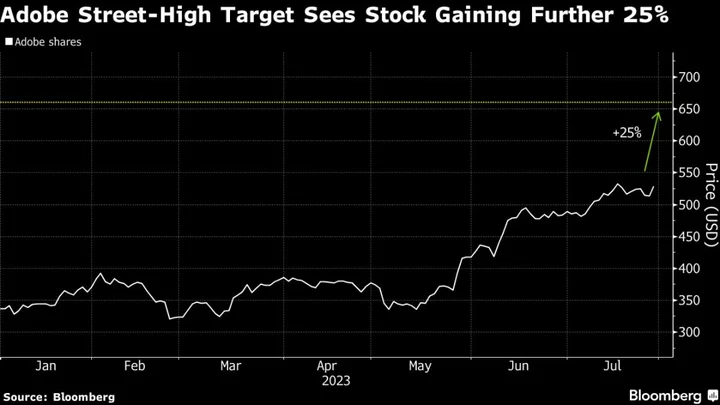
Adobe Could Add Another 25% to Its Blistering Rally, Morgan Stanley Says
Adobe Inc.’s blistering rally has further to go, according to Morgan Stanley analyst Keith Weiss, who sees the
2023-07-31 17:45

Experts have figured out the science behind optical illusions
Ever wondered how optical illusions actually work? Wonder no more. A new study by University of Exeter visual ecologist Jolyon Troscianko, and neuroscientist Daniel Osorio from the University of Sussex in the UK has weighed in on the debate over whether we perceive things weirdly because of certain errors in the ways our brain processes colour, shade, and shape or because of our eye's function or the brain's neurological wiring. They reckon it is all in the eyes. The pair found ways our visual neurons – cells that process information coming in from the eyes – work, showing how they can affect our perception of patterns on different scales. "Our eyes send messages to the brain by making neurons fire faster or slower," said Troscianko. "However, there's a limit to how quickly they can fire, and previous research hasn't considered how the limit might affect the ways we see colour." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The new model suggests limits in processing and metabolic energy force neurons to compress visual data coming in through our eyes when looking at simple patterns. "Our model shows how neurons with such limited contrast bandwidth can combine their signals to allow us to see these enormous contrasts, but the information is compressed – resulting in visual illusions," said Troscianko. "The model shows how our neurons are precisely evolved to use every bit of capacity." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-02 20:16

Home Office could force delays in tech security fixes under 'short-sighted’ proposals
When it’s not making disastrous decisions around the housing of migrants on barges found to contain Legionella, the Home Office is reviewing the 2016 Investigatory Powers Act and considering a proposal to require telecoms operators to notify the government of “technical changes” to their services before they are implemented – something which has been slammed as “catastrophically short-sighted”. Between 5 June and 31 July, the Home Office consulted on revising the legislation passed by Theresa May’s government, with one of the planned changes relating to “notification requirements” placed on businesses. The consultation document reads: “We propose to make changes that would support cooperation between government and industry by setting clear expectations about the circumstances in which operators might be expected to notify the Secretary of State of planned changes to their service that could have a negative impact on investigatory powers and, where necessary, mandating notification of planned changes. “This would be intended to facilitate early engagement between operators and the government so that, where necessary, appropriate steps can be taken in good time to ensure that any negative impact on investigatory powers is fully considered, and so that we can ensure continuity of lawful access to data against a background of changing technology.” However, it was a news article from Just Security on Tuesday which reignited concerns that the UK Government is about to do something “ultimately unsafe”. The piece explains: “While the proposal does not specify what technical changes would require notification, these may include changes in the architecture of software that would interfere with the UK’s current surveillance powers. “As a result, an operator of a messaging service wishing to introduce an advanced security feature would now have to first let the Home Office know in advance. “Accordingly, the Secretary of State, upon receiving such an advance notice, could now request operators to, for instance, abstain from patching security gaps to allow the government to maintain access for surveillance purposes.” If the idea of Suella Braverman being able to halt security fixes so the government can continue to spy on people doesn’t fill you with dread, we’re not sure what will. While the Home Office goes on to add in its consultation document that there is a proposed requirement for the home secretary to “consider the necessity and proportionality” of imposing such a duty on businesses, Twitter/X users remain fairly troubled by the prospect: The Investigatory Powers Act, which was dubbed “the snooper’s charter” by critics when it was first proposed, is separate to the Online Safety Bill, which the government is still trying to pass through parliament. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-23 22:29

Alchemer Hires Former Qualtrics Sales Executive As Chief Revenue Officer
LOUISVILLE, Colo.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 29, 2023--
2023-08-29 21:28

Amazon plays catch-up with Alexa generative AI, shows off refreshed hardware
By Greg Bensinger Amazon.com Inc on Wednesday unveiled a slate of new and refreshed devices and updated its
2023-09-21 00:56

Prime Day Deals so good, they're literally free
There's a big downside to Prime Day deals: even when you spot a great bargain,
2023-07-13 07:24
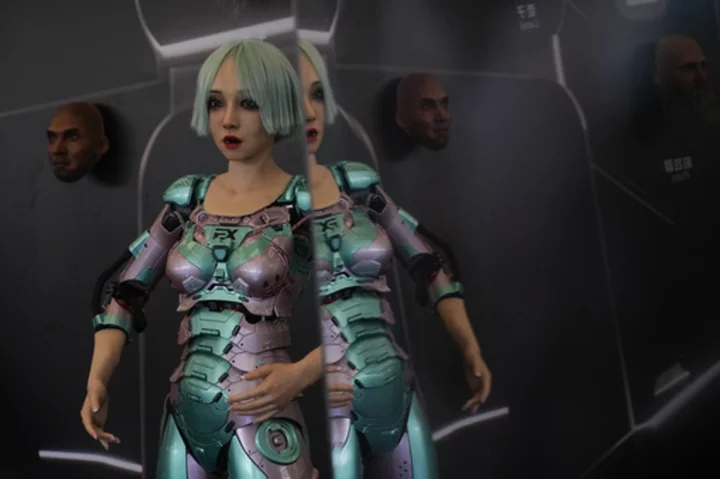

AP PHOTOS: Lifelike robots and android dogs wow visitors at Beijing robotics fair
BEIJING (AP) — Winking, grimacing or nodding their heads, robots mimicked the expressions of visitors at a robot expo in Beijing.
2023-08-18 16:49
You Might Like...

Meta Begins Blocking News in Canada in Response to New Law

Shipping's Greener Fuel Quest Runs Into Climate Complications
X's $100 million a year 'Promoted Accounts' ad feature is no more

Google rolls out AI chatbot Bard to Europe and Brazil and adds more languages

Chrome 117 Will Explain Why Your Favorite Extension Disappeared
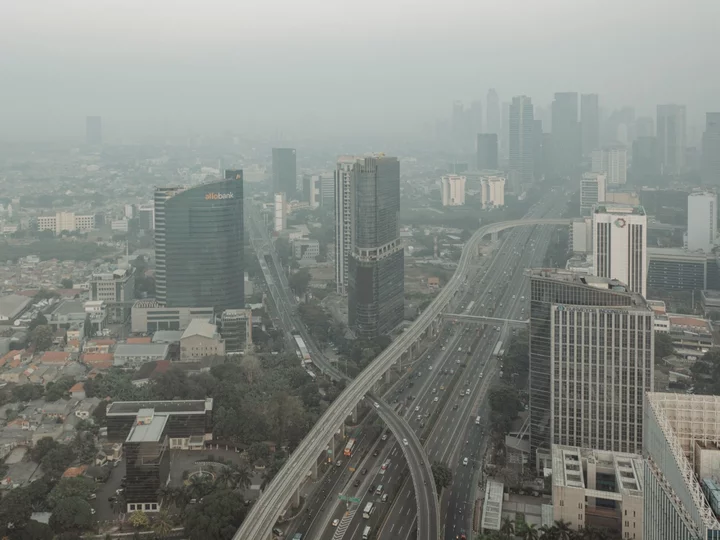

Jakarta Pollution Worst in World Amid Jumbled Policy Response

Ex-ByteDance employee claims China had 'supreme access' to all data
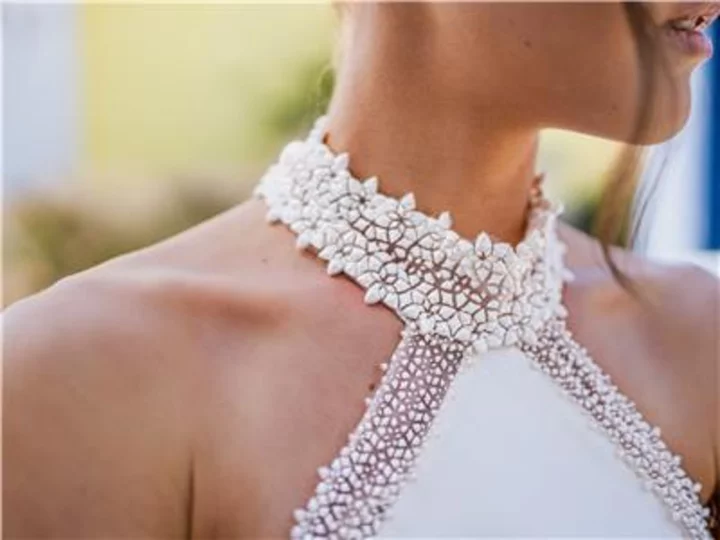

Designer Ada Hefetz Transforms Wedding Dress Design with Stratasys’ 3DFashion Technology
