
Optimum Names Kathleen Preston Vice President, General Manager of West Pacific Area
FLAGSTAFF, AZ--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 7, 2023--
2023-09-08 00:24

Amazon hit by strikes, protests across Europe during Black Friday trade
LONDON Amazon workers came out on strike at multiple locations across Europe on Friday as protests against the
2023-11-24 19:20

Prime Gaming Halloween 2023 Offerings
Players can get free Prime Gaming Halloween 2023 offerings by claiming in-game items for Valorant, Modern Warfare 2, Roblox, Diablo 4, and more.
2023-10-13 03:54
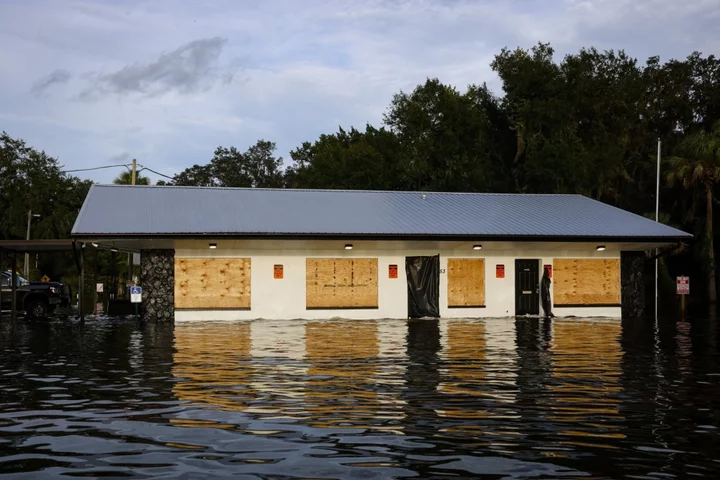

Hurricane-Proofing Buildings Isn’t Enough to Curb Florida’s Storm Losses
Since Hurricane Andrew in 1992, Florida has been toughening up building codes and touting them as a way
2023-09-26 18:27
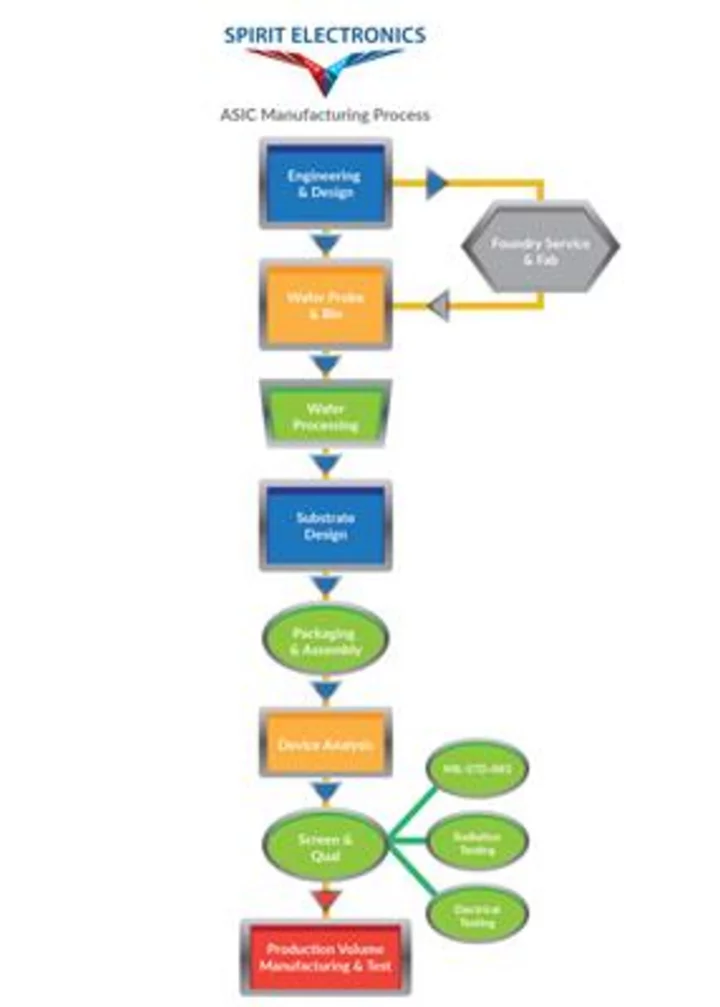
Spirit Electronics Offers Foundry Services for U.S.-based Manufacturing Amid Foundry Consolidation
PHOENIX--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 19, 2023--
2023-09-19 20:48

Netflix begins password sharing crackdown in the US
Netflix has finally revealed that it's cracking down on users who share passwords in the United States.
2023-05-24 21:56

Microsoft beats quarterly revenue estimates
Microsoft on Tuesday surpassed Wall Street estimates for fourth-quarter revenue and profit as its cloud business benefited from
2023-07-26 04:25

Kanye West allowed back on Twitter following his ban over antisemitic conspiracies
Social media platform Twitter, now called X, has reinstated the account of rapper Ye, the artiste formerly known as Kanye West, after he was suspended eight months ago for hate speech. The account was reinstated on Saturday eight months after the rapper was suspended for breaking the platform’s rules prohibiting incitement to violence. Ye got his account back after assuring the platform owned by Elon Musk that he wouldn’t use it to share antisemitic or otherwise harmful language, according to The Wall Street Journal, citing a person familiar with the matter. The artiste will also not be eligible to monetise his account, a new feature added by Mr Musk for paid subscribers, while advertisements won’t appear next to his posts either, the report said citing the social media platform. Ye has not posted anything new since coming back on the platform. His account showed his last post to be from December 2022, which was just two months after it was reinstated following an earlier lock out of his account. Mr Musk, who calls himself a free speech absolutist, had in November welcomed the return of the rapper to the platform, after his account was reinstated for the first time. But on December, one of his posts appeared to show a swastika symbol inside a Star of David, which led to Mr Musk suspending his account after he violated the platform’s policy against inciting violence. Ye lost his account and his partnership with Adidas and Gap for Yeezy products soon after, when he went on a string of antisemitic rants in interviews and on social media. Mr Musk had previously also reinstated former US president Donald Trump’s account after conducting a poll in which some 14.8 million Twitter users had voted with 51.8 per cent voting in favour of the reinstatement. But Mr Trump said he had no interest in returning to Twitter and would stick to his own platform Truth Social. Additional reporting by agencies Read More TikTok ‘failing to act’ as Andrew Tate videos still seen by children as young as 13 Kanye West used offensive phrases about Jewish people, ex-business partner claims As Twitter becomes X - Seven disastrous rebrands from Royal Mail to New Coke
2023-07-30 18:19

As net tightens, Iranians pushed to take up homegrown apps
Banned from using popular Western apps, Iranians have been left with little choice but to take up state-backed alternatives, as the authorities tighten internet restrictions for...
2023-05-14 13:26

Save on a 'Star Wars Jedi: Survivor' Xbox bundle, plus more gaming deals this week
UPDATE: May. 9, 2023, 5:00 a.m. EDT This list has been updated with the latest
2023-05-09 17:56
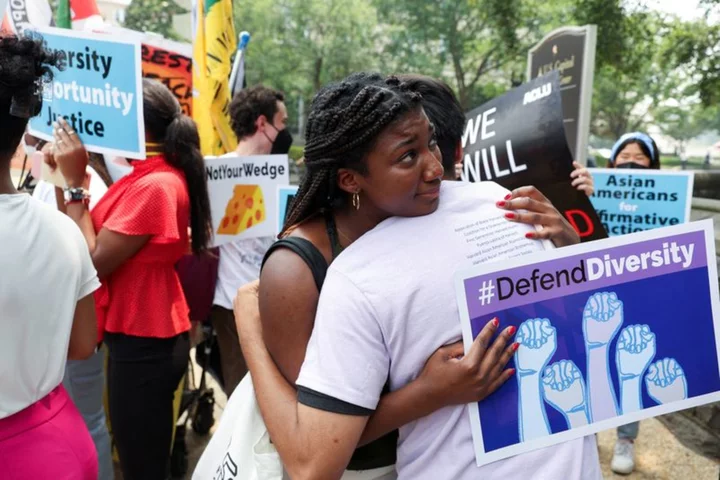

Biden administration urges colleges to pursue diversity after Supreme Court ruling
By Nate Raymond and Jarrett Renshaw The Biden administration on Monday issued new guidance to colleges and universities
2023-08-15 03:29

What is NPC trend on TikTok? Kai Cenat stuns fans by revealing 1-hour live stream earnings, trolls label him 'cringe monkey'
Twitch streamer Kai Cenat embraced the NPC trend on TikTok, imitating scripted reactions of video game characters during a live stream
2023-07-21 14:49
You Might Like...
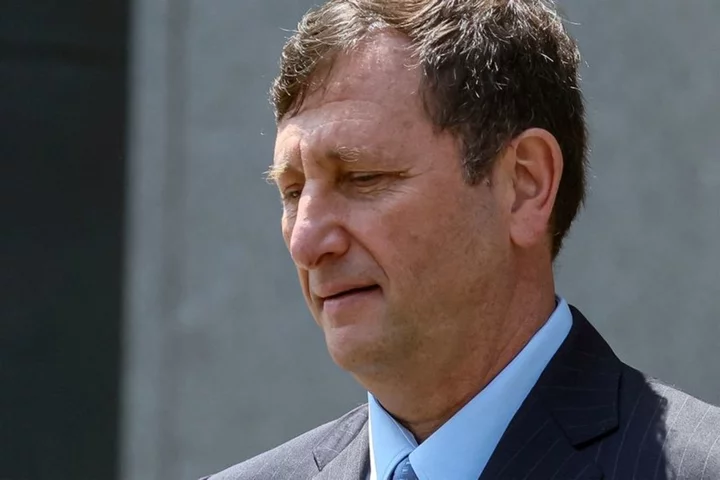

Founder of bankrupt crypto lender Celsius must face NY fraud lawsuit

TSMC says it's working hard to control costs, lifted partly by Ukraine war

Former CEO of China's Alibaba quits cloud business in surprise move during its leadership reshuffle
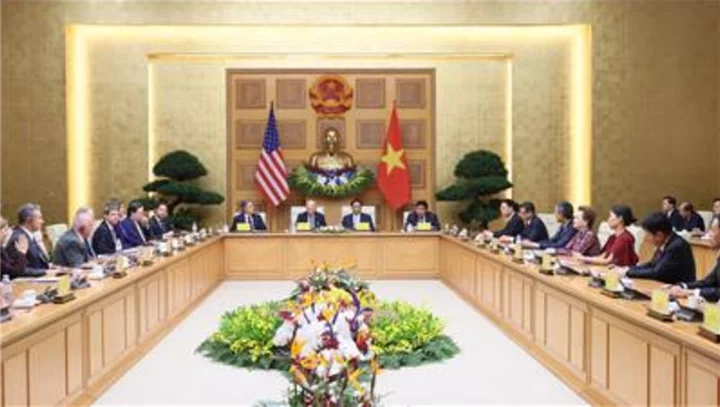

FPT Announces US Investment, Workforce Development for AI and Semiconductor amid Biden's Vietnam Visit

Meta to roll out broadcast channels to Facebook, Messenger
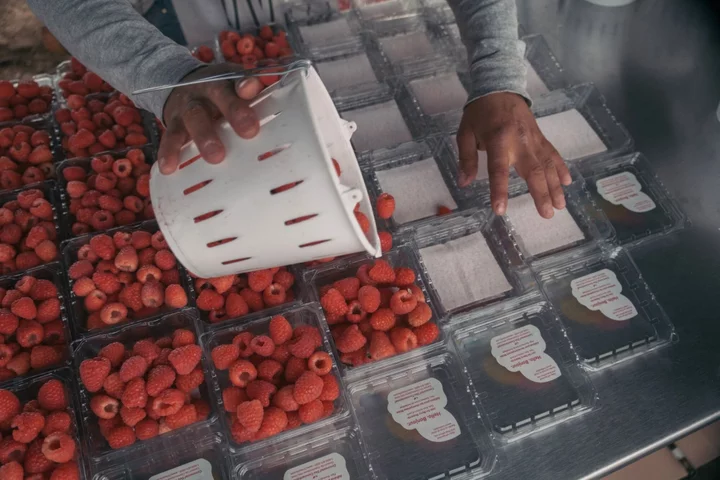

How the Food System Is Changing and What It Means for Investors
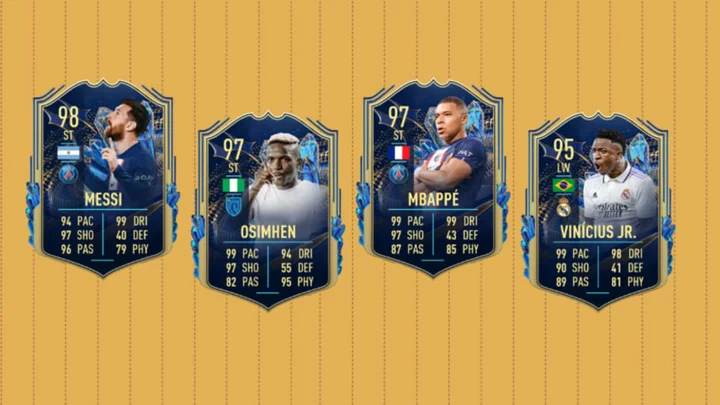
FIFA 23 TOTS or TOTS Moments Upgrade SBC: How to Complete

Does Kai Cenat like Pokimane? Twitch king asks for pro streamer's number during livestream, fans wonder if 'they will date'
