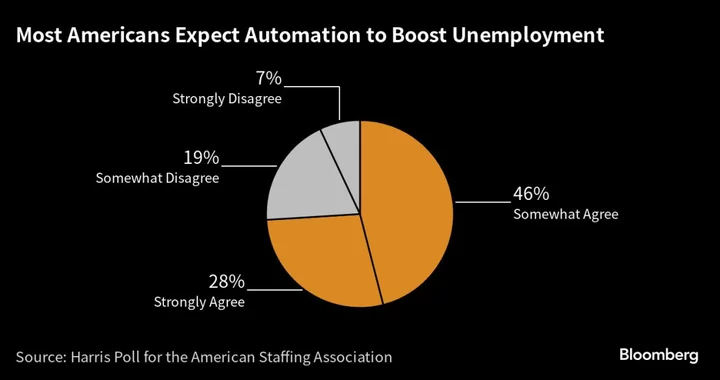
Almost Half of Americans See Automation Replacing Their Jobs
Close to half of Americans say automation could easily replace their jobs, according to an American Staffing Association
2023-08-17 19:47

Knightscope Building on Results to Deliver New Solutions for Parking and Public Safety on AWS
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 14, 2023--
2023-09-14 21:50

Summer, Sun, Discounts - Smart Vacuum Cleaner Prices From Tineco
NEUSS, Germany--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 15, 2023--
2023-08-15 15:25

Perfect Corp. Partners with Parfums Christian Dior to Launch Online Consultation with AR Makeup Virtual Try-On Experience at Viva Technology 2023
PARIS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 8, 2023--
2023-06-08 18:58

Lowercarbon Capital and Gradient Ventures Invest $9M in Quilt for Advanced Residential Heat Pump System
REDWOOD CITY, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 16, 2023--
2023-05-17 00:23

iPhone 15 release date: When Apple’s new phone will actually arrive?
Apple’s latest iPhone is coming. The company announced a new event, titled “Wonderlust”, this week. While it did not explicitly say that it will see the launch of the iPhone 15, it almost certainly will. At the event, on 12 September, it will show off four new variants of the iPhone 15: the base model as well as the iPhone 15 Plus, Pro and Pro Max. It is also expected to launch a new Apple Watch and Watch Ultra, and some new AirPods. The new iPhone is expected to have a relatively modest set of new features, including USB-C ports on the bottom. The iPhone 15 will borrow features from the 14 Pro, including its faster chip and “Dynamic Island”, while the Pro phones will get an improved processor, an action button on the side, and better cameras. Apple will show off all of those new features during the event, which begins at 10am local time, or 6pm in the UK, on 12 September. It will be live-streamed on the company’s website. Apple will not release those products at that event, however. While it will show them off during the event, the company has settled on a fairly regular delay for the actual release date. The company usually waits a week-and-a-half to release the new phones, on the following Friday. That means the launch date will probably fall on 22 September. However, not all phones might arrive on that day. At least some models could be delayed. That has happened in the past. Last year, for instance, the iPhone 14 Plus arrived in October, later than the others, and that has become a common occurrence of recent years. This time around, it may be the iPhone 15 Pro Max that is delayed. That will include new camera “periscope lens” camera technology to allow for a long zoom – but those components are proving difficult to manufacture in enough numbers, 9to5mac reported, which could lead to a wait before the phone is released. Read More Apple is about to reveal the new iPhone – and a lot more Apple announces major event to reveal new phone Threads finally adding yet another basic feature
2023-09-02 00:18

Caesars Entertainment Paid Millions to Hackers in Recent Attack
Caesars Entertainment Inc. paid tens of millions of dollars to hackers who broke into the company’s systems in
2023-09-14 03:49

Iteris Awarded Contract for Seminole County Traffic Signal Retiming Program
TAMPA, Fla.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 20, 2023--
2023-07-20 20:45

UK Energy Firms Meet Shapps to Discuss Security and Net Zero
Britain’s energy industry will sit down with Energy Security Secretary Grant Shapps on Wednesday to discuss energy security
2023-08-02 07:54

Cyber insurance rates drop 10% in June -report
LONDON Cyber insurance rates dropped around 10% in June compared with a year earlier, reversing recent sharp rate
2023-07-05 08:19

'It's cause of y'all': Kai Cenat drops hints on involvement in NBA 2K24 game as streamer shares exclusive clip with fans
Twitch streamer Kai Cenat announced his participation in NBA 2K24 and shared a clip of himself getting scanned for the game with fans
2023-09-03 17:49

Missed October Prime Day? Here Are the Best Amazon Deals You Can Still Get Online
Some Prime Big Deal Days sales are still going strong, even though October Prime Day is over. Discover the best Amazon deals you can still shop here.
2023-10-17 05:26
You Might Like...

Exclusive: Nearly 610,000 public sector workers got student loan forgiveness after Biden loosened the rules

One Investor’s Uphill Battle to Turn Rewilding Into a Multi-Billion Dollar Industry

Broadcom’s $61 Billion VMWare Deal Gets Interim UK Clearance

Broadband customers plagued by issues despite inflation-busting price hikes

Grin Announces New Appointment to Advisory Board with Dr. Kyu Rhee Former CVS Health Physician Executive and Aetna Chief Medical Officer

LinkedIn becomes latest tech company to conduct layoffs
Microsoft Outlook users hit with Monday morning outage

Unlocking Climate Trillions With a Global Plan From a Sinking Island
