
LEAK: Call of Duty 2025 Will Feature Remastered Black Ops 2 Maps
A new leak claims Call of Duty 2025 will be a continuation of Treyarch's Call of Duty 2024 and feature remastered Black Ops 2 maps like Raid, Standoff, and Slums.
2023-09-12 03:29
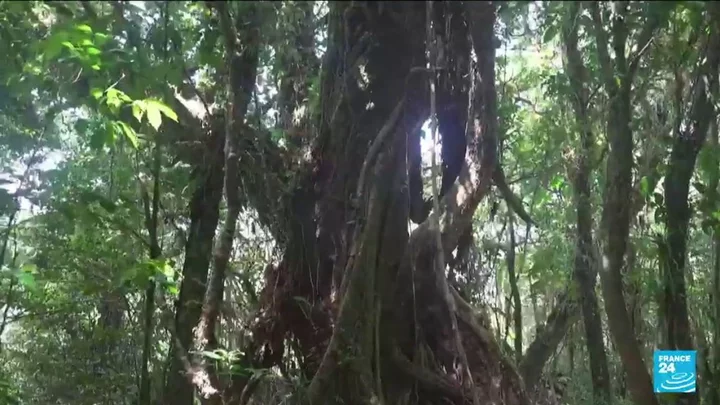

Ancient forest discovered which could contain totally unknown species
A giant sinkhole home to an ancient forest in China could potentially be home to unknown species. Chinese scientists in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China discovered the 630-foot deep hole last year, with trees as tall as 130 feet. It was found by cave explorers, who took a deep dive into the forest – which surprisingly has a gap making room for sunlight for the flourishing forest. The area where such sinkholes exist is often referred to as karst landscape. They're caused when water erodes the bedrock. Zhang Yuanha a senior engineer at the Institute of Karst Geology told local media that three caves were also discovered in the forest. Chen Lixin, who led the cave expedition team has now suggested the forest could have animals unknown to science. He said: "I wouldn’t be surprised to know that there are species found in these caves that have never been reported or described by science until now." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The executive director of the National Cave and Karst Research Institute (NCKRI) in the US, sister organisation of the China Geological Survey, George Veni said: "Not only do sinkholes and caves offer refuge for life, they are also a conduit to aquifers, or deep stores of underground water. "Karst aquifers provide the sole or primary water source for 700 million people worldwide. But they're easily accessed and drained — or polluted. "They are the only types of aquifers that you can pollute with solid waste. "I've pulled car batteries and car bodies and barrels of God-knows-what and bottles of God-knows-what out of the active cave stream." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-06 00:22

OpenAI releasing version of ChatGPT for large businesses
By Anna Tong Artificial intelligence leader OpenAI said on Monday it is releasing a version of ChatGPT targeted
2023-08-29 01:27

Microsoft to lodge appeal against UK regulator's block of Activision deal - Sky News
Microsoft Corp will lodge an appeal by the end of Wednesday against British regulators' decision to block its
2023-05-25 00:47
Medical Billing Automation Takes Giant Leap Forward With GPT-Enabled Virtual Agents From Outbound AI
SEATTLE--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 9, 2023--
2023-05-09 21:26

Former Apprentice star bares all in ‘world’s largest AI-generated billboard'
A man known for flying 4,000 miles to track down a thief who stole his AirPods is at it again – and this time, he’s baring all. With artificial intelligence technology on the rise, former Apprentice contestant, Lewis Ellis, is on a mission to find out if robots are going to come for our jobs. In a bizarre experiment, the 32-year-old, who is no stranger to unusual projects – having previously auctioned off his bum cheek for the highest bidder to choose a tattoo – he used ChatGPT to re-create an image for a billboard. And the result is hilarious. The giant billboard, featured at Victoria Warehouse in Lewis' hometown of Manchester, shows the entrepreneur stark naked – as a mermaid. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter He used the famous Burt Reynolds Cosmo centre-fold for the main image and asked ChatGPT to “create the content”. ”Whatever it creates, that goes live,” Lewis says in a YouTube video. “I’m not sure if it’s is a good idea, I’m not sure if it’s going to be a complete waste of time but I guess we’ll find out.” Measuring in at 17.6m x 17.4 billboard, it is believed to be the second largest in Europe – however Lewis believes it is the “world’s largest AI-generated billboard. The Apprentice star photoshops his face and tattoos onto the nude Reynolds. The billboard went live at 9am on Wednesday (21 June) and… it’s definitely interesting. Lewis said: ”I was silly to assume that AI would pull it together for me – I won’t really have to do much. ”Turns out it's way harder than I thought. ”And it looks so bad.” The sorry-looking AI generated advert morphed the image of Lewis and Burt Reynolds into the sea creature. In the background, there is a cartoon drawing of a lighthouse and beach. The sign reads: “Feast your eyes on this tragic masterpiece. ”The world’s largest AI-generated billboard. ”AI is going to take over the world. ”That may be true… but it’s not going to be today.” The billboard ad is a recreation of his company, Hussel Marketing’s previous marketing campaign. Lewis took his inspiration for the experiment from the likes of McDonald's, Burger King and Subway, with the brands using ChatGPT for recent ads. To make it even harder, he gave himself just 24 hours to complete the challenge. The entrepreneur certainly isn’t shy in pushing the boundaries of what is possible and using technology to do so. In the past, he has shelled out £2,300 on flights, accommodation and food to fly 4,000 miles to track down his headphones, saying his mum describes him as “mental”. He told Jam Press: “We had no real plan but just hoped to find them again. “The fact you can track tiny headphones around the world is unbelievable. “I didn’t really expect to get them back and I joked that flying to Doha to get them is the pettiest thing I’ve ever done. “But it’s just great that we managed to find them – and now I don’t need to buy a new pair!” What does the marketing guru have up his sleeve next? It’s anyone’s guess. But one thing is certain – AI bots aren’t going to take over his job just yet. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-26 23:29

NBA 2K24 Sept. 14 Update 1.2 Patch Notes: Full List of Changes
The NBA 2K24 Sept. 14 patch notes for update 1.2 delivered numerous changes to MyCAREER mode, including quest and progression updates.
2023-09-14 23:47

New open world video game PAW Patrol World coming in September
'PAW Patrol World' is a family-friendly open world video game.
2023-06-07 19:15

EA Sports FC 24 Radioactive Promo Leaked for Thunderstruck Follow-up
EA Sports FC 24's next promotion is apparently Radioactive according to community leaks. Here's what you need to know including a leaked card design, popular players that could be included, and a prospective release date.
2023-11-28 04:26
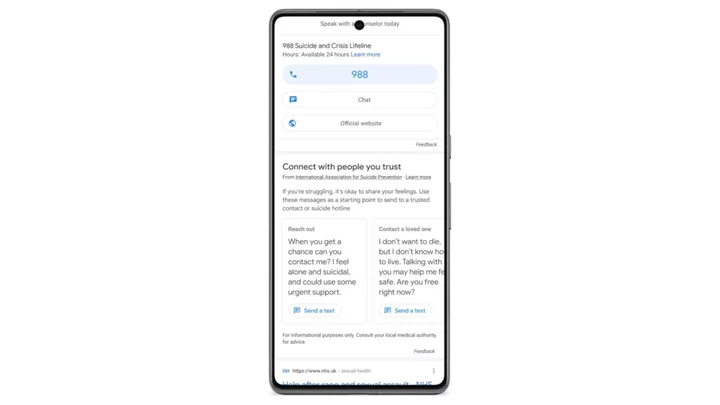
Suicide-related Google searches will provide message templates for reaching out
It's Mental Health Awareness Month in the U.S., the month when we acknowledge that we're
2023-05-16 10:52

Japan Utility Tohoku to Test Use of Hydrogen in Power Generation
Tohoku Electric Power Co. is accelerating plans to test the co-firing of hydrogen at a natural gas power
2023-09-27 16:22

Is RiceGum broke and 'working at McDonald’s'? YouTuber addresses boxer Jake Paul's claims
RiceGum broke his silence and addressed the claims about working at McDonald's
2023-05-29 15:25
You Might Like...

EarthTronics Introduces Two LED Wall Packs with Watt and Color Selectability for Precise Exterior Security Illumination

Stanford Medicine and Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence announce RAISE-Health, a responsible AI initiative

Most of Europe Poised for Cooler Temperatures by Next Weekend
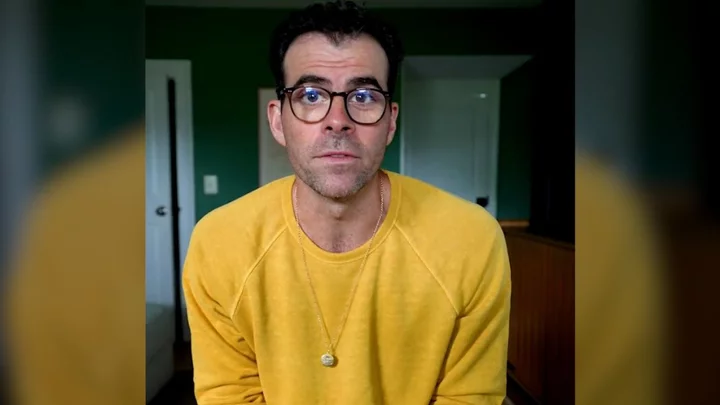

Instagram boss’s launch video for Twitter rival Threads roasted in ‘genius’ parody
ServiceNow delivers comprehensive automation solutions with the Now Platform Vancouver release

Prime members can get 3 months of Kindle Unlimited for free
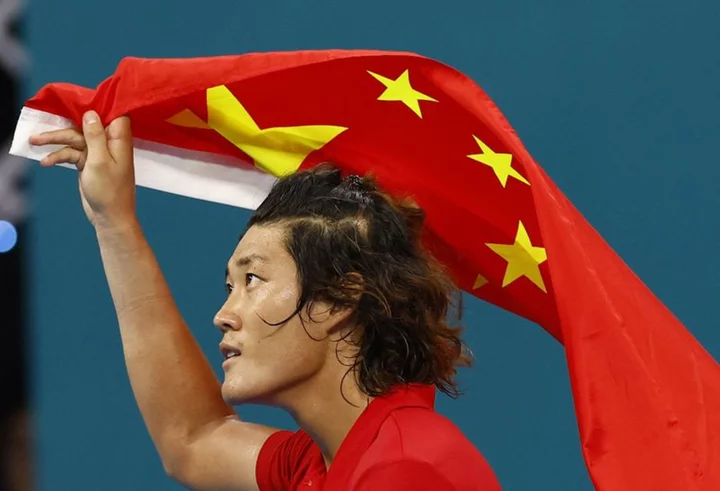

Games-North Korea cheer weightlifting world record, Zhang wins tennis gold

GoDaddy Web Hosting Review
