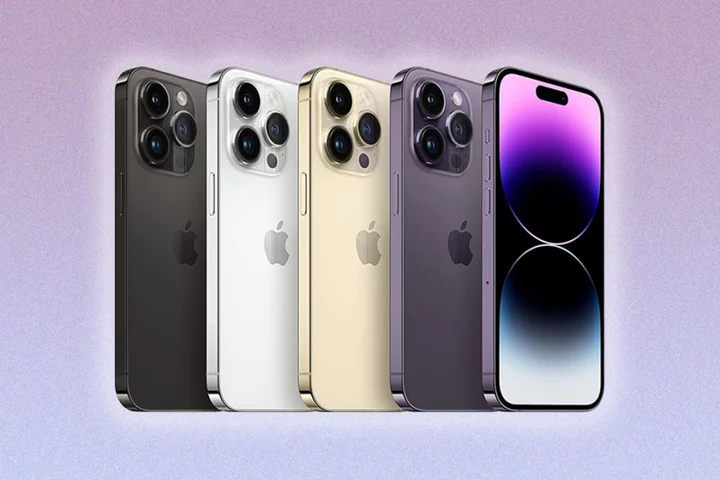

Apple’s iPhone 15 release date leaked amid reports of ‘severe shortages’
Apple is expected to release its next-generation iPhone 15 smartphone on 22 September despite rumoured shortages, according to reports. The release date will follow an unveiling event for the iPhone 15 on 12 September or 13 September, Bloomberg reported, which will also see other Apple hardware announced. A separate report from 9to5Mac suggests the launch will take place on Wednesday, 13 September, as mobile carriers have requested that workers not to take that day off due to a major smartphone announcement. Most iPhone launches typically take place on the second Tuesday of September, with the official release taking place later in the month, however last year the unveiling took place on a Wednesday. The switch came amid significant supply disruptions that forced Apple to delay sales of its iPhone 14 Plus to October. Previous rumours surrounding Apple’s 2023 iPhone event suggested at least one of the iPhone 15 models will be delayed due to “severe shortages”. The supply issues relate to a new screen design that is expected to be introduced on the iPhone 15 Pro and Pro Max, according to The Information. The premium models will feature a much narrower bezel – the border around the device’s screen – but require a new manufacturing process that Apple has struggled with. Other updates expected for the iPhone 15 include a mysterious button on its side, which could function as a customisable ‘action button’ to allow owners to programme it to perform a variety of tasks. The possible customisations will be camera, flashlight, focus, magnifier, translate, accessibility, shortcuts, silent mode and voice memos, according to Macrumours. Sales of iPhones have dipped this year, Apple’s latest financial results revealed, with analysts blaming “waning growth in the smartphone market”. The Independent has reached out to Apple for comment on the latest reports, though the US tech giant does not typically comment on leaks and rumours relating to unreleased products. Read More Apple iPhone 15 rumours: Pro and Pro Max release date, price, cameras, specs and more
2023-08-07 20:22

Apple Wants to Catch Up With Microsoft, Google on AI. How Much It Needs to Spend.
Apple is likely to spend billions on chips from Nvidia to power its AI investment, according to analyst Ming-Chi Kuo.
2023-10-24 18:15

Enhance your car's interior with this wireless car display for $105
TL;DR: As of September 12, you can get a 9" wireless heads-up car display with
2023-09-12 17:22
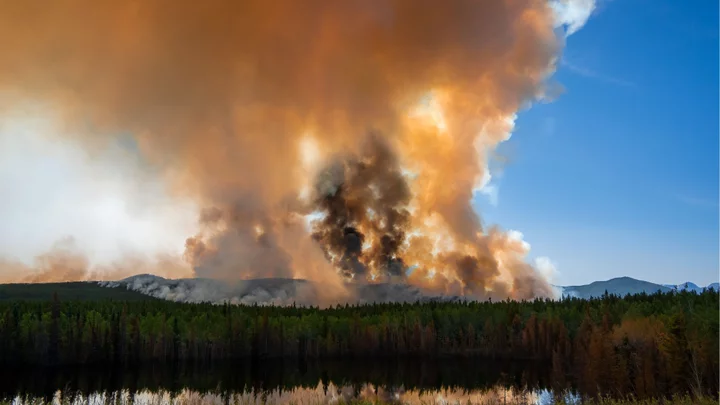

Canada Demands Meta End News Ban Amid Wildfires
The Canadian government has reportedly demanded Meta remove its ban on domestic news in the
2023-08-20 03:19

Earth-like planet that humans could live on found just 31 lightyears away
A planet with conditions on the surface resembling Earth has been discovered a relatively short distance from us. In fact, it’s just 31 light-years away, which is the space equivalent of 'down the road'. Scientists are always excited when it comes to the discovery of new exoplanets, and this is no different. The planet, named Wolf 1069 b, is the sixth closest exoplanet to Earth has been found and the findings were published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It orbits the red dwarf - which is named Wolf 1069. As such, the planet has been given the name Wolf 1069 b. The planet was discovered during a study called CARMENES which is a long-term study based around finding exoplanets. Encouragingly, scientists believe that the planet sits in the habitable zone around its sun where water can exist in liquid form. The study was undertaken by a team led by astronomer Diana Kossakowski of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy. Kossakowski said: "When we analyzed the data of the star Wolf 1069, we discovered a clear, low-amplitude signal of what appears to be a planet of roughly Earth mass. "It orbits the star within 15.6 days at a distance equivalent to one-fifteenth of the separation between the Earth and the sun." It comes after a new planet was discovered with a surprisingly fluffy composition - like candy floss. The exoplanet, WASP-193b, was discovered 1,232 light-years away and while it's nearly 50 percent bigger than Jupiter, it's light and fluffy making it as dense as the sweet treat. According to a team led by astronomer Khalid Barkaoui of the University of Liège in Belgium, the planet orbits a Sun-like star named WASP-193. This star is around 1.1 times the mass and 1.2 times the radius of the Sun and is very close to the Sun in temperature and age. The planet orbits the star around once every 6.25 days. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-26 23:15

Red Dead Redemption and Undead Nightmare Now Available for Nintendo Switch and PlayStation 4
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 17, 2023--
2023-08-17 20:19

Study finds that divorced diabetic men have higher risk of amputation
Divorced men with diabetes are at the highest risk of having some or all of their feet and legs amputated because of it, research has found. According to a study of almost 67,000 people with diabetes in Sweden, people with the condition who are divorced are 67 per cent more likely to have to undergo a lower limb amputation than those who are married. Meanwhile men are at 57 per cent greater risk than women. On average, 184 people a week in England have some part of a lower limb removed surgically to stop infection spreading and killing them. Lasantha Wijesinghe, a consultant vascular surgeon in England who performs lower limb amputations, said they were usually necessary because the person’s life was at risk because of sepsis. The authors of the study, which has not been peer-reviewed yet, said they could not be sure why divorcees of both sexes ran such a greater risk than married people, but speculated that this “may be due to a change in self-care and food habits observed in people when they divorce and are more likely to be living alone”. “Specifically with men, this is often related to more social isolation, with a secondary effect of low physical activity,” they added. Older people are also at higher risk of an amputation and patients who are on insulin treatment, have a pre-existing foot condition such as neuropathy or who smoke are also at higher risk. The study also concluded that obese people have a lower risk than those with a standard weight. The authors could not explain this finding but suggested it could be down to chance. Dr Faye Riley, the research communications manager at Diabetes UK, said: “This study identifies a range of factors that may be linked with a higher risk of amputation among people with diabetes, and raises interesting questions about how social support can influence our health behaviours and outcomes. By pinpointing which people with diabetes are most at risk, support can be targeted where it’s most needed.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-18 18:45

Climate Funds Look to Regain Footing After Three Down Years
Clean energy funds are in the dirt. They’ve slumped roughly 30% this year after losing almost 5% of
2023-11-22 19:52

World-Class Software Sales Executive Melissa Campbell Joins SmartBear as Chief Revenue Officer
SOMERVILLE, Mass.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 6, 2023--
2023-09-06 20:21

Marco’s Pizza® Pilots Leadership Education Program for Front-Line Employees with Bellevue University
BELLEVUE, Neb.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 9, 2023--
2023-05-09 20:24
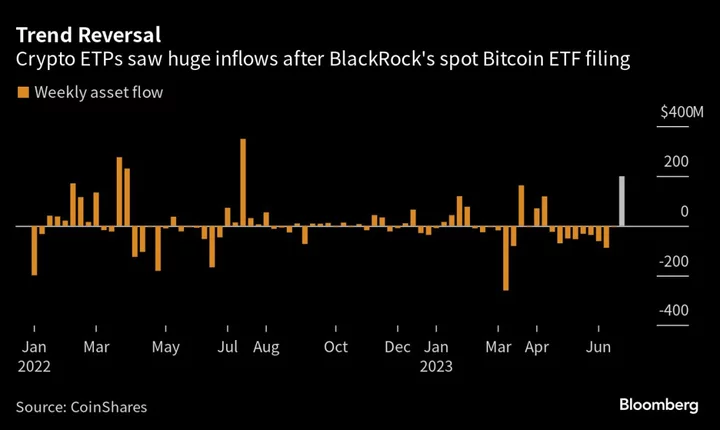
Digital Asset Inflows Highest in a Year After BlackRock’s Spot-Bitcoin ETF Filing
Digital-asset investment products added $199 million last week, the biggest weekly inflows in nearly a year, as a
2023-06-26 23:20
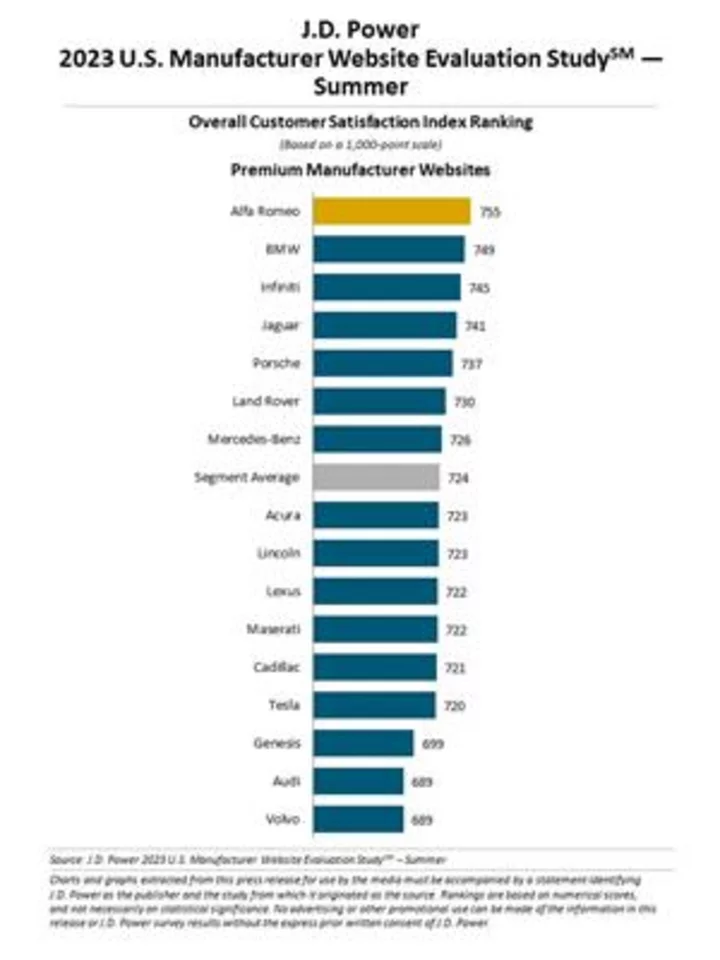
Satisfaction with Websites is Volatile but Automotive Manufacturer Websites Shine, J.D. Power Finds
TROY, Mich.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 18, 2023--
2023-07-18 20:28
You Might Like...
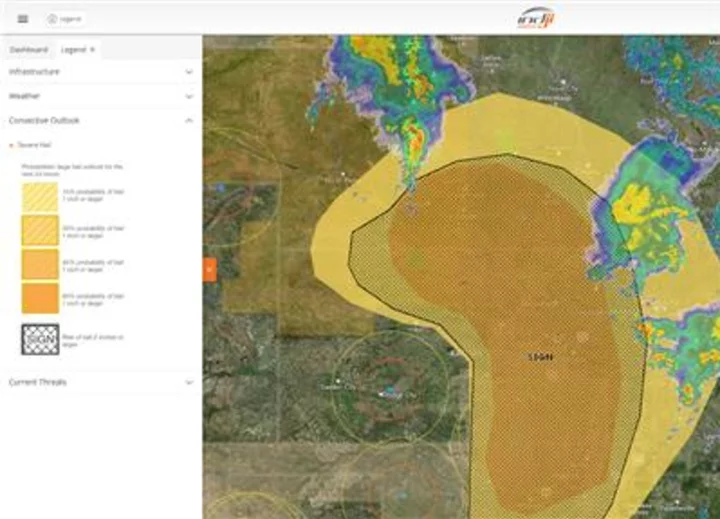
Indji Systems Launches Cutting-Edge Hail Detection Technology for the Solar Industry

The Best PC Games for 2023

Bella Poarch's meet with K-pop group Aespa sends fans into frenzy over possible collaboration

BearingPoint appoints 22 new Partners, reflecting record-breaking revenue and growth ambitions

The Best Audiophile Headphones for 2023
Why Threads, Meta's Twitter Killer, Needs a Desktop Version

NBA 2K24 Best 3 Point Shooters

Influencers in the Wild on 'Shark Tank': Here's how and where to buy the cardboard game and film your win
