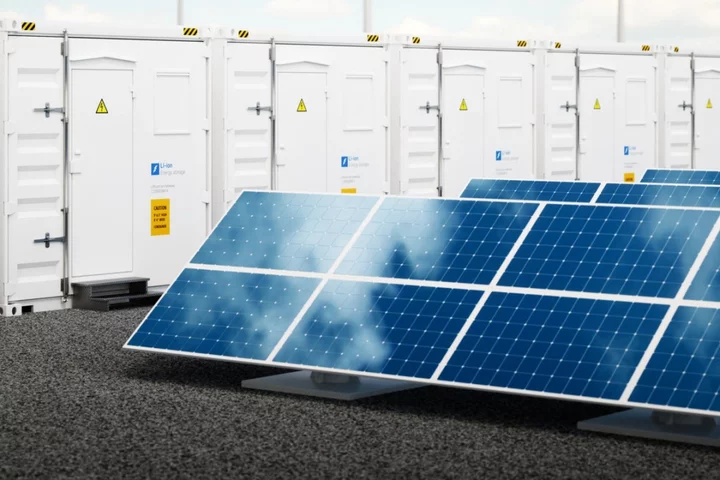

Breakthrough solar system outperforms military-grade diesel generator
Solar panels combined with next-generation batteries now outperform military-grade diesel generators, according to new analysis. Researchers at the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that the novel clean energy solution was both cheaper and more reliable than its fossil fuel-powered counterpart. Tests of the two systems were carried out in accordance with the US Department of Defense’s requirements to sustain critical electric loads during a power outage over a 14-day period. The solar systems proved to have a higher resilience and lower cost compared to the diesel-based systems that are currently used, while also being less vulnerable to interruptions in the diesel supply. The researchers also highlighted the net present value (NPV) of the solar storage system, meaning it pays for itself in the long term. “The diesel-fuel-free LDES system outperforms the traditional diesel-based system and provides a large net saving that can be used to pursue third-party financing,” the researchers noted. “The continued rapid decline in photovoltaic (PV) costs allows for utility-scale PV to be economically attractive at many locations. These declines are expected to continue, which will further increase the positive NPV in the future.” The tests were performed on three separate military bases, using an innovative carbon-based battery rather than the more expensive lithium-ion batteries that are typically found in such renewable energy storage systems. The batteries tested in the experiments were Antora Energy’s battery energy storage system (BESS), which the researchers warned were not yet ready for full-scale deployment. The results of the study, however, mean decision makers are already anticipating their roll out. Michael McGhee, the Acting Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense, described the new system as “the most likely way to easily and simply generate power without the need for off-base supply chains”. The results of the research were published in a study, titled ‘Long-duration energy storage: resiliency for military installations’. Read More Solar panel advances will see millions go off grid, scientists predict
2023-11-13 19:49

Three Adani Firms Lose Endorsement of UN-Backed Climate Group
Three Adani Group companies, including Adani Green Energy Ltd., have lost their endorsement from the world’s leading arbiter
2023-05-09 14:17
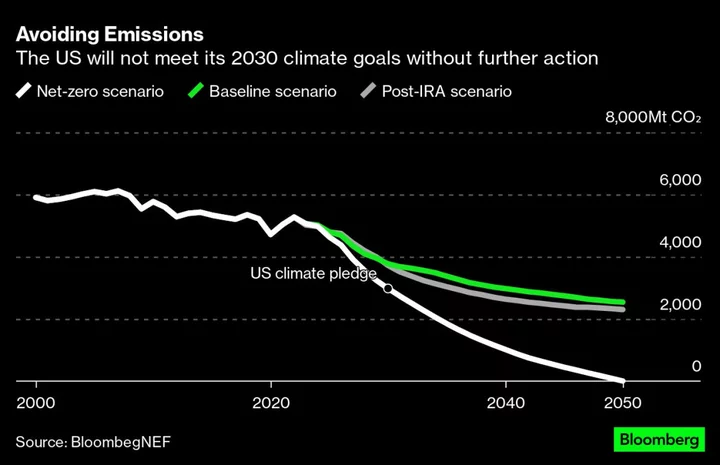
Biden's Climate Law Only Halves US Greenhouse Gas Emissions by 2050: Study
US President Joe Biden’s signature climate law, the Inflation Reduction Act, could slash US greenhouse gas emissions in
2023-08-02 19:20
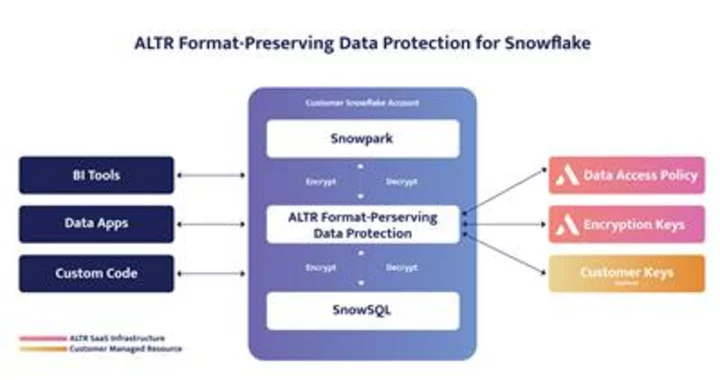
ALTR Rolls Out Snowflake Native Format-Preserving Data Protection Using Snowpark
LAS VEGAS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 27, 2023--
2023-06-28 03:16

Andrew Tate sparks controversy as he denounces reading as 'bulls**t cowardice,' Internet says 'at least it prevents verbal diarrhea'
Andrew Tate claimed reading is 'brain masturbation' for 'middle-brain losers' in a highly problematic tweet
2023-07-02 21:19

Salesforce Extends Its Lead as Dow’s Top Performer. What Analysts Say It Needs to Do Now.
Salesforce stock rises after the software company's latest earnings report. But analysts are still looking for evidence Salesforce can return to its historical revenue growth rates.
2023-11-30 18:48

5 Multiplayer Games to Play (and 2 to Skip) This Weekend, July 14
Which multiplayer games should and shouldn't be on your list?
2023-07-14 03:45

Appeals Court Refuses to Allow US to Limit Oil Drilling Auction
A federal court upheld a ruling forcing the Biden administration to expand its sale of offshore drilling rights
2023-09-26 10:46

Five Takeaways From a Sweeping Report on Climate Change in the US
A major US government report published today describes how intensifying climate change is disrupting lives and businesses nationwide,
2023-11-14 18:26

Amazon Prime Day 2023 Is Coming Soon—and Here Are the Best Early Deals You Can Already Shop
Discover the best early Prime Day deals happening now for Amazon Prime Day 2023 on Apple products, robot vacuums, and more.
2023-06-24 06:21

Andrew Tate blames American parents' 'lack of responsibility' for causing school shootings, Internet says 'you are just larping'
Andrew Tate claimed that American parents are failing to instill the values and respect connected with their family names and instead blame the system
2023-06-20 13:21
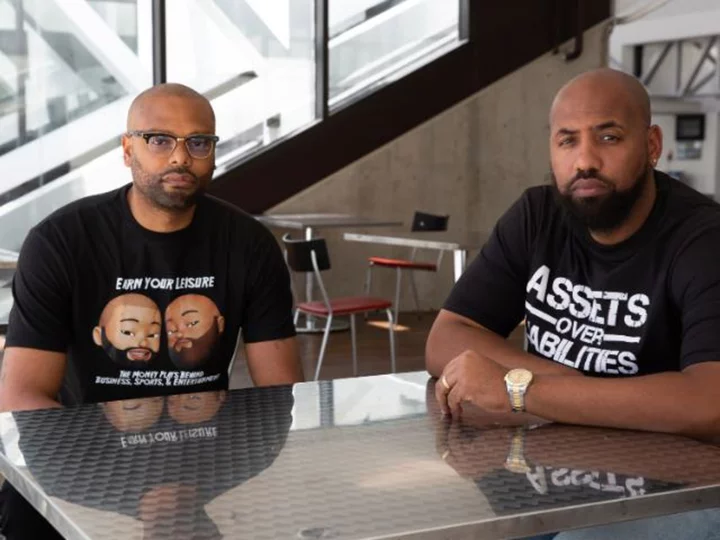

Lifelong friends create platform to teach financial literacy in the Black community
Rashal Bilal and Troy Millings sat on a blue leather couch in a swanky tapas lounge in Atlanta's Castleberry Hills neighborhood. Famed Atlanta rapper 2 Chainz, who owns the place, sat across them as a female bartender walked over with their drinks.
2023-06-15 20:52
You Might Like...

Hurricane Otis Lashes Mexico After Landfall Near Acapulco

Microsoft Puts NYC Times Square Offices on Market Amid Pullback

PCMag Editorial Mission Statement

Cassette Beasts Review

Learn a new language via audiobook with this app, now $30

EA Sports FC 24 Pre-Season Best of Batch 1: Full List of Players

Five Nights at Freddy's Movie Cast, Release Date

Will GTA 6 trailer break MrBeast's YouTube record for views? Reddit debates if video game preview will 'break the Internet' anew
