
Google to delete accounts that have been inactive for at least two years
If you haven't logged into your Google account in a long time, you better use it or lose it.
2023-05-17 03:22
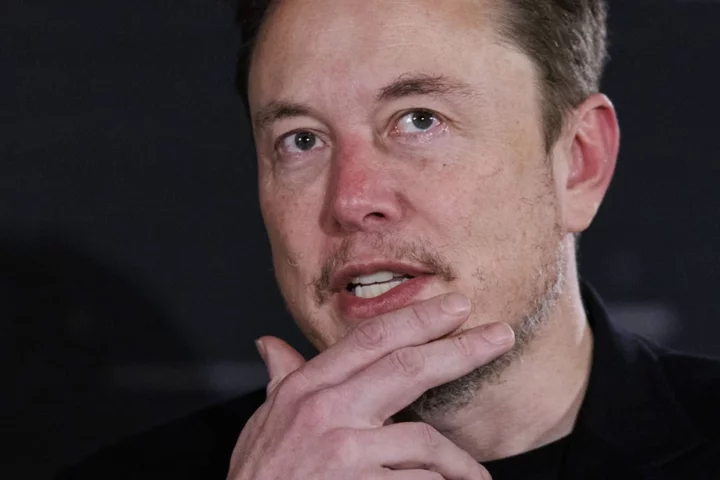

Tesla CEO Elon Musk On The EV Slowdown And ‘Terrible’ Human Drivers.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk had plenty to say on Wednesday in an interview with Dealbook's Andrew Ross Sorkin, including cursing out some advertisers formerly on X.
2023-11-30 20:58

Assassin's Creed: Codename Jade closed beta start date confirmed
'Assassin's Creed: Codename Jade' will launch its first closed beta next month.
2023-07-18 19:29
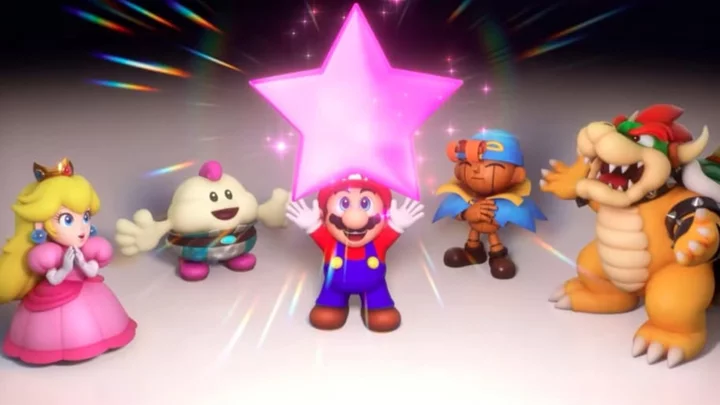

Super Mario RPG Hidden Chest Mushroom Kingdom
If you're having trouble finding the hidden chests in Super Mario RPG's Mushroom Kingdom, you've come to the right place.
2023-11-21 04:47
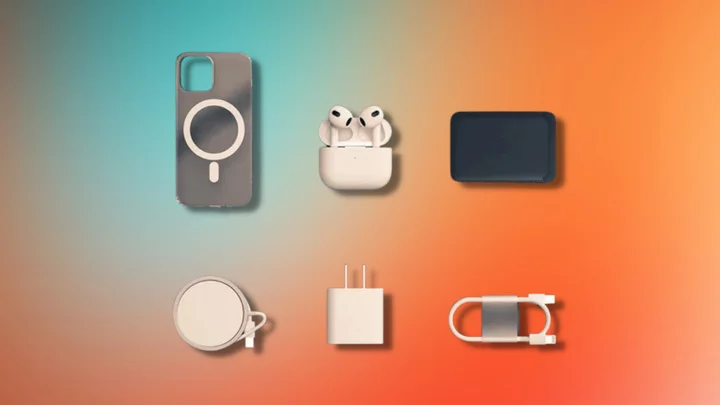

Charge and protect your iPhone 14 Pro with this 6-piece accessory set on sale
TL;DR: As of May 20, iPhone 14 Pro users can snag a six-piece Apple-compatible accessory
2023-05-20 17:51
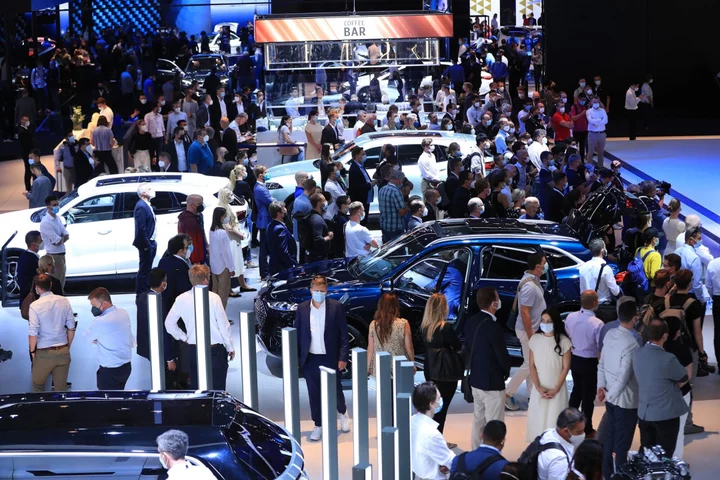

China Crashes Germany’s Least-German Car Show in History
The I- in IAA, the name of Germany’s annual auto show, stands for international. This year’s event is
2023-09-01 14:56
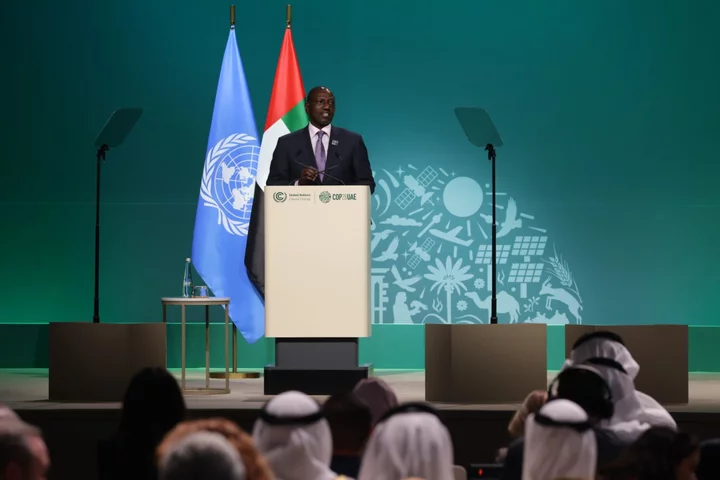

Kenya to Consider Sovereign Green Bonds to Fund Climate Projects
Kenya is weighing selling sovereign green bonds and debt-for-nature swap deals to fund climate projects, President William Ruto
2023-12-02 20:48
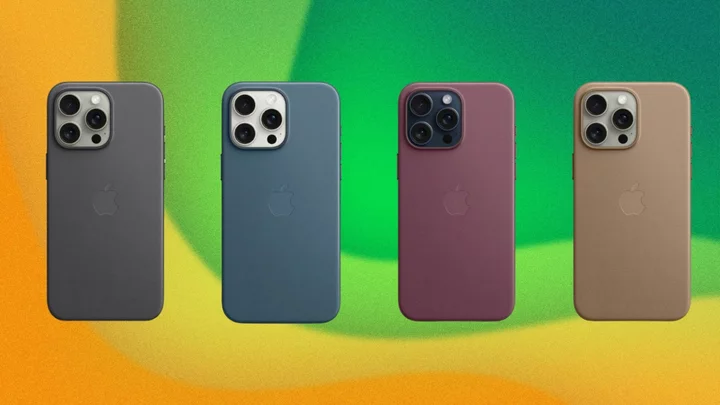

Apple's new iPhone 15 FineWoven cases are on sale
SAVE 5%: As of Sept. 20, Apple's new FineWoven iPhone 15 cases and wallet attachments
2023-09-20 23:45
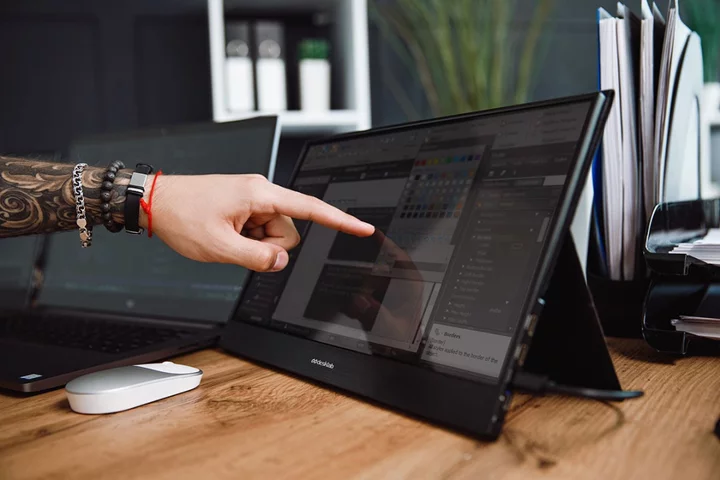

Upgrade your productivity for $250 with this portable touchscreen monitor
TL;DR: As of June 27, you can get the Desklab 4K Portable Touchscreen Monitor for
2023-06-27 17:55

The Supreme Court's affirmative action ruling could hurt the job prospects for candidates of color
The Supreme Court's landmark decision shooting down affirmative action could hurt the college-to-career pipeline many companies lean on to diversify their ranks.
2023-06-30 18:27
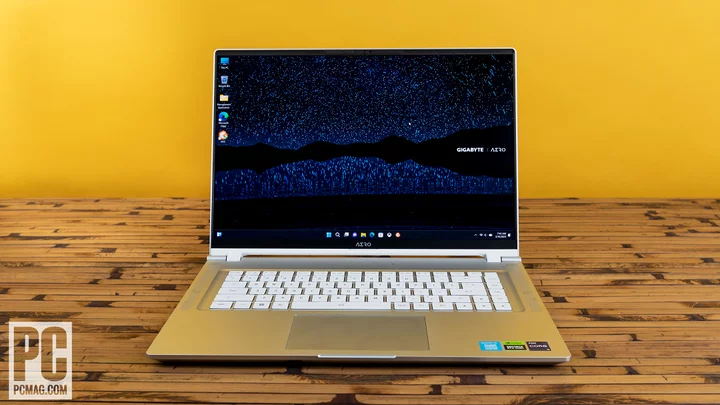

Gigabyte Aero 16 OLED (2023) Review
This 2023 Gigabyte Aero 16 OLED (starts at $1,999; $2,199 as tested) had the honor
2023-08-17 03:51
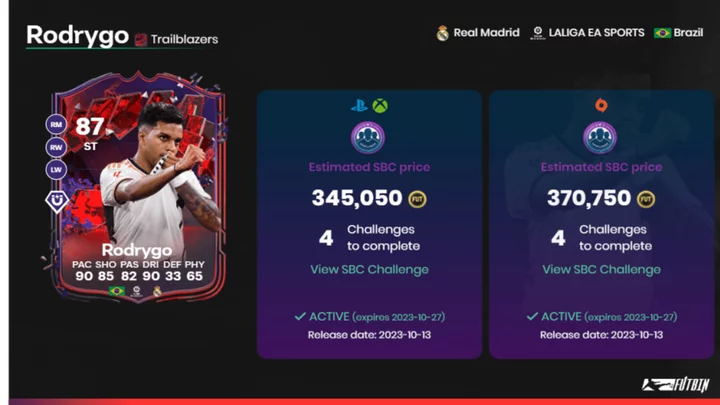
Rodrygo FC 24: How to Complete the Trailblazers SBC
Rodrygo FC 24 Trailblazers SBC is now live during the new Ultimate Team promotion from EA Sports. Here's how to complete the SBC and if it's worth it.
2023-10-14 01:54
You Might Like...
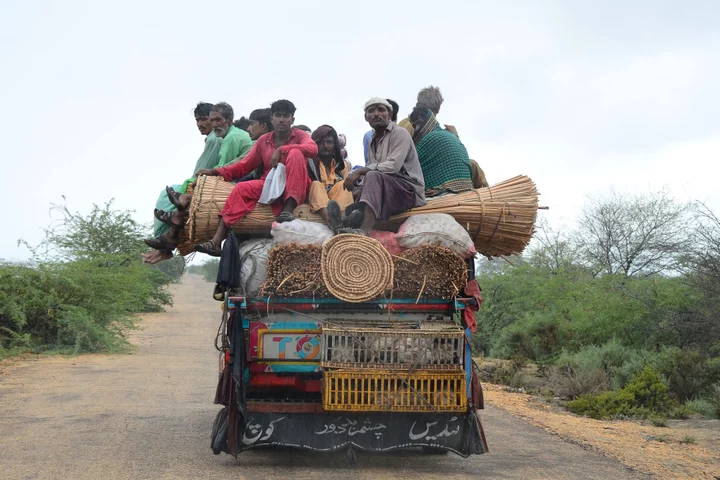

India and Pakistan Evacuate Thousands as Cyclone Makes Landfall

Tampere – Finland’s Most Desirable City to Live in – Attracts Tech Talent From Europe

Simulation discovers what personality traits you would need to go to Mars
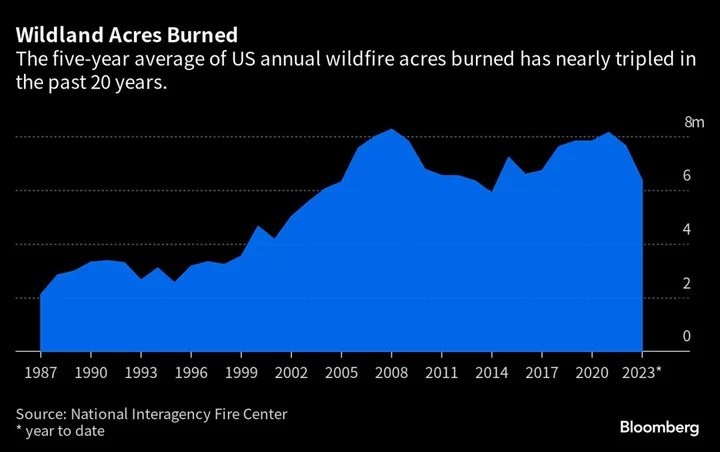
AI, Robots and Satellite Sensors Are Helping in the Fight Against Wildfires
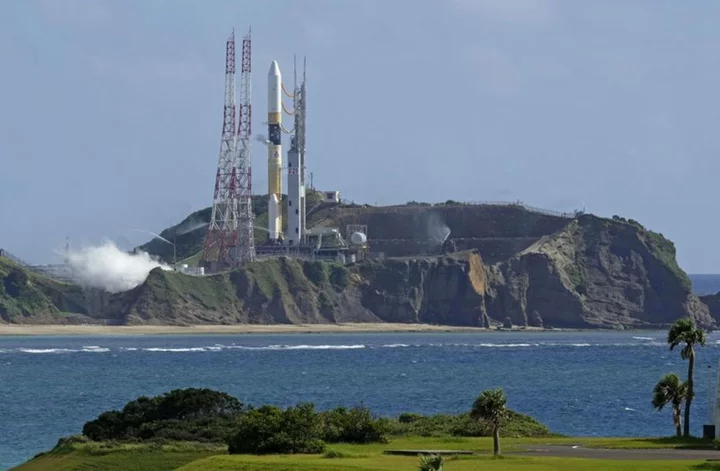

Japan launches rocket carrying moon lander SLIM after three delays

Apple to update iPhone 12 in France after fears over radiation

Kai Cenat and IShowSpeed flirt with girls on Japan trip, Internet slams pro streamers for 'harassing women'

Stock Plays for October: 3 to Watch, According to J.P. Morgan
