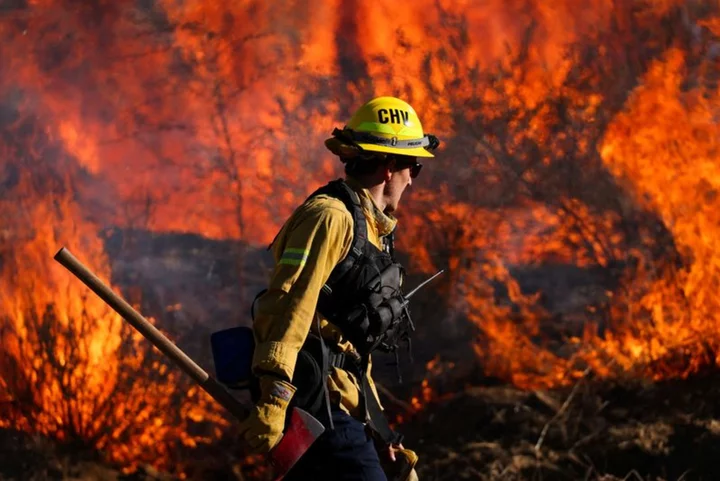

California wildfire, fueled by desert winds, forces evacuations
By Omar Younis TEMECULA, California (Reuters) -A Southern California wildfire fueled by desert winds burned 2,200 acres (890 hectares) and
2023-11-01 06:56

Featuring a Fresh Breed of Young Content Creators and Creative Storytellers, blinx Digital Media Hub Launches to Empower Middle Eastern Youth with Elevated Storytelling and News
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 14, 2023--
2023-09-14 20:28

Pokimane: Twitch streamer 'graduates' from OfflineTV to take on mystery project
For over half a decade, Pokimane has been an integral part of OfflineTV, a tight-knit group of content creators and her close friends
2023-05-20 12:46

Disney Plus and Hulu price increases are coming. How to avoid them
Disney+ last got a price increase in December 2022. Less than a year later, it's
2023-08-11 00:20

The tech that could make the iPhone 15 last hours longer – and change phones forever
Apple is rumoured to be working on a brand new type of battery for its next iPhone, potentially signalling an era-defining transition for the smartphone industry. The stacked battery design will feature on the entire lineup of iPhone 15 devices, according to anonymous leaker @RGcloudS, setting the standard for smartphone manufacturers and transforming the way people use their phones. The next-generation battery technology could result in faster charging, greater capacity and an iPhone that can run for several hours longer between charges. So how does it work and why is it so important? What is stacking technology? The word ‘stack’ refers to the configuration of the elements within a battery cell. The positive and negative electrodes within a typical battery cell are rolled up in a process known as winding, whereas stacked battery cells folds the electrodes up into layers. This makes the most of the space available within a battery cell, while also reducing resistance to lower the amount of heat generated when charging or using the battery. The design allows for a significantly higher charge capacity without changing the form of the battery, meaning no other existing components need to be altered to fit it. Why would Apple change its battery design? Lithium-ion batteries have been the standard power units in smartphones since the first iPhone was unveiled by Apple in 2007. There have been iterative upgrades to improve performance and make them more durable, though the underlying design has largely remained the same. With Apple now working on brand new devices, such as its Vision Pro headset, it makes sense for the world’s richest company to explore new battery innovations. One of the biggest criticisms of its mixed reality device was the external battery pack, so improving capacity could overcome this deficiency. Who else is working on stacked battery technology? Larger lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles already use stacking technology, though condensing them into a size that fits in a phone has proved tricky. Reports emerged earlier this year that Samsung, Apple’s chief smartphone rival, was working on adapting the technology to fit in its flagship Galaxy S24 Ultra phone. The inclusion of a stacked battery could allow the South Korean electronics giant to maintain the battery capacity and performance of its current S23 range, while squeezing it into a smaller form factor. This could allow for new hardware to be added, from a new camera lens, to a major upgrade to the device’s GPU. Read More Battery breakthroughs are about to trigger a transport revolution Rare ‘Holy Grail’ iPhone sells for almost $200,000 Apple’s next iPhone may include new battery technology, report suggests You can now download the huge new iPhone update – if you dare
2023-07-18 18:45
Save 86% on a lifetime license to Microsoft Office
TL;DR: As of May 20, you can get a lifetime license to Microsoft Office (for
2023-05-20 17:48

Redkey Will Launch the First "Smart Screen" Vacuum Robot Soon: Everything Can Be Achieved Without an App
SHENZHEN, China--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 7, 2023--
2023-06-07 17:59

Factbox-Elon Musk's growing legal challenges
By Tom Hals (Reuters) -Elon Musk was sued by the U.S. securities regulator related to his takeover of Twitter, the
2023-10-07 05:15

Indonesia bans X.com (Twitter?) under country's laws on pornography
Elon Musk's unsettling rebranding of the Bird App to "X" has gotten the site banned
2023-07-26 19:20

Germany to Boost Climate, Chips Fund to More Than €200 Billion
Germany will top up a pot to fund climate-protection measures and investment in semiconductor production by about €20
2023-08-04 18:16

When Connections Matter Most, T-Mobile is Ready
BELLEVUE, Wash.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 15, 2023--
2023-06-15 21:15
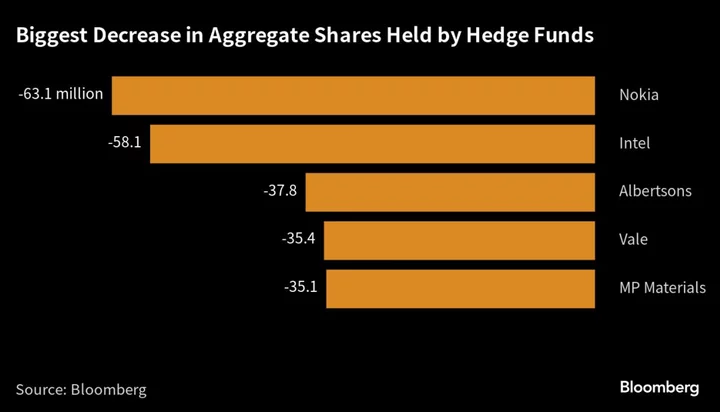
Hedge Funds Dump Intel While Snapping Up Rivals
While hedge funds were busy chasing the technology rally in the second quarter, there was one stock that
2023-08-16 19:15
You Might Like...
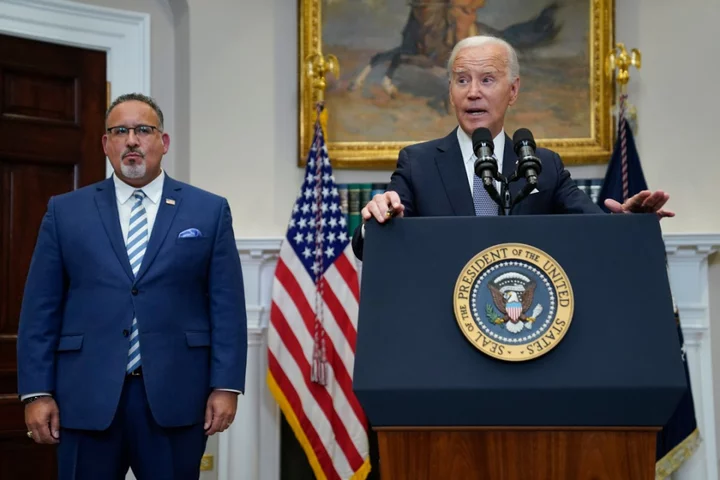

Biden reveals ‘new path’ to student debt relief after Supreme Court strikes down president’s plan

First Solar Urges US to Get Tough on Trade as Module Prices Sink
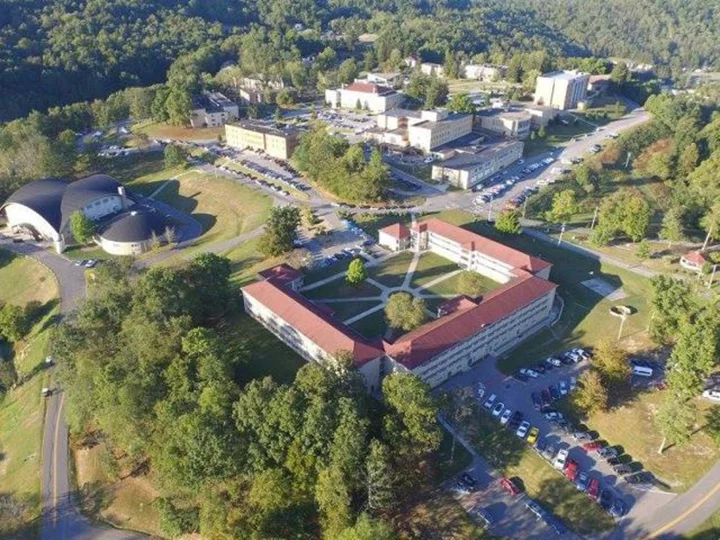

Financially struggling university in West Virginia closes down, leaving students scrambling

BNP Paribas Exits Bond Arranging for New Oil, Gas Ventures

Nintendo annual net profit beats forecast on strong game sales

Scientists found the oldest water on the planet and drank it

Google I/O Keynote 2023: Products, AI Tools to Expect During Stream
Chip wars: How ‘chiplets’ are emerging as a core part of China’s tech strategy
