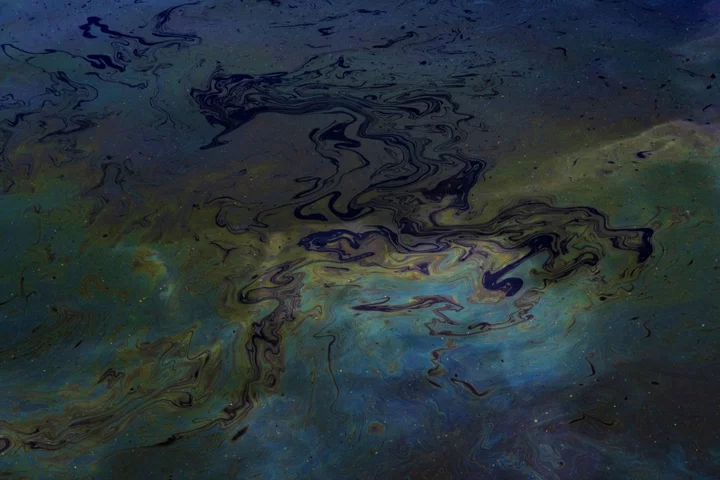
Large Oil Spill Reported Near Site of Pemex Platform Blast in Gulf of Mexico
A large oil spill has been spotted in the Gulf of Mexico near the site of a deadly
2023-07-19 00:56

Not a Prime Member? Save Now During Best Buy's Black Friday in July Sale
Best Buy is not letting Amazon Prime Day have all the deals glory this month.
2023-07-10 15:54

EA SPORTS™ FIFA Women’s World Cup 2023™ Update Available Worldwide
REDWOOD CITY, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 27, 2023--
2023-06-27 23:19
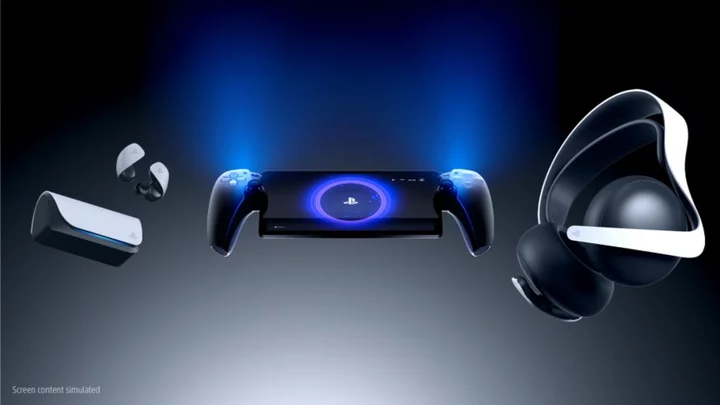

How to Pre-Order PlayStation Portal
Fans can pre-order the PlayStation Portal for $199.99 from the PlayStation Direct store once Sony makes the device available to buy.
2023-08-24 01:45
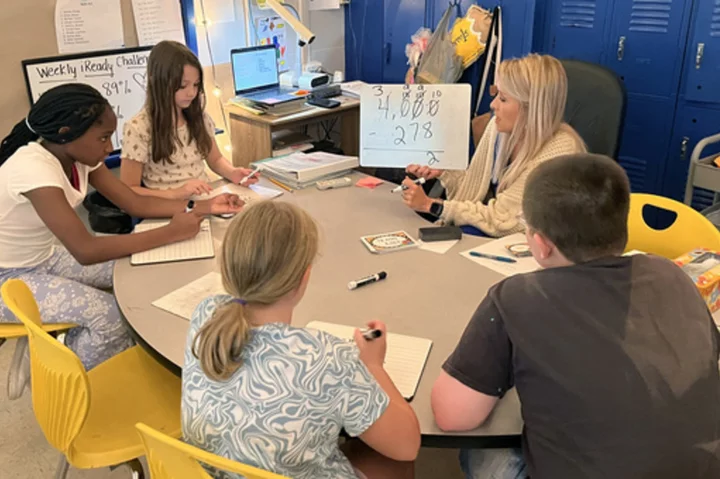

How a rural Alabama school system outdid the country with gains in math
While the rest of the country’s schools were losing ground in math during the COVID pandemic, student performance in a rural Alabama school district was soaring
2023-09-19 20:48

How Seeding the Oceans With Minerals Could Grab Carbon From the Atmosphere
The Hajar Mountains reach nearly 10,000 feet above sea level, tracing the coastline of Oman and the United
2023-09-28 19:25
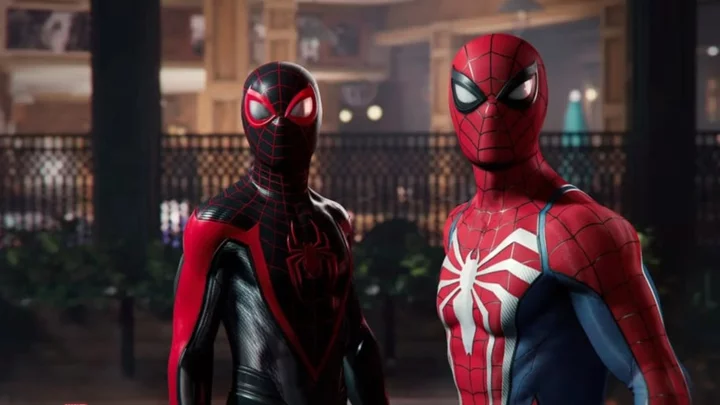

How to Get Every Alternate Spider-Man 2 Suits
If you're looking for every suit in the new Marvel's Spider-Man 2, you've come to the right place.
2023-10-26 02:23

Fortnite Chapter 1 Map Release Date Confirmed
Fortnite Chapter 1 map will return to live servers on Nov. 3 in a new season bringing back classic locations like Tilted Towers and more.
2023-10-28 01:18

Spotify makes AI voice clones of podcasters and uses them to speak other languages
Spotify has cloned the voices of its top podcasters and will use them to translate podcasts into other languages. Presenters including Lex Fridman and Kristen Bell now have podcasts on Spotify in which they interview their guests in Spanish – despite those conversations never actually having happened. Instead, Spotify took those podcasts and used a range of artificial intelligence technologies to create a match of their voice. They then translated the podcasts and used the voice clone to read them back out, giving an interview that is in another language but nonetheless sounds as if it was being spoken by the actual presenters. The company hopes that the technology means that people can listen to natural-sounding podcasts that were originally English – even if they do not speak the language. The technology is available for a limited number of podcasts in Spanish already, and Spotify will collect them in a devoted part of the app, and will also appear as a suggestion when someone starts listening to a relevant podcast. Soon it expects to use the technology for French and German, and will apply it to more podcasts. “By matching the creator’s own voice, Voice Translation gives listeners around the world the power to discover and be inspired by new podcasters in a more authentic way than ever before,” said Ziad Sultan, Spotify’s vice president of personalisation, in a statement. “We believe that a thoughtful approach to AI can help build deeper connections between listeners and creators, a key component of Spotify’s mission to unlock the potential of human creativity.” Spotify has already rolled out a number of other AI-powered features, including its AI DJ, which not only chooses songs but uses an artificial voice to introduce them. Like that AI DJ, the new translation technology is built on tools provided by OpenAI, the creators of ChatGPT. It said the current techologies are “just the beginning”. “The creator and audience feedback from the pilot will provide important insights for future expansion, iterations, and innovations,” Spotify said in its announcement, and it said it would “continue exploring new ways to overcome barriers to storytelling”. Read More Tesla robot shown practising yoga Meta plans to develop ‘sassy robot’ chatbot for young users, report says Nasa just delivered a piece of a distant asteroid to Earth
2023-09-25 21:29

FC 24 Trailblazers Leaks: Every Player Leaked So Far
FC 24 Trailblazers leaks including every player already announced, the new card design, release date and more for the Ultimate Team promotion.
2023-10-12 03:49
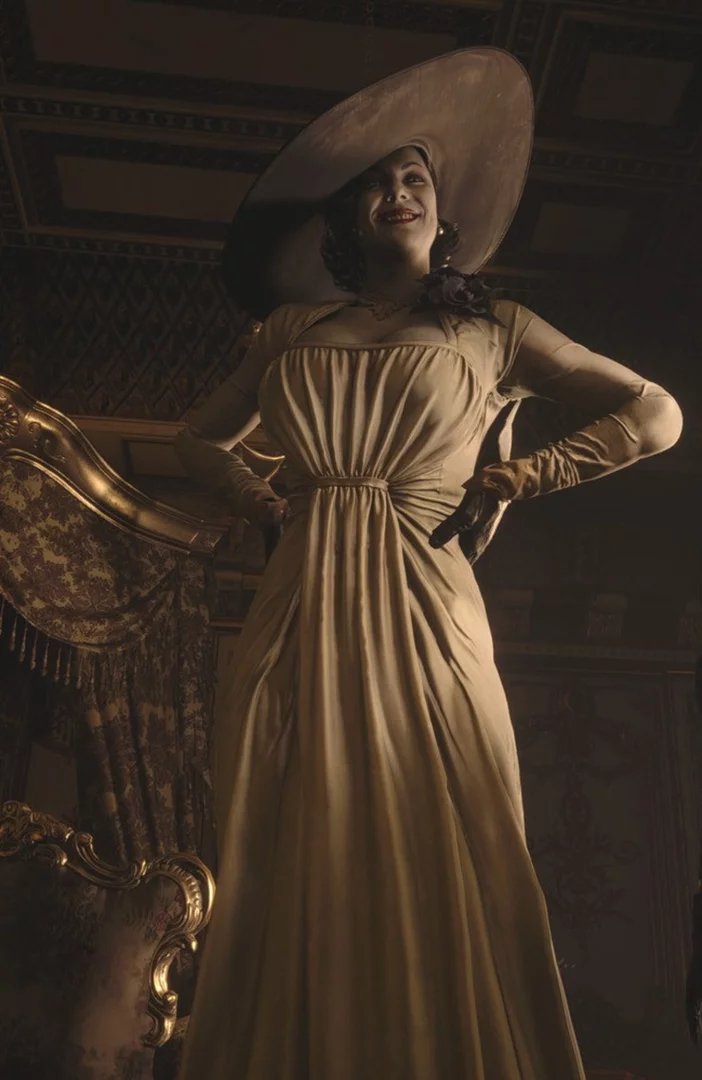

Apple reveals Resident Evil 4, Assassin's Creed Mirage and more for iPhone 15 Pro.
Apple has announced some huge games for the iPhone 15 Pro.
2023-09-13 19:17

Instagram Threads hits 100 million users, becoming easily the fastest growing app ever
Instagram’s Threads app has reached 100 million users, making it easily the fastest growing app ever. The site reached the number early on Monday morning, according to a tracker that looks at the numbers that are made public on each Threads account.
2023-07-10 15:51
You Might Like...

Solvay settles drinking water pollution claims with New Jersey
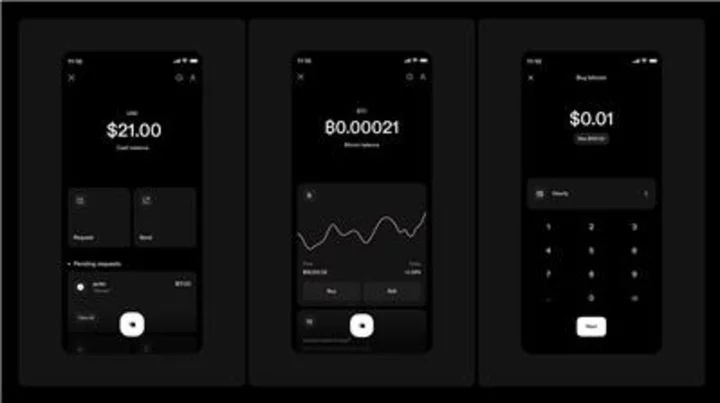
Strike launches global money app to 3 billion people in over 65 countries

ASML Stock and 11 Other Cheaper Ways to Play a Broad Tech Rally
Microsoft Is Bringing OpenAI’s GPT-4 AI model to US Government Agencies

CloudPay Appoints Roland Folz As Chief Executive Officer

Laptop vs. Chromebook: Which Type of Budget PC Is Right For You?

Amazon Prime Video might get an ad-supported tier

SpaceX's Starlink falls short of growth expectations despite revenue surge - WSJ
