
What Is COP28 and Why Is It Important?
World leaders are due to gather for annual climate change talks in Dubai in December. On the agenda:
2023-11-24 19:18

Oklo Announces Sites for Two Power Plants in Southern Ohio
PIKETON, Ohio--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 18, 2023--
2023-05-18 17:47
Arm's IPO could value the chip company at $52 billion. Apple, Google and Nvidia show interest
A who's who of Big Tech companies is set to invest in one of the most highly anticipated initial public offerings in recent memory, a blockbuster event that could value a British chip designer at as much as $52.3 billion.
2023-09-05 21:50

NWN Carousel Named Largest & Fastest Growing Private Technology Services Company in Massachusetts by the Boston Business Journal
BOSTON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 31, 2023--
2023-05-31 22:23

Colin Bower Joins VivoSense as Chief Executive Officer
NEWPORT COAST, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 2, 2023--
2023-08-02 20:21

Singapore Wealth Fund Sees More Growth in Fintech After Downturn
Singapore’s sovereign wealth fund said it still sees more growth in the financial technology sector, even after a
2023-05-09 10:55
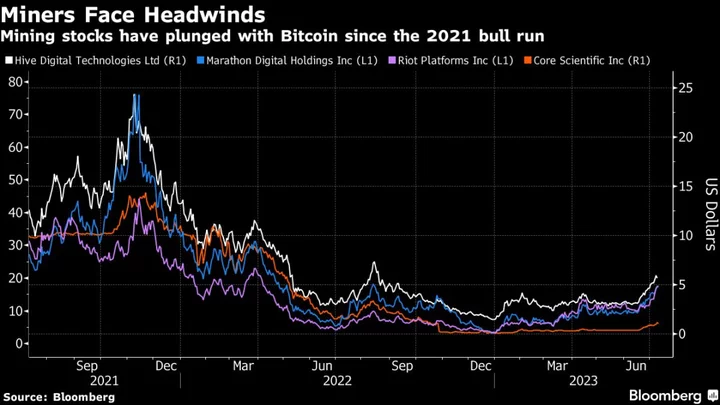
Crypto Miner Hive Drops ‘Blockchain’ From Name in Pivot to AI
The crypto-mining company formerly known as Hive Blockchain Technologies is pivoting to artificial intelligence and web3, and has
2023-07-13 01:50
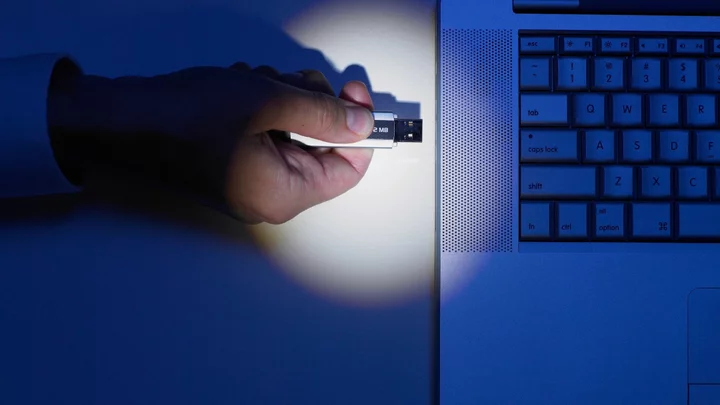

China-Linked Malware Spotted Infecting USB Drives To Spread Attack
A malware linked to a Chinese hacking group has managed to spread to Europe, thanks
2023-06-22 23:29
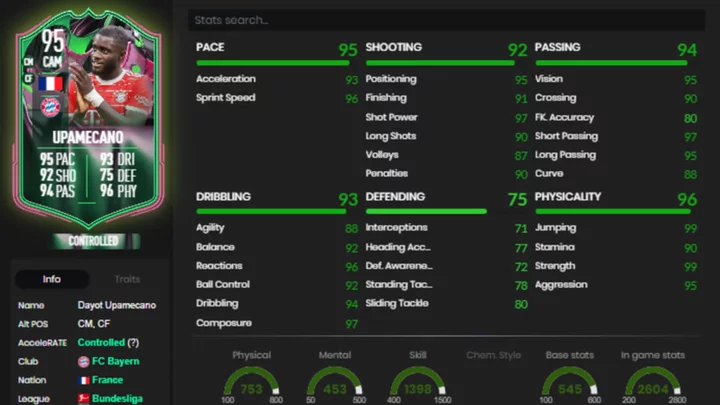
Dayot Upamecano FIFA 23: How to Complete the Shapeshifters SBC
Dayot Upamecano FIFA 23 Shapeshifters SBC is now live. Here's how to complete the SBC and if it's worth it.
2023-06-17 01:59

Apple to stop using leather in iPhone, Apple Watch and all new products
Apple will stop using leather, it has announced. It will offer no new products using materials taken from animals, it said. That includes iPhone cases and Watch bands, both of which make heavy use of leather. Lisa Jackson, Apple’s vice president of environment, policy and social initiatives, noted that leather is a popular material for accessories. But it has considerable environmental impact, she noted, especially at the scale that Apple uses it. As such, it has committed to phasing out those materials. Instead, it will rely on new materials that have been especially developed. For the Apple Watch’s sport loop, for instance, it has changed the material to use 82 per cent recycled yarn. For the straps that are currently made out of leather, it will rely on a new seemingly custom developed material called “FineWoven”. That will presumably also be used for the cases made for the new iPhone 15. And Apple has developed new straps with Nike and Hermès. The latter collaboration has relied heavily on leather – but recently Apple has been rumoured to be selling off those products cheaply. The new materials will help make the new Apple Watch Series 9 the first carbon neutral product the company has made. Read More Here’s the brand new Apple Watch Apple is about to reveal the new iPhone – and a lot more Here’s when you will actually be able to get the new iPhone
2023-09-13 01:58

Banuba TINT Virtual Try-on Platform Massively Enhances Cutting-Edge Skin Care Feature
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 13, 2023--
2023-09-14 00:29

How did Annabelle Ham die? Influencer who created videos on life was 22, sister says she was 'light to the world'
Annabelle Ham had more than 73,000 followers on Instagram and an additional 77,000 subscribers on YouTube
2023-07-19 04:26
You Might Like...

Harvard Legacy Admissions Targeted in Minority Groups’ Complaint

iHeartMedia and Paris Hilton’s 11:11 Media Announce “The History of the World’s Greatest Nightclubs” Hosted by Ultra Naté

Scientists have located a legendary Egyptian city that never appeared on maps

Sanborn Hires Richard Butgereit as Chief Information Officer

EU backs Microsoft buying Call of Duty maker Activision Blizzard. But the $69B deal is still at risk

WisdomTree Files to Start a US Spot Bitcoin ETF on the Heels of BlackRock’s Application

Kai Cenat and Duke Dennis reflect on Fourth of July fireworks incident at AMP house, Internet says 'they got money they don’t care'
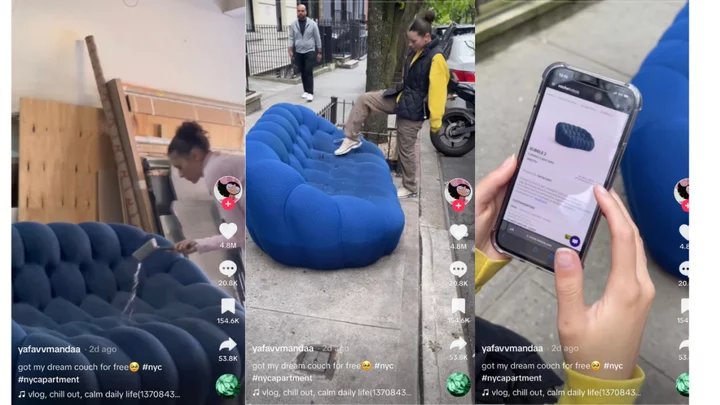
Woman who found an '8k couch' on the street sparks viral debate about bed bugs and knock offs
