
AI pioneer warns Government offering little defence against threat of technology
One of the pioneers of artificial intelligence has warned the Government is not safeguarding against the dangers posed by future super-intelligent machines. Professor Stuart Russell told The Times ministers were favouring a light touch on the burgeoning AI industry, despite warnings from civil servants it could create an existential threat. A former adviser to both Downing Street and the White House, Professor Russell is a co-author of the most widely used AI text book and lectures on computer science at the University of California, Berkeley. He told The Times a system similar to ChatGPT – which has passed exams and can compose prose – could form part of a super-intelligence machine which could not be controlled. “How do you maintain power over entities more powerful than you – forever?” he asked. “If you don’t have an answer, then stop doing the research. It’s as simple as that. “The stakes couldn’t be higher: if we don’t control our own civilisation, we have no say in whether we continue to exist.” In March, he co-signed an open letter with Elon Musk and Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak warning of the “out-of-control race” going on at AI labs. The letter warned the labs were developing “ever more powerful digital minds that no one, not even their creators, can understand, predict or reliably control”. Professor Russell has worked for the UN on a system to monitor the nuclear test-ban treaty and was asked to work with the Government earlier this year. “The Foreign Office… talked to a lot of people and they concluded that loss of control was a plausible and extremely high-significance outcome,” he said. “And then the Government came out with a regulatory approach that says: ‘Nothing to see here… we’ll welcome the AI industry as if we were talking about making cars or something like that’.” He said making changes to the technical foundations of AI to add necessary safeguards would take “time that we may not have”. “I think we got something wrong right at the beginning, where we were so enthralled by the notion of understanding and creating intelligence, we didn’t think about what that intelligence was going to be for,” he said. We've sort of got the message and we're scrambling around trying to figure out what to do Professor Stuart Russell “Unless its only purpose is to be a benefit to humans, you are actually creating a competitor – and that would be obviously a stupid thing to do. “We don’t want systems that imitate human behaviour… you’re basically training it to have human-like goals and to pursue those goals. “You can only imagine how disastrous it would be to have really capable systems that were pursuing those kinds of goals.” He said there were signs of politicians becoming aware of the risks. “We’ve sort of got the message and we’re scrambling around trying to figure out what to do,” he said. “That’s what it feels like right now.” The Government has launched the AI Foundation Model Taskforce which it says will “lay the foundations for the safe use of foundation models across the economy and ensure the UK is at the forefront of this pivotal AI technology”. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live TikTok ‘does not want to compete with BBC for Eurovision final viewers’ Eurovision’s preparations for potential Russia cyberthreat ‘in good place’ UK-based tech company claims quantum computing ‘breakthrough’
2023-05-13 09:51

Caltech ends high-stakes US patent fight with Apple and Broadcom
By Blake Brittain The California Institute of Technology has reached an agreement to end a patent lawsuit against
2023-10-13 00:45
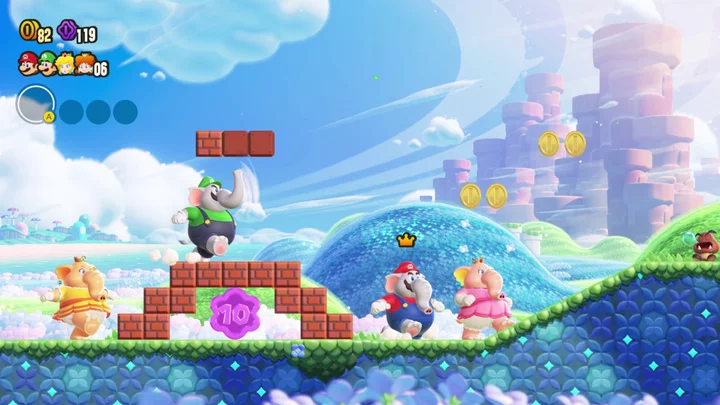

'Super Mario Bros. Wonder' is about being nice to people on the internet
Super Mario Bros. Wonder isn't the first Mario game with online play, but it might
2023-09-01 02:24

When Pokimane addressed Andrew Tate's misogynistic views and influence on social media: 'Really sad'
Pokimane feels Andrew Tate is promoting toxic masculinity
2023-05-31 17:58

xQc: Was Twitch streamer legally married to Adept? Ex couple's relationship timeline explored
The couple has had an unstable relationship, and their publicized disagreements on-screen garnered significant attention in the streaming community
2023-05-12 19:55

How to cancel Tinder Gold
We've all been there: You're under the covers, scrolling through Tinder way past your bedtime.
2023-07-25 21:53

Jim Jordan scraps committee contempt vote on Mark Zuckerberg
House Judiciary Chair Jim Jordan announced Thursday that he is scrapping his plans to move forward with a contempt vote in light of Facebook turning over more documents to the committee.
2023-07-28 02:58
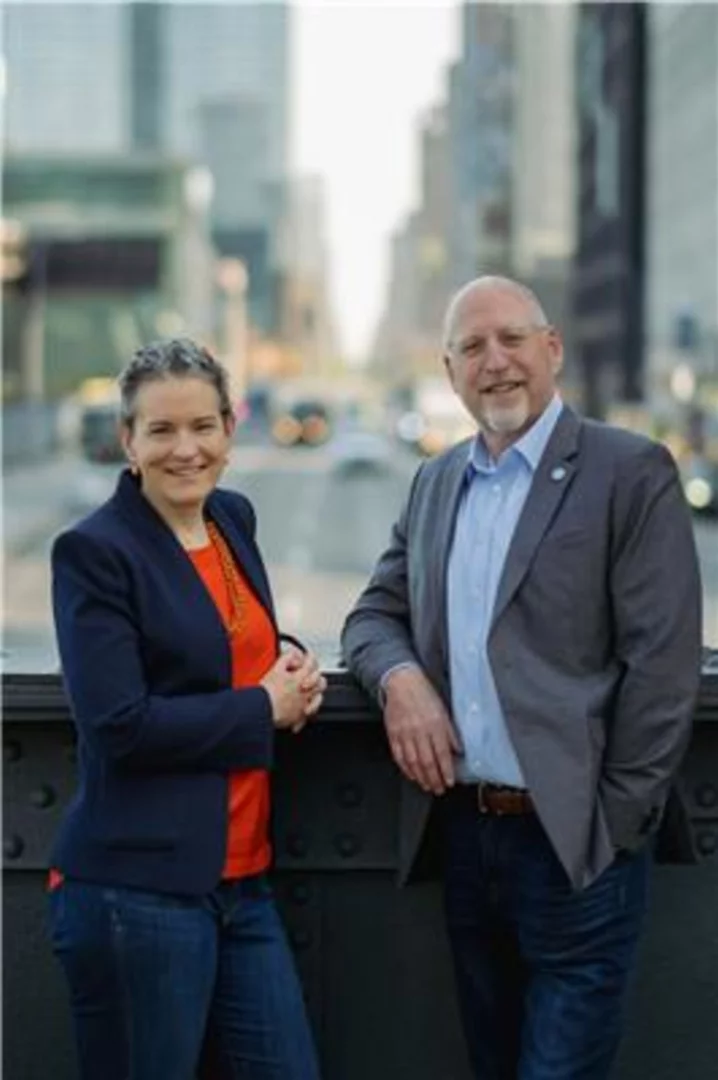

Luke Lambert to Retire from G&S Business Communications; Anne Green Named Agency’s Next CEO
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 15, 2023--
2023-06-15 20:15
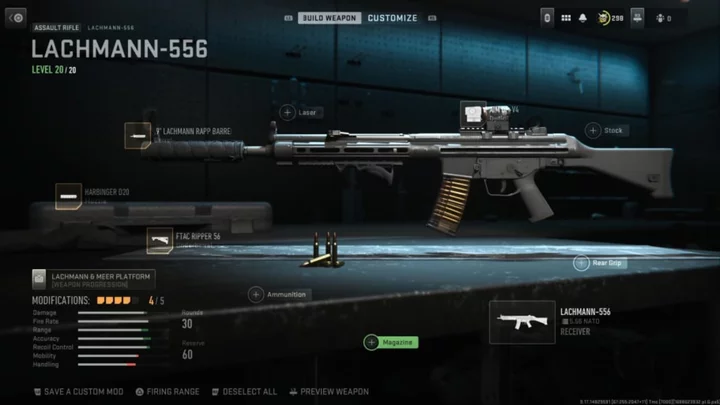
Most Broken Weapons in Warzone Season 4
The Lachmann-556 and SO-14 are the two most broken guns in Warzone Season 4 that will win almost any long range gunfight if you hit your shots.
2023-07-07 01:26
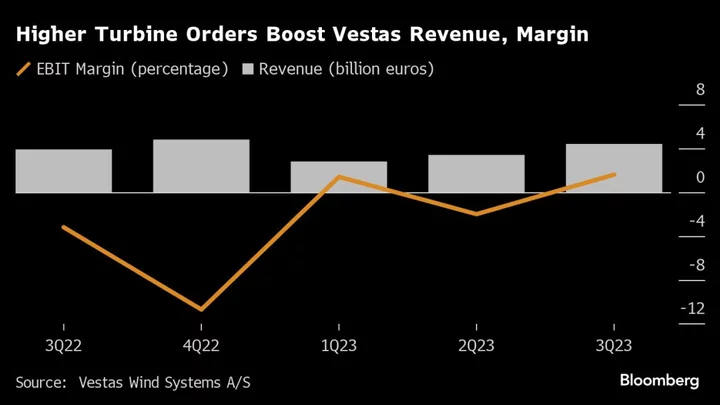
Vestas Seizes on Positive Profit Momentum to Raise Bonds
Vestas Wind Systems A/S is seeking to capitalize on an improving profit outlook to engage with investors and
2023-11-22 19:20

'Free Kai' trends as Kai Cenat's fans extend support to 'pure soul' amid NYC arrest following PS5 giveaway chaos
'Pure soul man !!! you can tell kai love what does, just want bring people together smile'
2023-08-05 16:24

Kai Cenat asks xQc to collaborate with him after successful first episode with IShowSpeed on Rumble: ‘Can we just come together for a weekend?’
Kai Cenat proposed xQc collaborate with him as they have already met for a fun-filled outing at Universal Studios and Super Nintendo World
2023-05-29 15:28
You Might Like...

The Hidden Link Between 'Succession' and David Fincher's 'The Game'
Use ChatGPT to craft content and more with this $60 WordPress Plugin

EU hits Intel with $400 million antitrust fine in long-running computer chip case

A Paid Version of Facebook and Instagram May Be Coming to the EU

Why the Pay Gap Is Still so Large for the Women’s World Cup: Big Take Podcast

Perfect Corp. Exhibits at Viva Technology 2023, Showcasing the Latest Innovations in Beauty, Skincare, Jewelry, and AIGC Technologies

TikTok Shop launches in the U.S. as the company bets big on e-commerce

SEC sues Coinbase, Binance crypto exchanges, alleging sale of unregistered securities
