
The best handheld gaming consoles of 2023
The Nintendo Switch has dominated the conversation around handheld gaming consoles for several years now
2023-05-09 03:26

Ice Cream Cones Tarkov: How to Complete EFT Quest
Here's a guide of how to complete the Ice Cream Cones Quest in Escape from Tarkov, including where to find the three AK-74 5.45x39 6L31 60-round magazines.
2023-08-16 03:51

SBI Forms Joint Venture to Set Up Carbon Exchange in Japan
Japanese financial conglomerate SBI Holdings Inc. and climate tech startup Asuene Inc. have entered a joint venture to
2023-06-07 17:52

Hithium Exhibits at RE+ in Las Vegas, Launching First 5 MWh Container Product
LAS VEGAS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 14, 2023--
2023-09-15 03:15

How to stream Netflix India for free
SAVE 49%: Unblock Indian Netflix from anywhere in the world with ExpressVPN. A one-year subscription
2023-07-20 12:24

How Many Levels Are There in Super Mario Bros. Wonder?
Super Mario Bros. Wonder may have more levels than you may think.
2023-10-24 02:23

Did Kick terminate Adin Ross' $180M contract? Fan's cryptic tweet sparks major speculations
The fan who goes by the name, Ryan, shared a tweet about Ross' $180M contract, stating that it was officially terminated.
2023-07-25 15:59

The Best Cheap Gaming Laptops for 2023
No laptop is a true gaming machine unless it comes with a dedicated graphics processor
2023-07-07 08:47

Ameresco Wins Environmental Initiatives Award at The 2023 SEAL Business Sustainability Awards
FRAMINGHAM, Mass.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 31, 2023--
2023-06-01 03:56
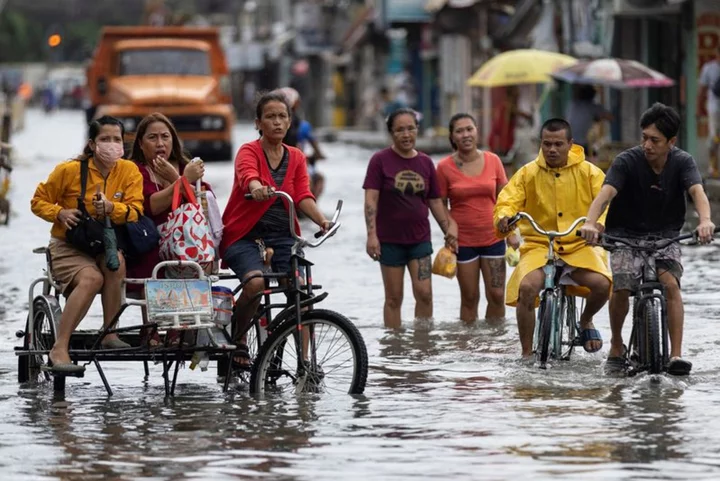

Typhoon Doksuri destroys power lines, closes factories as it rips into China
By Bernard Orr and Yimou Lee BEIJING/TAIPEI (Reuters) -Typhoon Doksuri swept into China's southeastern Fujian province on Friday unleashing heavy
2023-07-28 12:51
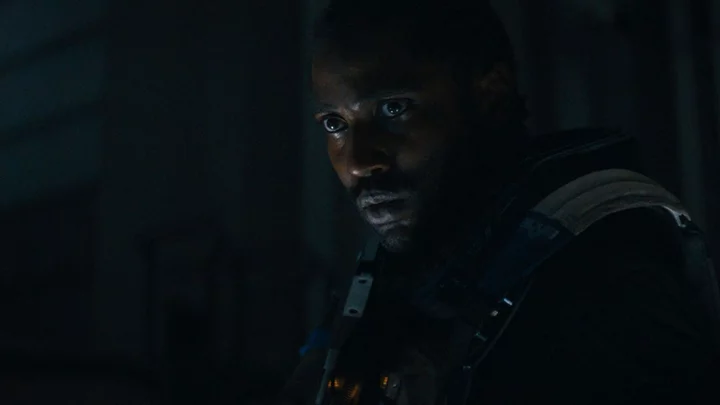

'The Creator' trailer drops John David Washington in a war between humans and AI
Action movies have long hypothesised the inevitability of the technological singularity, the war between once-sentient
2023-07-17 18:19

iPhone 15 Pro: How Apple made the smartphone into a camera like none before it
The iPhone is a lot of things. It's a social networking portal, it's a games console – sometimes it's even a phone. For Apple's Jon McCormack, Apple's vice president for camera software engineering, it's "primarily a camera that you can text from". It wasn't always this way. When Steve jobs introduced the iPhone in 2007, he famously described it is an iPod, a phone and an internet communications device; the first iPhone had a camera, new iPhones are cameras. The pictures that first iPhone turned out were more useful than beautiful. Today, however, the iPhone's pictures have grown up, and it is now the most popular camera in the world. Now the question is how sharp the pictures should be, and there has even been some criticism that the pictures it turns out are too sharp, if anything. The iPhone's camera is no longer just a useful addition but is used in professional contexts, and is often given as the main reason to upgrade to new models. The new iPhone 15s, in particular the premium Pro and Pro Max, continue Apple's mission to turn its smartphones into cameras like nothing in the history of photography. They have new image formats, the addition of extra focal lengths, and the iPhone 15 Pro Max even includes a 5x lens that makes use of a "tetraprism" lens that bounces light around inside the phone to add dramatically more zoom without making the phone any bigger. All of that additional hardware works in collaboration with improved software: users no longer have to click into portrait mode, for instance, because the camera automatically captures depth information when taking a picture of people, so that background blur can be added and edited even after the photo has been taken. Apple has also added a host of features that many people are unlikely ever to even look at, let alone use, but are important to professionals. They include the addition of Log encoding and the Academy Color Encoding System – both key to those who need them. Apple also says that the new iPhone has "the equivalent of seven pro lenses", despite really only having three; what they mean is that you can choose different crops, which is in part an attempt to appeal to those professional photographers who stubbornly say that they will only ever work with a 50mm lens, for instance. (Those new lens choices are not only a cropped version of the existing lenses, says McCormack, since the phone also has custom neural networks specifically designed to optimise images at that focal length.) Those complex new features are a reminder that the iPhone is many things to many users: some may simply want to remember important events, or snap pictures of their pets. Others might be truly professional photographers, needing to rely on their iPhone to capture valuable and fleeting events. Some people are, no doubt, both – and Apple is aware that the iPhone has to be both, too. "For us, what we feel is really important – especially since computational photography started to blur the line between hardware and software, and really enable anybody to take stunning shots with minimal effort – is making sure that that tool that we have in your pocket is adapting to your needs," says Maxime Veron, Apple's senior director for iPhone product marketing. "So if you're just trying to take a quick photo of your kids can get out of the way and just allow you to do that. And if you want to create a professionally created Hollywood style video, it can also give you the customisation and the power to do that." McCormack says that Apple builds the camera from "the core belief that everybody has got a story that is worth telling". For some people that story might be their child taking their first steps, captured in a video that will be shared with only a few people. Or it might be a photojournalist taking images that are going to be shared with millions. "Our belief is that your level of technical understanding shouldn't get in the way of you being able to tell that story," he says. High-end cameras have often required their users to think about a whole host of questions before they even get to actually pressing the button to take a picture: "the temperature of light, the amount of light, the direction of light, how fast is the subject moving? What are the skin tones?" notes McCormack. "Every second that you spend thinking about that, and playing with your settings and things like that, are seconds that you are drawn out of the moment," he says. "And what we want to create is this very deep connection between the photographer, the videographer and the moment." He points to the action button on this year's Pro models, which can be programmed to launch the camera with a push. "It's all about being able to say all of this crazy complexity of photography, or videography – Apple's taken that, and understood that, and hidden that from you," he says. "You as a photographer, you get to concentrate on the thing that you want to say, and finding that decisive moment, finding that beautiful framing, that says the thing that you want to say. "But the motivation for all of this and using all of this crazy, great computational photography, computational videography, is that we don't want to distract you from telling the story that you want to tell." That has meant building the iPhone's camera in a way that the features "unfold", he says. "Out of the box, we are going to give you an amazing thing that is going to cover most of your moments, with lots of dynamic range, lots of resolution, zero shutter lag, so you can capture the moment. "But of course, there are folks who are going to look at this and say, you know, I've got a very specific and very prescriptive vision," he says. He points to a variety of new tools that are built into the phone, such as the ProRAW format, which makes huge files and is not especially useful to most – but can be key to someone who really wants to ensure they are able to process every detail of a photograph after it is taken. Those are hidden within settings, there for the people who need them but not troubling those who don't. Veron also notes that many of those extra features are enabled by "an amazing ecosystem of third party partners" who make apps that allow people to get features they are looking for. It is a reminder of just how much is going on as soon as someone takes a picture with the iPhone. First, light travels through one of Apple's three lenses and hits a 48 megapixel sensor – but that's just the beginning of a long process of computational photography that analyses and optimises that image. The picture that is taken is not just the one image, for example: it is actually made up of multiple exposures, with more or less light, that can then be merged into a picture with the full dynamic range. "This year for the first time, we merge them in a larger resolution," says McCormack. It takes one image in 12 megapixels, to give a fast shutter speed and plenty of light, by combining pixels together; then it grabs a 24-megapixel frame, which collects the detail. "Then we register those together and use a custom machine learning model to go and transfer the detail from the 48 over into what has now become a 24." That creates something like the negative in old camera terms, which the iPhone’s processor can then get to work on, using parts of its chip focused on machine learning. "We use the neural engine to go decompose that photograph, bit by bit." It will notice if people have different skin tones, and develop those parts of the image accordingly; hair, eyes, a moving background and more are all taken to pieces and optimised on their own. (The intensity of that process has occasionally led to questions over whether the phone is working too hard to make its images look good.) Then there's yet more work for the camera system. The iPhone uses tonemapping to ensure that images pop on the bright screens of modern iPhones, but also that they still look bright on a compressed image that might be sent around the internet; one of the many changes that smartphones have brought to photography is that, for the first time, the photos are mostly looked at on the same device they were taken with, but that they can also be sent and seen just about anywhere. If the image is taken using night mode, then there's even more work, with new tools that ensure that colours are more accurate. And that isn't even mentioning portrait mode, which when it registers that there is a person (or a pet) in the frame will gather the relevant depth information to ensure that the background can be manipulated later. That whole process – those five paragraphs, and thousands of calculations by the phone – happen within the tiniest moment after pressing the button to take the photo. The phone may look as if it is serenely offering up an image to its users, but it has been busily working away in the background to ensure the picture is as accurate and vibrant as possible. All that work done by the camera and the rest of the device depends on a variety of choices made not only by the iPhone but by Apple, which accounts for the look of the modern iPhone picture – Veron says that its aim in making those decisions is to make "beautiful, true-to-life memories in just one click". McCormack is clearly keenly aware of the responsibility of that task; his vision decides what the world's memories look like. "This is your device that you carry with you all time the time, and we want to be really, really thoughtful of that," he says. That responsibility carries into the design of the camera within the phone: rumours had suggested that this year's model would include a "periscope" design for the long zoom, bouncing the light through the length of the iPhone, but McCormack says that Apple went for the five-way prism to ensure that it could "both retain the industrial design that we want, to just make iPhone feel so good in your hand, but also be able to get that extra focal length". "It is just of one of those crazy things – only Apple is going to do something like that. And I'm really glad that that's the way we think about product." Read More Tim Cook says Vision Pro release is on track: ‘I watched Ted Lasso Season 3 on it’ Apple Store goes offline as Apple opens pre-orders for iPhone 15 Apple to update iPhone 12 after fears over radiation iPhone 12 is not emitting dangerous radiation, Apple says, amid fears of Europe ban France’s iPhone 12 ban could spread across Europe, regulators say Everything Apple killed off at iPhone 15 event
2023-09-18 22:27
You Might Like...
ESG Targets of Europe’s 20 Biggest Banks Slammed in New Report

Greece orders fresh evacuations as wildfires erupt on mainland

Macron Urges Investors to Boost Climate Funding: Paris Update

FC 24 Radioactive Player Chemistry Explained

Commerzbank receives crypto custody licence in Germany

Analog Devices' fourth-quarter forecasts disappoint as consumer demand weakens

How to watch the Berlin Marathon 2023 online for free

Scientists invent double-sided solar panel that generates vastly more electricity
