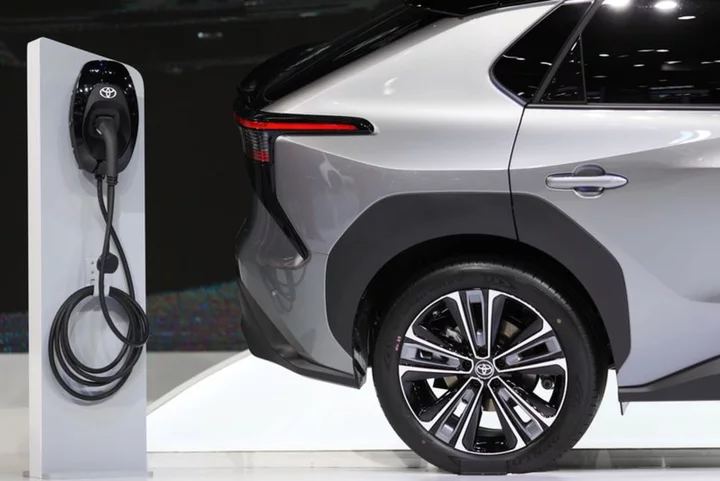

Toyota says to boost EV development and technology in China
TOKYO Toyota will strengthen its development of electric vehicle technology in China, the automaker said on Monday, as
2023-07-31 14:51
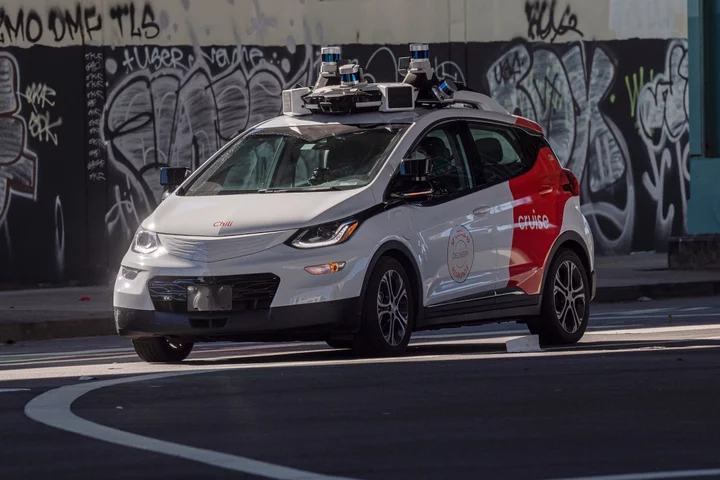

GM’s Cruise to Expand Robotaxi Service to Dallas and Houston
Cruise, the self-driving vehicle unit majority owned by General Motors Co., plans to expand its robotaxi service to
2023-05-11 00:55

Child influencers in Illinois can now sue their parents
Illinois is the first state in America to pass a law protecting child influencers and
2023-08-14 19:26
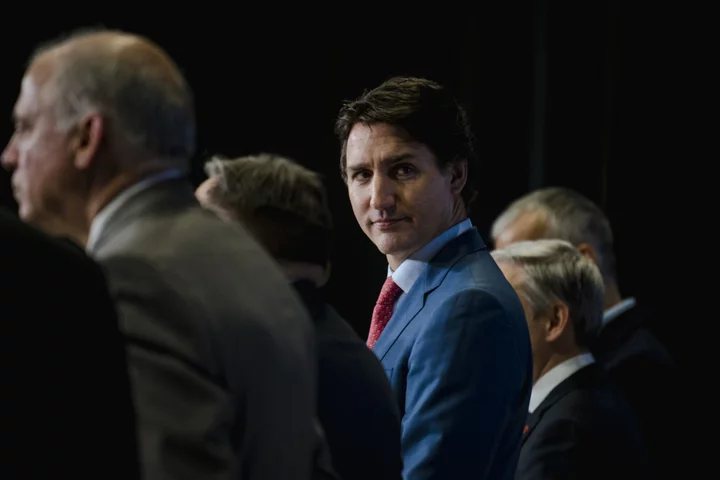

Trudeau Faces Calls to Exit With His Party Trailing in Polls
Sagging badly in opinion polls, with voters angry about housing and inflation, Justin Trudeau is facing calls to
2023-11-15 18:45
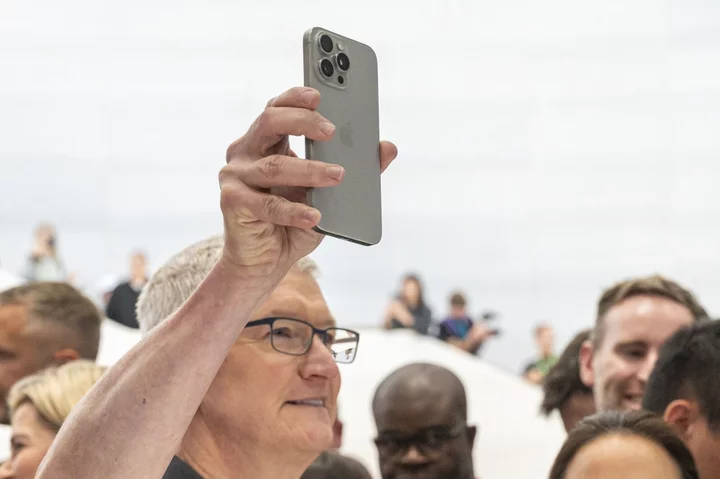

UK’s Apple Users Get a £100 Price Cut on New iPhone 15 Pro Model
Apple Inc.’s new iPhone 15 Pro will go on sale in the UK for about £100 ($125) cheaper
2023-09-13 16:21

Microsoft’s $69 Billion Activision Deal Wins EU Approval
Microsoft Corp.’s $69 billion takeover of Activision Blizzard Inc. won European Union approval, just weeks after the UK’s
2023-05-15 22:47
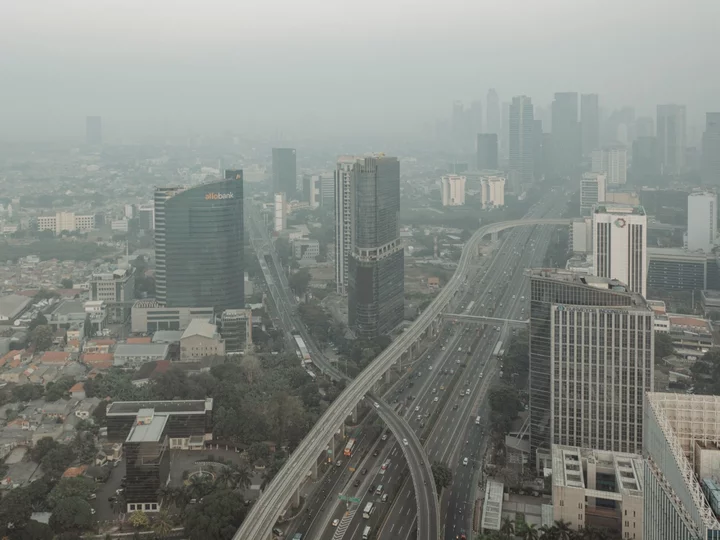

Jakarta Pollution Worst in World Amid Jumbled Policy Response
Jakarta has been blanketed in smog that has made its air quality the worst in the world as
2023-08-25 15:24

Bill Gates says AI risks are real but nothing we can't handle
Bill Gates sounds less worried than some other executives in Silicon Valley about the risks of artificial intelligence.
2023-07-13 00:29

Acxiom Names Adobe Veteran Judith Hammerman as Cloud Growth Leader
CONWAY, Ark.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 12, 2023--
2023-06-12 22:27
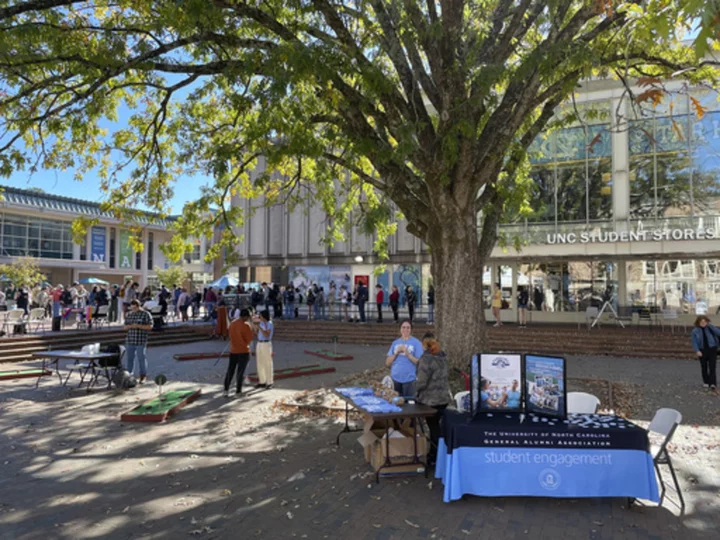

With affirmative action out, North Carolina's flagship school bars use of race, sex in admissions
The board of North Carolina’s flagship public university has voted to strictly bar the use of “race, sex, color or ethnicity” in admissions and hiring decisions following recent U.S. Supreme Court rulings striking down affirmative action in forming student bodies
2023-07-29 00:59

Uber Eats’ New AI Chatbot Will Offer Recommendations to Customers
An artificial intelligence chatbot under development at Uber Technologies Inc. will offer recommendations to food-delivery customers and help
2023-08-29 02:58

Alix Earle makes it to Forbes 30 under 30 list with her TikTok success and Bitcoin mining
Despite the male-dominated startup scene in Miami, Alix Earle has managed to secure a spot on the Forbes 30 Under 30 list through her notable achievements
2023-08-10 14:22
You Might Like...

Google announces a decade of Chromebook updates to help devices last longer

Predators Exploit AI Tools to Depict Abuse, Prompting Warnings
Battery breakthrough brings ‘unprecedented performance’ to next-gen cells
Family Dollar Prepares to Launch New Mobile App Experience

Nintendo Download: Wish Upon a Star Road

10 of the Most Valuable Cassette Tapes From the ‘80s and ‘90s

Is Alabama Barker OK? Travis Barker's daughter claps back at body-shamers, reveals she has an autoimmune disease

Wordle comes with ads now, unless you are a New York Times Games subscriber
