
Can You Earn Rewards in Fortnite Ranked?
Epic Games has revealed Fortnite Ranked, but will players be able to earn rewards and items in this new competitive mode?
2023-05-15 23:55

Temasek, Morgan Stanley Join $300 Million Australian Fund
Main Sequence, the venture capital firm founded by Australia’s national science agency, raised A$450 million ($305 million) from
2023-07-26 15:58

A Chatbot That Won't Take Bribes for Giving Advice Is a Hit in India
ChatGPT quickly found a home in the sophisticated echelons of investment banks and drug design firms. Now, the
2023-06-15 07:24
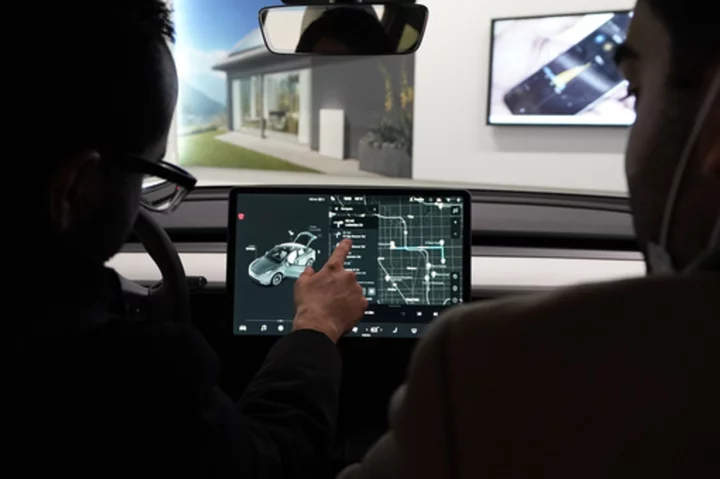

Tesla shouldn't call driving system Autopilot because humans are still in control, Buttigieg says
The top U.S. transportation official says Tesla shouldn’t call its partially automated driving system Autopilot because the cars can’t drive themselves
2023-05-11 23:20
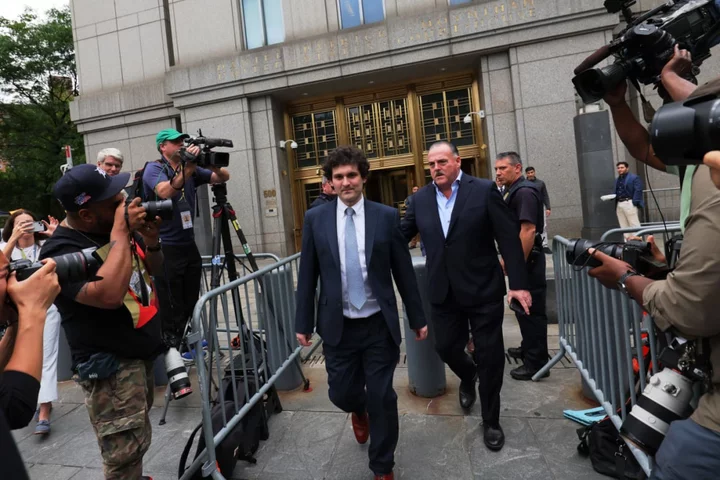

Sam Bankman-Fried’s Trial Is Is a Reminder for Crypto Traders to Be Wary
It's a reminder to investors how little recourse they have should the trading platforms they do business with go under.
2023-10-02 13:22
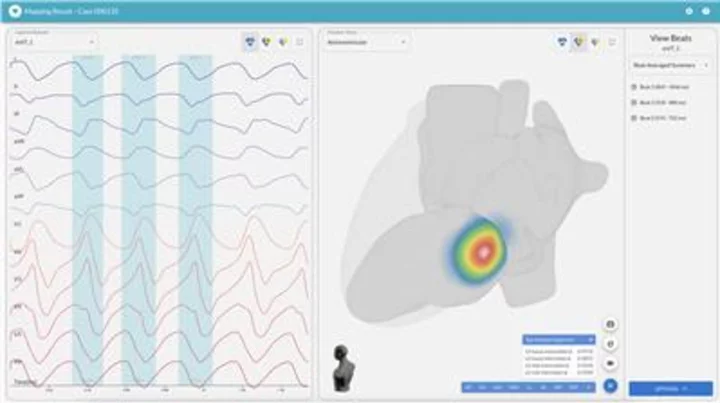
Vektor Medical Unveils Enhanced vMap Technology for Accurate, Non-invasive Mapping of Cardiac Arrhythmias
SAN DIEGO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 6, 2023--
2023-09-06 18:15

ClearOne Launches Powerful New Dante®-Compatible BMA 360D Beamforming Microphone Array Ceiling Tile at InfoComm 2023
SALT LAKE CITY--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 13, 2023--
2023-06-13 21:25

Apple's plan for climate-friendly watches: Clean energy in factories
By Stephen Nellis CUPERTINO, California (Reuters) -Apple on Tuesday said that three of its Apple Watch models will come in
2023-09-13 03:21
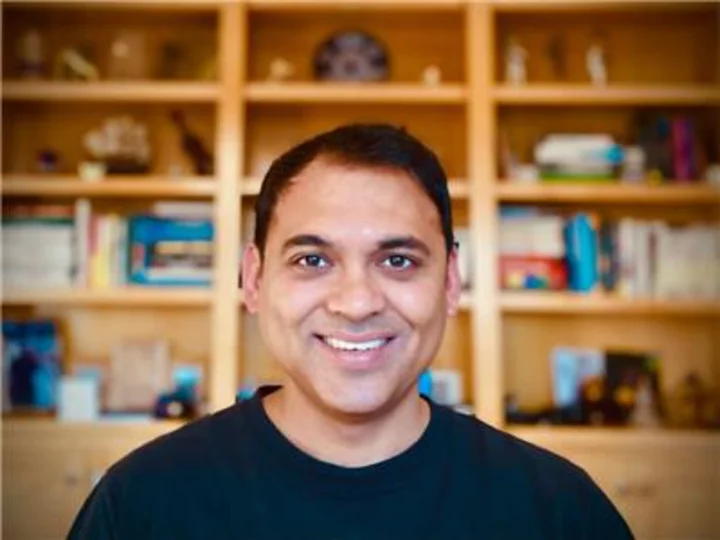

Komodo Health Appoints Vikas Mehta as Chief Financial Officer; Names Sarah Shin as Chief People Officer
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 5, 2023--
2023-06-05 20:27
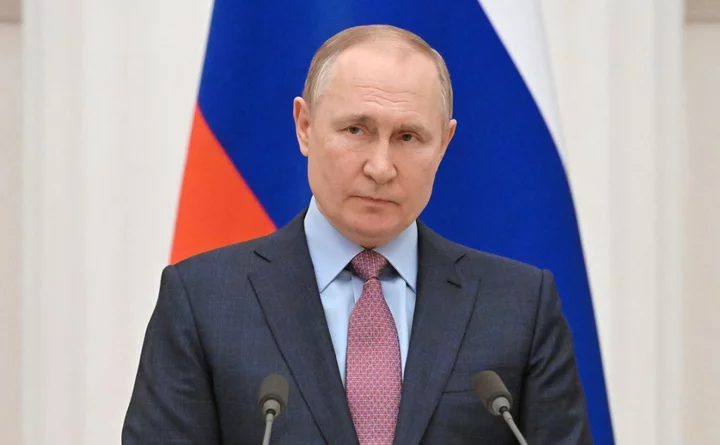

Putin unveils Russia’s new AI strategy to rival Western advances in artificial intelligence
Vladimir Putin has unveiled what he calls Russia’s new strategy to counter Western dominance of the field of artifical intelligence, claiming that new AI models “cancel Russian culture”. The president addressed an AI conference in Moscow on Friday where he said Russian investment in AI development was being increased across all sectors. Citing the example of Gazprom Neft, Mr Putin said one of Russia’s largest oil producers was using AI to slash the cost of oil well development and to address complicated logistics safety issues. “I hope we will be more active in this area. When I say ‘we,’ I am referring not only to the government but also to the regions and industries, and individual plants,” Mr Putin said. The Russian leader said the country would intensify its research into the domains of generative AI and large language models which currently lag behind the leading Western-developed tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard chatbots. Speaking about such AI models, he said their full potential had only started to emerge in the past year, while he criticsed “Western search engines” and generative AI models, calling them “very selective and biased”. “They do not take into account and sometimes simply ignore and cancel Russian culture. In simple terms, the machine is given some creative assignment and performs it using only the English language database,” he said. “Thus, the algorithm may tell the machine that Russia, our culture, science, music and literature simply do not exist. They are cancelled in the digital space, as it were,” the Russian president said at the conference. AI created according to “Western standards”, he said, may emerge as a “kind of xenophobe”, he said. “Our domestic models of artificial intelligence must reflect the entire wealth and diversity of world culture, the heritage, knowledge, and wisdom of all civilisations,” he said. English speaking countries currently dominate AI development, with Stanford’s Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) claiming the US and UK were further ahead in the technology than the rest of the world. The Russian president said that the “monopolistic dominance” of the technology was “unacceptable, dangerous and inadmissible”. “Our innovations should rest on our traditional values, the wealth and beauty of the Russian language and languages of other peoples in Russia,” Mr Putin added. To achieve such development, he called for the scaling up pf Russia’s supercomputing power and to improve its top-level AI education. Read More AI breakthrough could help us build solar panels out of ‘miracle material’ OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman ousted as CEO YouTube reveals bizarre AI music experiments AI-generated faces are starting to look more real than actual ones Breakthrough ‘safe’ liquid fuel cannot start accidental fires, scientists claim Meta sued over ‘open secret’ of ‘pursuing,’ signing up millions of underage users
2023-11-27 15:52
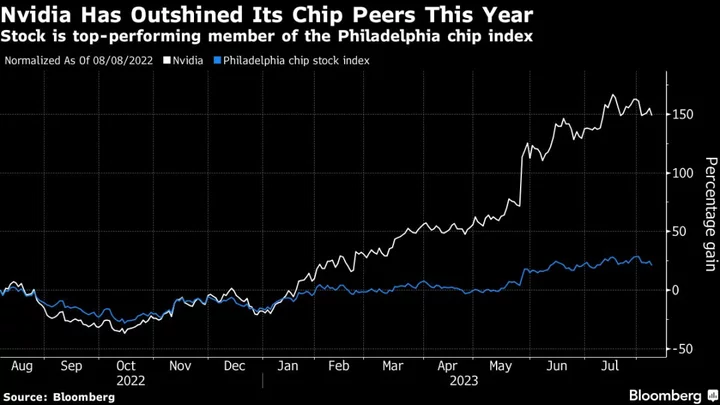
Nvidia Unveils Faster Chip Aimed at Cementing AI Dominance
Nvidia Corp. announced an updated AI processor that gives a jolt to the chip’s capacity and speed, seeking
2023-08-09 00:24

Biden Set to Tighten Fuel-Efficiency Standards for Automakers
The Biden administration is poised to issue a proposal as early as Friday ordering automakers to increase the
2023-07-28 07:25
You Might Like...

Biden administration announces clean hydrogen goal to slash planet-warming pollution by 10% by 2050

How to Change Fortnite Lobby Background

Amazon Alexa Voice Remote Pro Review
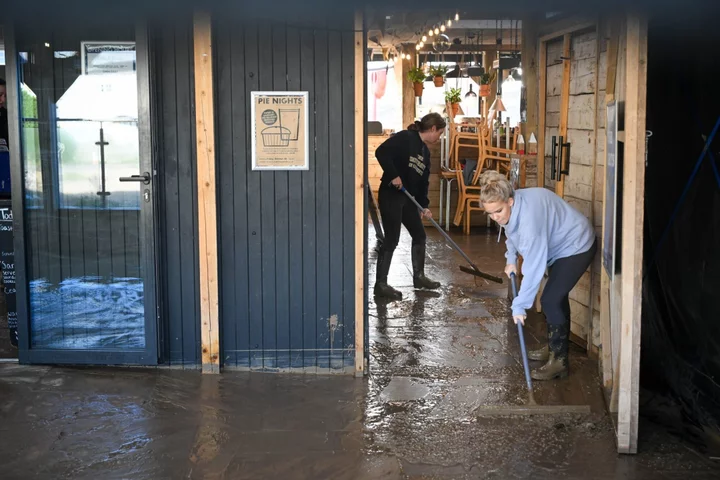

UK Failing to Meet Flood-Defense Goals as Storms Batter Homes
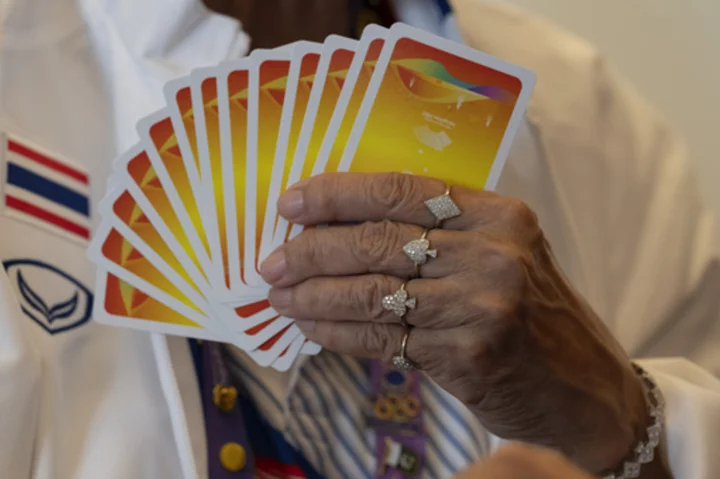

The centuries-old card game of bridge offers a sharp contrast to esports at the Asian Games

Meteor crashes through man's roof and he sells it for millions
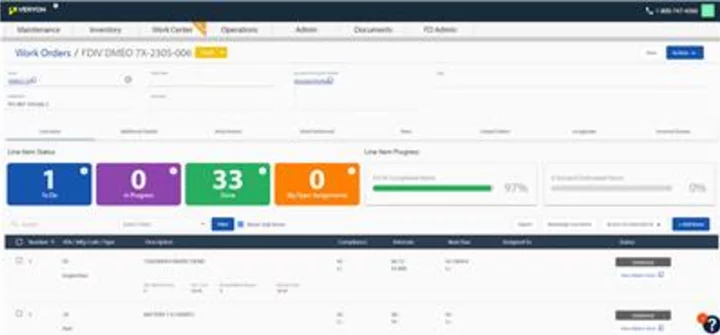
Veryon Expedites Aircraft Return-to-Service With Launch of Work Center
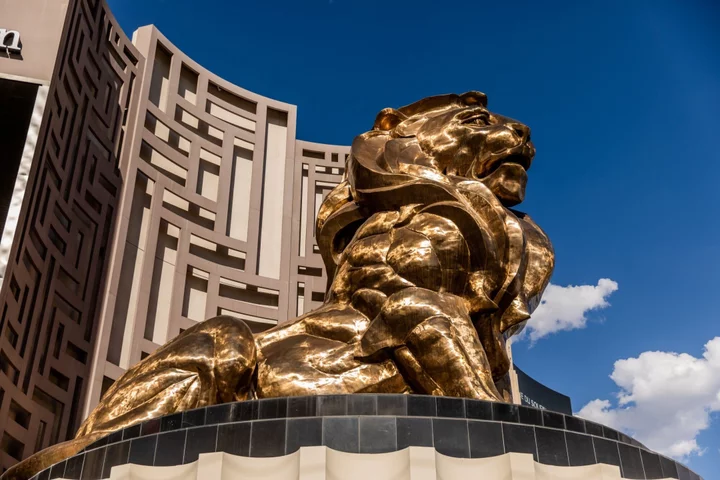

MGM Resorts’ Hack Fallout Includes Paper Vouchers, Cash Bar
