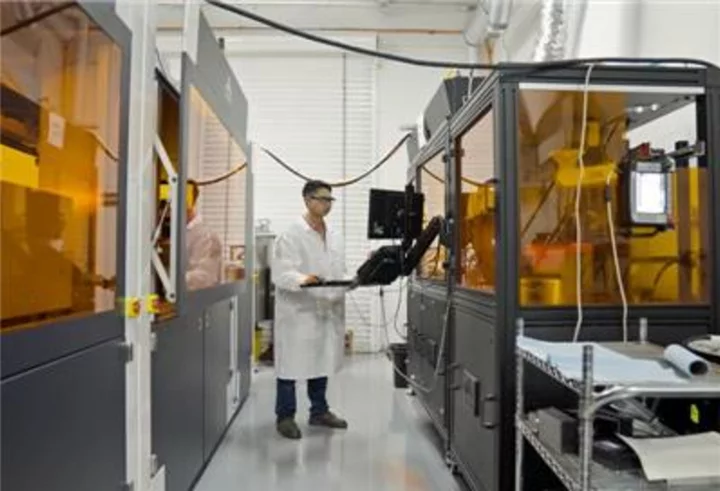

Intrepid Automation Secures Series A Fundraise to Accelerate Deployment Support Initiatives
SAN DIEGO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 30, 2023--
2023-05-31 03:47

YouTube unveils a slew of new AI-powered tools for creators
YouTube on Thursday unveiled a slew of new artificial intelligence-powered tools to help creators produce videos and reach a wider audience on the platform, as companies race to incorporate buzzy generative AI technology directly into their core products.
2023-09-22 05:18

Video Game Developer Behind Grand Theft Auto Predicts Strong Rebound
Take Two Interactive Software Inc., known for the Grand Theft Auto video-game franchise, soared in extended trading after
2023-05-18 05:53
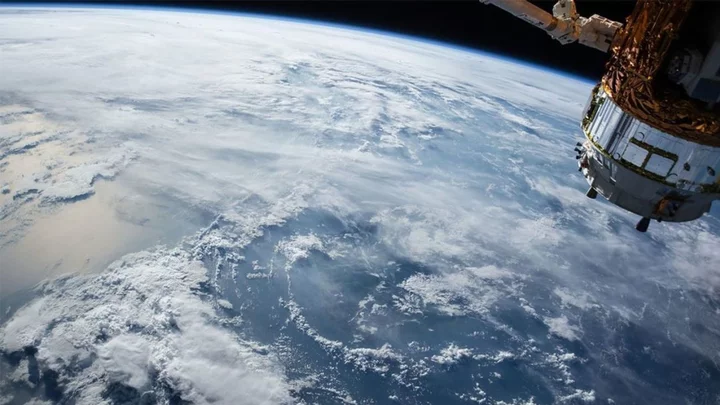

Two ancient humans become astronauts after being blasted into space
Space travel might be a relatively modern phenomenon, but a pair of ancient human ancestors are getting to experience it too – albeit two million years after their death. The remains of a hominin species called Australopithecus sediba which date back two million years have been blasted into space as part of the Virgin Galactic’s spaceship, VSS Unity. The remains of a 250,000-year-old species named Homo naledi was also included in the craft, which was sent into space on September 8. Bone fragments from the two ancient skeletons were taken into orbit by Professor Lee Berger. They reached a height of around 50,000 feet by the VMS Eve mothership before being separated from the VSS Unity spaceship. Berger said: “The journey of these fossils into space represents humankind’s appreciation of the contribution of all of humanity’s ancestors and our ancient relatives. “Without their invention of technologies such as fire and tools, and their contribution to the evolution of the contemporary human mind, such extraordinary endeavors as spaceflight would not have happened.” Berger’s son, Matthew Berger, who was a part of the discovery of the remains as a child went on to explain the significance of the unusual cargo, saying: “These fossils represent individuals who lived and died hundreds of thousands of years ago, yet were individuals who likely gazed up at the stars in wonder, much as we do,” “I imagine they never could have dreamed while alive of taking such an incredible journey as ambassadors of all of humankind’s ancestors.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-09-13 20:46

Perfect Corp. Announces Expanded Functionality of Revolutionary AI-Powered Live Skin Analysis Solution
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 5, 2023--
2023-09-05 19:22
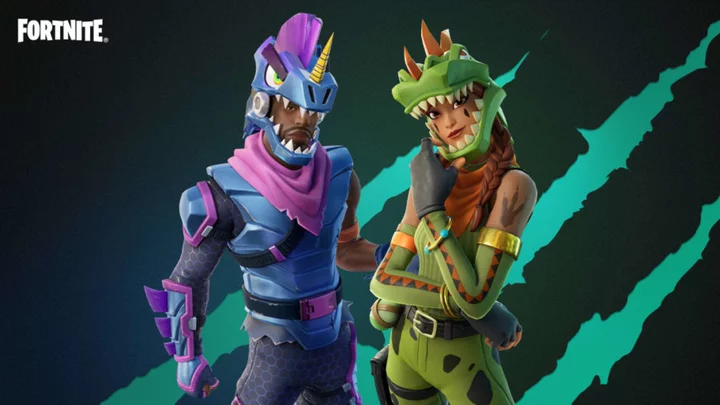

Here's All the Fortnite OG Bundles Coming to the Item Shop in November
Here's the full schedule of all the Fortnite OG Bundles coming to the Item Shop in November for fans to purchase, including Customize Your Hero skins.
2023-11-09 03:21
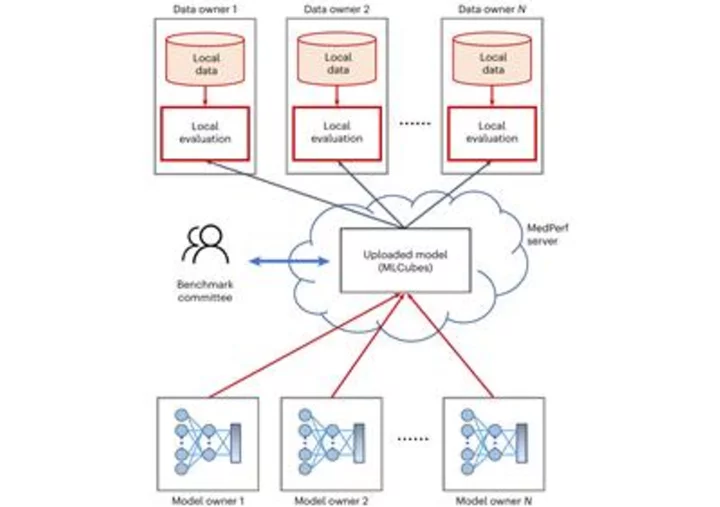
Announcing MedPerf Open Benchmarking Platform for Medical AI
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 17, 2023--
2023-07-17 23:24
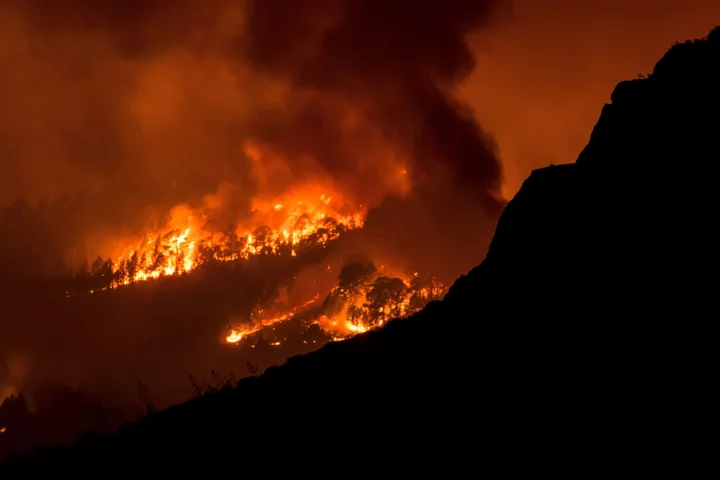

Heat Stifles Parts of Europe as Tenerife Fires Force Evacuations
Temperatures are rising across the continent as wildfires destroy parts of a Spanish island and Germany issued red
2023-08-17 18:18

TikTok to launch e-commerce platform in US to sell China-made goods - WSJ
(Corrects to add source in headline) (Reuters) -TikTok is planning to launch in early August an e-commerce platform to sell
2023-07-25 20:47
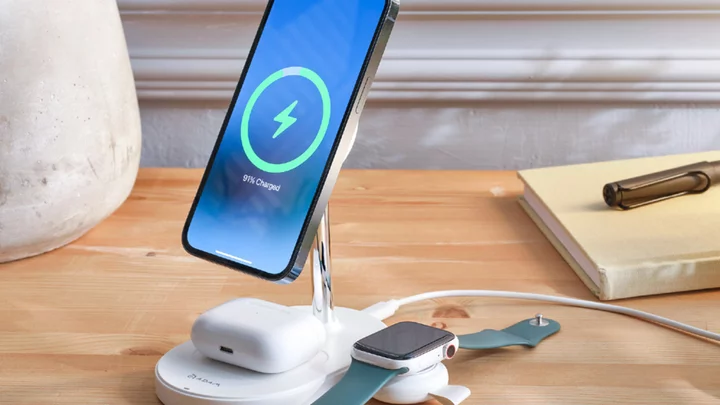

Power up your iPhone, AirPods, and Apple Watch with this $148 wireless charging station
TL;DR: As of June 7, the OMNIA M+ MagSafe Wireless Charging Station and A1 Apple
2023-06-07 17:46

15 of the best Photoshop courses you can take online for free
TL;DR: Find a wide range of free Photoshop courses on Udemy. Whether you're a professional
2023-07-08 12:29

Microsoft Closed Its Activision Deal. These Stocks Stand to Gain.
Microsoft's success could embolden other big technology companies seeking a better foothold in videogames.
2023-10-16 05:26
You Might Like...

7 of the best Midjourney courses you can take online for free

NTT Succeeds at Frequency Stabilization of an Electro-Optic Modulation-Based Optical Frequency Comb

Bitay Announces Strategic Expansion into the UAE's Burgeoning Crypto Market

Why Amazon's Prime Day is in July
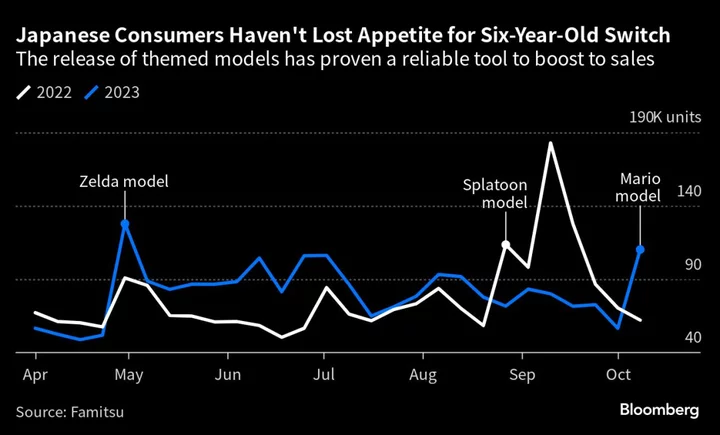
Mario-Themed Switch Console Proves a Hit for Nintendo in Japan
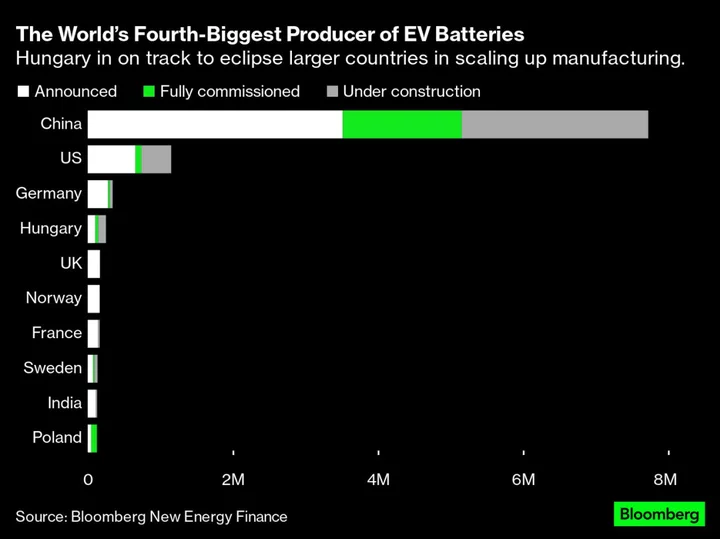
The Mission to Create Europe’s Battery Hub, Whatever the Cost

'Game of Thrones' author, other writers sue ChatGPT creator over copyrights

VARK Inc. Raises Approximately One Billion Yen in the First Close of Series C
