
Google I/O 2023 live: Major AI news expected alongside new Pixel devices
Google is set to unveil its latest artificial intelligence offerings at its annual developers conference on Wednesday, alongside new products ranging from Pixel phones to the Android 14 operating system. Google I/O 2023 will offer Alphabet the chance to show what its massive investments into AI have delivered, as it seeks to take on OpenAI’s hugely popular ChatGPT chatbot. Integration of its Bard AI in to its Maps, Gmail and search is expected, while various leaks have hinted that the company will also launch a large language model (LLM) called PaLM 2, capable of operating in more than 100 languages. This AI tool is rumoured to be able to pass exams in everything from computer coding and mathematics, to creative writing and critical thinking. A live stream of the keynote will be available when it begins at 10am local time (6pm BST), which you can watch right here. Until then, you can follow all the latest news, updates and analysis in our build-up coverage below.
2023-05-10 18:17
Hydrafacial Debuts Custom Syndeo Device on Dior Spa Cruise 2023
LONG BEACH, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 17, 2023--
2023-07-17 20:19

Nvidia, India's Reliance strike AI partnership for apps, language models
By Munsif Vengattil and Dhwani Pandya BENGALURU (Reuters) -U.S. chip firm Nvidia and telecom-to-retail giant Reliance on Friday announced an
2023-09-08 20:20
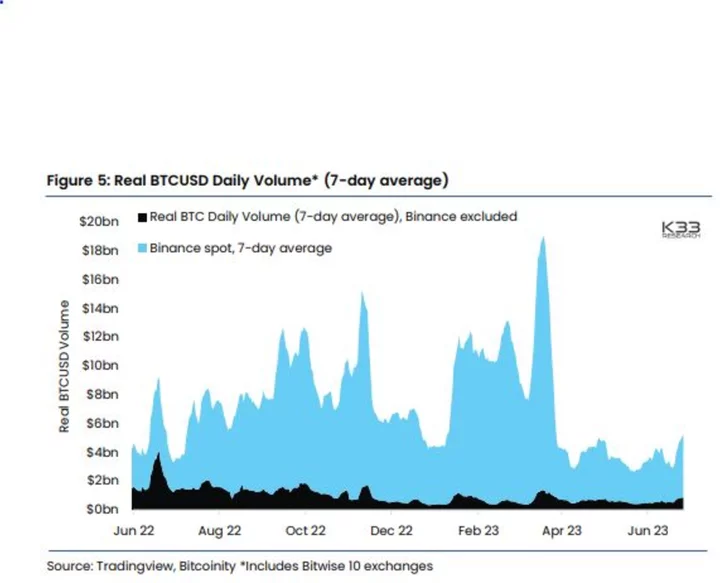
Bitcoin Prices Settle Into Narrow Range as ETF-Inspired Euphoria Dissipates
Bitcoin has quickly settled into a narrow trading range after reaching a fresh one-year high, leaving reinvigorated enthusiasts
2023-06-30 02:47

What East Coast Cities Can Learn About Wildfire Policies From the West
Hazardous smoke from wildfires has become a near-annual occurrence on the West Coast since 2017. But the hazy
2023-06-10 00:25
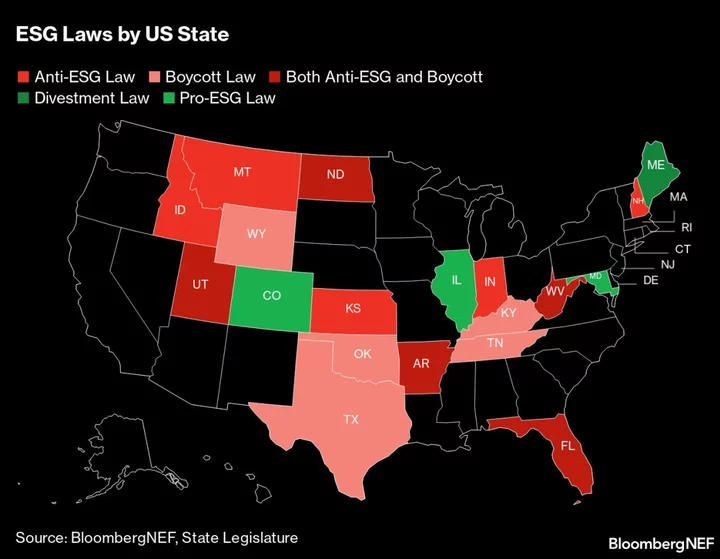
‘ESG’ Is Too Important to Ax, Investors Say
As Republican legislators in the US try to wipe ESG off the map, most global investors and executives
2023-11-08 09:16
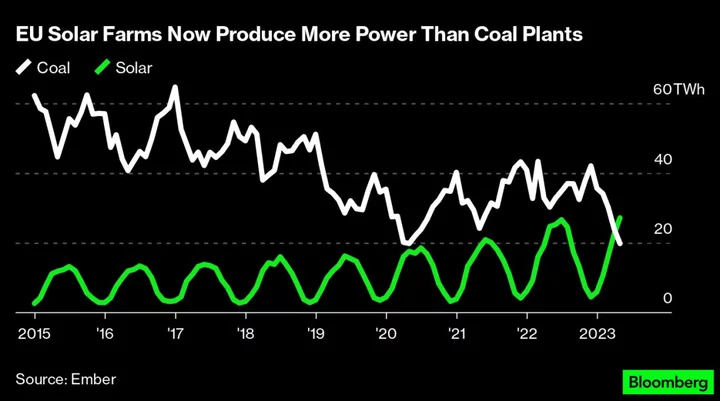
Solar Beats Coal in Europe for First Time - But There’s a Glitch
The European Union’s transition to clean energy marked a milestone in May, when solar panels generated more electricity
2023-06-03 14:18
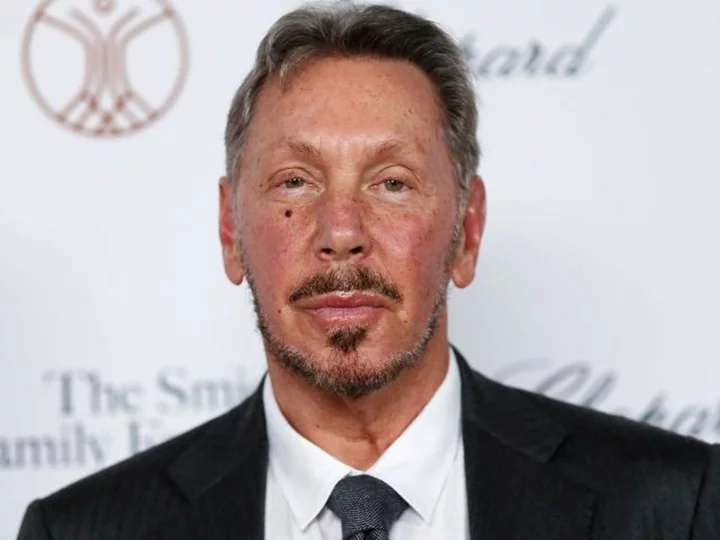

Larry Ellison edges past Bill Gates as world's fourth-richest person, Bloomberg says
Oracle founder Larry Ellison is reaping the benefits of artificial intelligence popularity, edging past Microsoft founder Bill Gates to land the number four spot on the Bloomberg Billionaires Index on Monday, according to Bloomberg.
2023-06-13 07:23

Save 37% on NordPass Premium with this exclusive deal
TL;DR: NordPass Premium is a powerful password manager developed by the cybersecurity experts behind NordVPN.
2023-06-21 12:21

Google courts businesses with ramped up cloud AI
Google on Tuesday said it was weaving artificial intelligence (AI) deeper into its cloud offerings as it vies for the business of firms keen...
2023-08-29 22:45
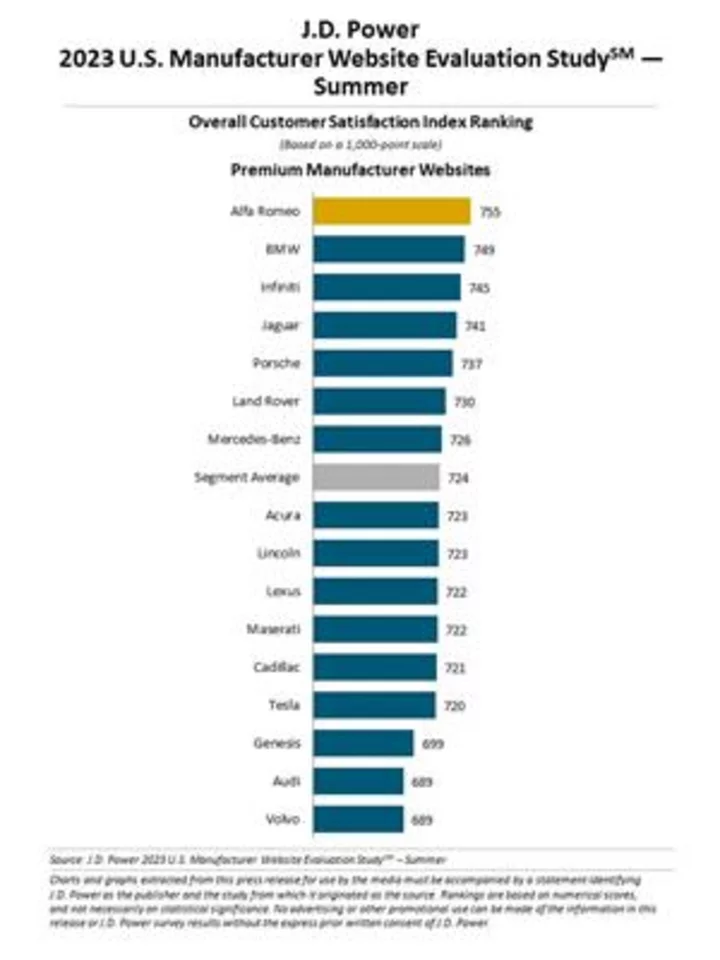
Satisfaction with Websites is Volatile but Automotive Manufacturer Websites Shine, J.D. Power Finds
TROY, Mich.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 18, 2023--
2023-07-18 20:28

Deep dive into Meta's algorithms shows that America's political polarization has no easy fix
A team of some of the world's leading social media researchers has published four studies looking at the relationship between the algorithms used by Facebook and Instagram and America's widening political divide
2023-07-28 02:17
You Might Like...

Google Calendar Can Now Tell Coworkers the Exact Times You'll Be in the Office

Women Are Leading the Fight to Stop Climate Change

The Google Pixel 7a and Pixel Fold Land at the Nation’s Most Awarded 5G Network

Stop the Madness: How to Block Spam Calls and Robocalls

COP28 Chief Al Jaber Says Fossil Fuel Decline Inevitable

Who is Adam Peaty? Gordon Ramsay's daughter Holly and 'AGT' star make their relationship official
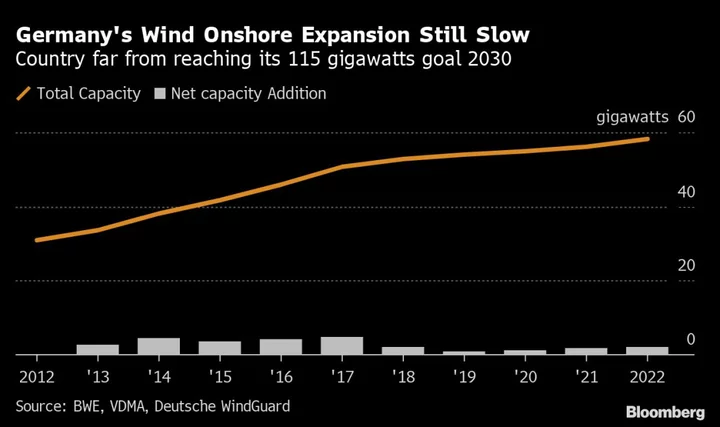
Aging Autobahn Thwarts Germany’s Plan to Erect Massive Windmills

Facing $1.5B deficit, California State University to hike tuition 6% annually for next 5 years
