
DoorDash rightfully bothers users who don't tip
They might as well call this feature the "Jerk Alert." To be more specific, DoorDash
2023-08-14 23:57

The TCL RayNeo X2 is the all-in-one smart assistant
These glasses are the first in the world of Augmented Reality. The TCL RayNeo X2
2023-08-24 04:20

Australian telco Optus tells lawmakers it had no plan to address total outage
By Byron Kaye SYDNEY Australia's second-largest telco, Optus, had no crisis plan when a network-wide outage left nearly
2023-11-17 10:24

Fortnite Chapter 4 Season 4 Battle Pass: What We Know So Far
The Fortnite Chapter 4 Season 4 Battle Pass is set to feature heist-inspired skins and cosmetics, along with a secret skin, that will be released on Friday, Aug. 25.
2023-08-22 01:58

AI Can Help Economies Thrive. Don’t Let Geopolitics Undermine It.
The open global economy is increasingly at risk, especially when it comes to data, writes David Schwimmer in a guest commentary.
2023-10-19 14:24

Alpha and Omega Semiconductor Introduces MRigidCSP™ Package Technology Strengthening its Battery Management MOSFETs
SUNNYVALE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 29, 2023--
2023-08-29 20:28

Scientists cook ‘alien haze’ that could help us find extraterrestrial life
Scientists have cooked up the "alien haze" of distant planets, in an effort to help with the search for alien life. The haze is a simulation of the hazy skies that appear on water-rich exoplanets, or worlds outside of our solar system. That haziness can get in the way of observations of those planets, making it difficult to understand what is happening there. Haze can also affect conditions on the planet themselves. If the atmosphere has hazes or other particles then it can drastically change the temperature, amount of light an other factors – some of which might be make or break for alien life there. Scientists hope the homemade haze will let them better understand the atmospheres of other planets, and model how the planets themselves form and grow. They could allow us to better understand how the have distorts our picture of those planets – distortions that could give us the wrong understanding of the makeup of their atmospheres. Getting that wrong could mean potentially missing habitable worlds, for instance. The observations are used to come up with the estimates about the temperature and atmospheric conditions that are then used to determine whether a planet might be able to host alien life. “The big picture is whether there is life outside the solar system, but trying to answer that kind of question requires really detailed modeling of all different types, specifically in planets with lots of water,” said co-author Sarah Hörst, from Johns Hopkins University. “This has been a huge challenge because we just don't have the lab work to do that, so we are trying to use these new lab techniques to get more out of the data that we’re taking in with all these big fancy telescopes.” The team cooked up the haze using a custom-designed chamber in Hörst’s lab. The haze they made is formed out solid particles, suspended in gas, which changes how light interacts with the gas itself. To test the hazes they made, scientists shot ultraviolet light through them, measuring how much they absorbed and reflected. They found that hate haze matched the chemical signatures of a well-studied exoplanet. Scientists hope to develop yet more hazes, with different gas mixtures, that will let them better understand different atmospheres. The work is described in a new paper, 'Optical properties of organic haze analogues in water-rich exoplanet atmospheres observable with JWST', published in the journal Nature Astronomy. Read More SpaceX rockets are punching holes in atmosphere, causing blood-red ‘auroras’ Chinese rocket that slammed onto Moon may have carried mysterious undisclosed payload Nasa’s ‘Message in a Bottle’ will send your name into space
2023-11-29 21:52

Semtech and Oxit Team Up to Simplify IoT Device Connectivity with Seamless Integration to AWS IoT Core for Amazon Sidewalk and AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN®
CAMARILLO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 30, 2023--
2023-08-30 23:17

Top 7 Fortnite streamers that every gamer should follow in May 2023
Get to know about the top Fortnite streamers to follow in May!
2023-05-19 21:25

Elon Musk's 25-year obsession with 'X' explains what he did to Twitter
Elon Musk put so much of his fortune into X.com, he had a mere $4
2023-07-29 04:19
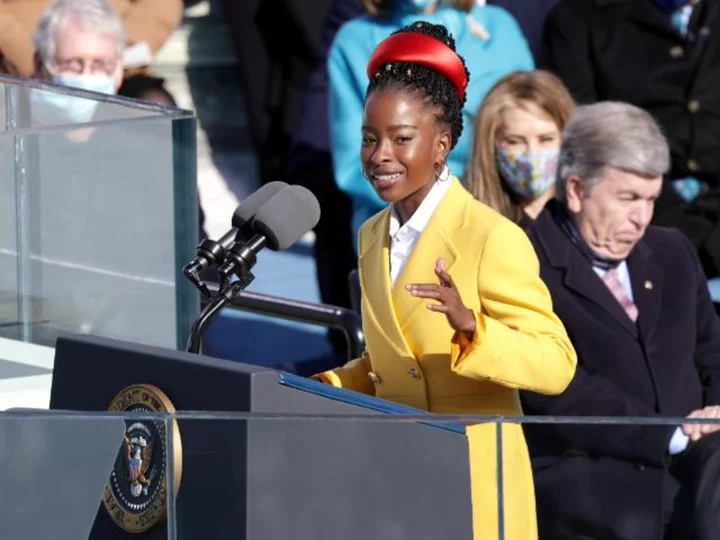

Miami-Dade school moves Biden inaugural poem out of elementary section of library after complaint
"The Hill We Climb," the poem written by Amanda Gorman for President Joe Biden's inauguration, was moved out of the elementary section of one Miami-Dade County public school, the district confirmed Tuesday. It remains available to older children.
2023-05-24 11:56
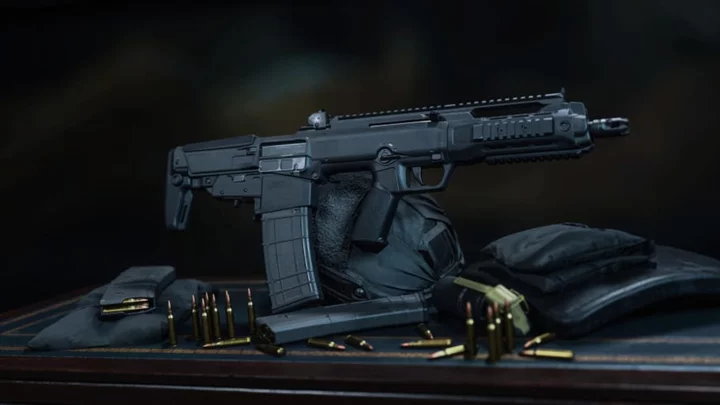

Warzone Forgotten AR Provides "Phenomenal" Sniper Support
The forgotten Tempus Razorback offers phenomenal sniper support in Warzone Season 5 Reloaded. Check out the best Tempus Razorback loadout.
2023-09-19 01:59
You Might Like...

Warzone 2 Ranked Play: Full List of Rewards

Is xQc getting banned from Kick just days after joining? Internet says 'imagine paying $100M to this fool'
Relax Fund Portfolio Manager, AI Isn’t Taking Your Job—Yet

Microsoft, Google strategy to test AI search ads irks some brands

Meta may allow Facebook, Instagram users in EU to pay to avoid ads - NYT
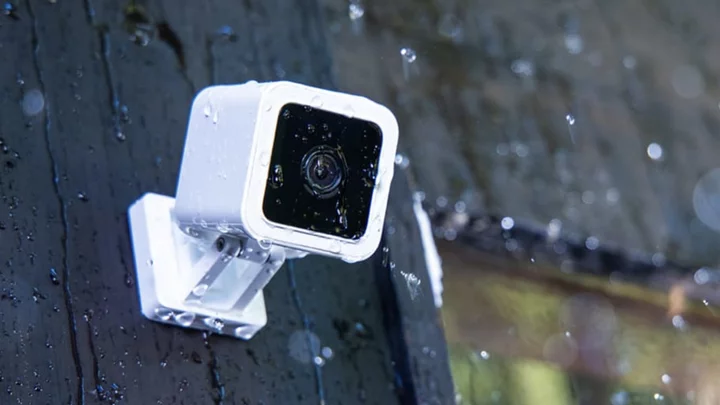

This Security Camera Is Great for Outdoor Areas and Costs Just $33
Ayar Labs Adds $25 Million in Expansion of Its $130 Million Series C

FBI disrupts Russian hacking tool used to steal information from foreign governments
