
SoftBank’s Arm Indicated to Open Higher in New York Debut
Arm Holdings Plc is indicated to open higher at $57 a share in its much-anticipated trading debut in
2023-09-15 00:26

Apex Legends Season 19 Ranked Changes Explained
Apex Legends Season 19 Ranked changes are set to include no more premade restrictions, more bonuses to get players up to their skill levels quicker and more.
2023-10-19 02:53
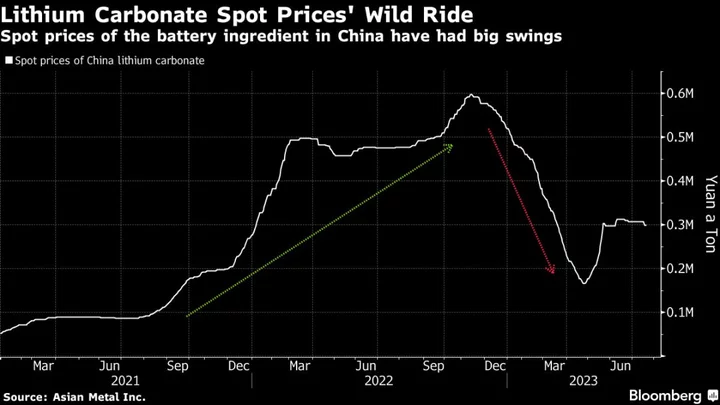
China’s First-Ever Lithium Futures Tumble on Trading Debut
China’s first-ever futures for lithium — an essential ingredient for electric vehicle batteries — got off to a
2023-07-21 12:50

Elon Musk loses bid to modify, throw out agreement with SEC over tweets
NEW YORK (Reuters) -A federal appeals court on Monday rejected Elon Musk's bid to modify or end his 2018 agreement
2023-05-15 22:19
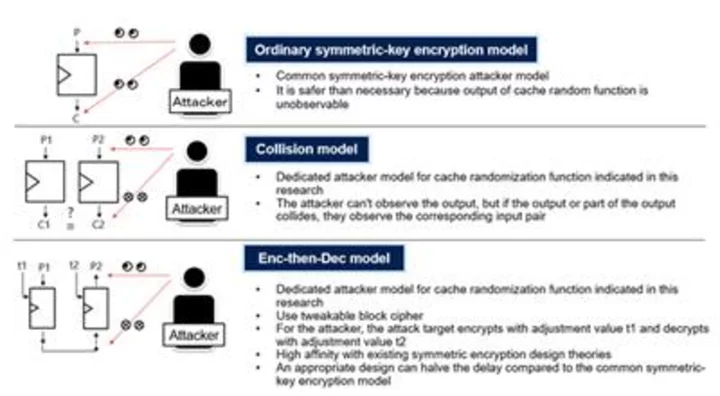
Development of Cache Random Function to Enable Fast and Secure Data Access Between CPU Memories
TOKYO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 16, 2023--
2023-08-16 20:27

AP, other news organizations develop standards for use of artificial intelligence in newsrooms
The Associated Press has issued guidelines for its journalists on use of artificial intelligence, saying the tool cannot be used to create publishable content and images for the news service
2023-08-17 04:48
Amazon invests $4 billion in Anthropic AI in exchange for minority stake and further AWS integration
Amazon said on Monday that it's investing $4 billion into the artificial intelligence company Anthropic in exchange for partial ownership and Anthropic's greater use of Amazon Web Services (AWS), the e-commerce giant's cloud computing platform.
2023-09-25 21:23

Who is Ludwig dating? 3 unknown facts about exclusive couple
Ludwig and QTCinderella are considered a power couple in the streaming community
2023-06-10 16:57

Brenmiller Signs MoU with India’s Largest Solar Panel Manufacturer Waaree Energies to Deploy Thermal Energy Storage Projects in India
ROSH HA’AYIN, Israel & MUMBAI, India--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 26, 2023--
2023-07-26 22:46

Caroline Ellison faces cross-examination at Sam Bankman-Fried's trial
By Jody Godoy NEW YORK (Reuters) -Sam Bankman-Fried's confidant Caroline Ellison took the stand again at the FTX founder's trial
2023-10-12 21:59

Stop Trackers Dead: The Best Private Browsers for 2023
Online privacy is a major concern for everyone, and by far the biggest personal privacy
2023-08-16 19:16
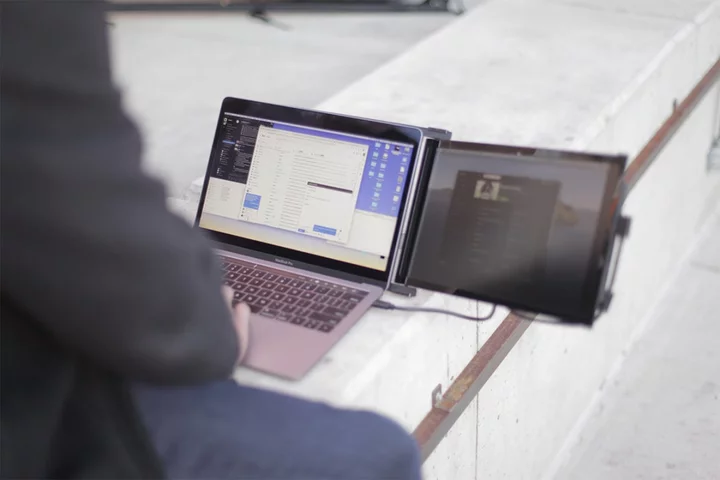

Get a portable second monitor for your laptop for $250
TL;DR: As of August 4, you can get the Mobile Pixels DUEX Plus: Portable Dual-Screen
2023-08-04 17:58
You Might Like...

Save 54% on a lifetime of language lessons from Rosetta Stone

Police to trial use of drones as first responders to emergencies
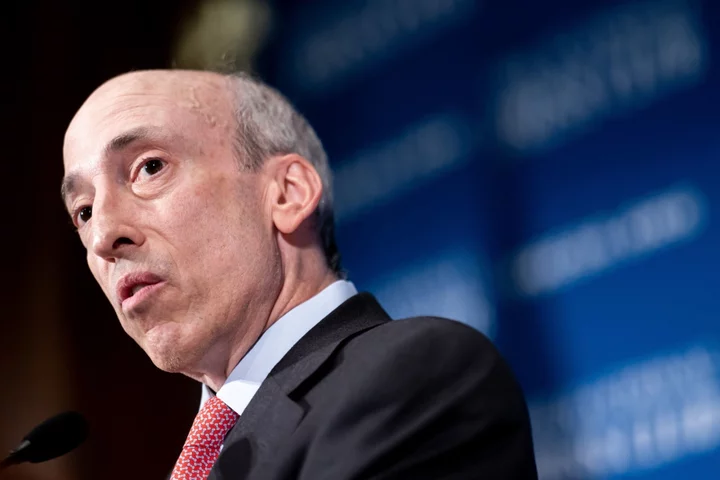

Wall Street’s Use of AI and Data Analytics Faces New SEC Rules
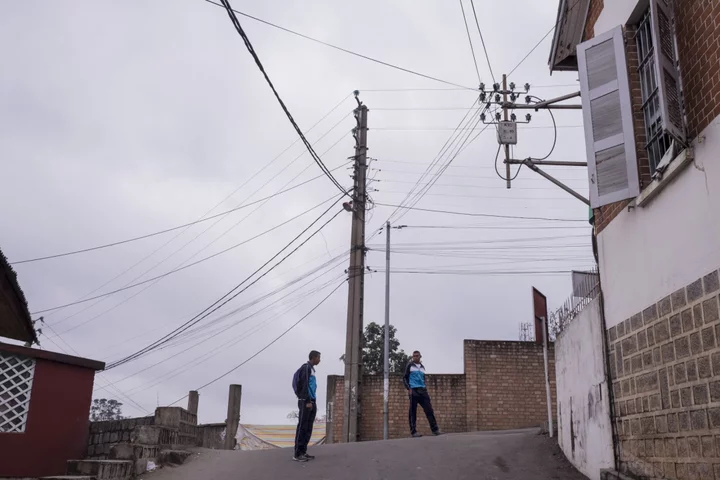

Hydro Venture Plans to Boost Madagascar Power Generation by 50%
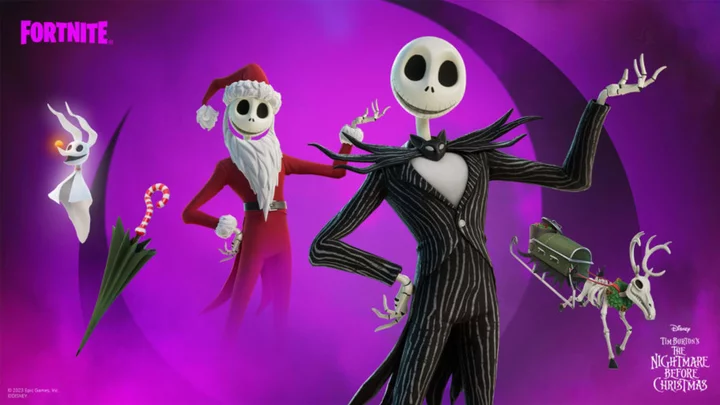

All Fortnitemares 2023 Skins: Michael Myers, Jack Skellington, Alan Wake
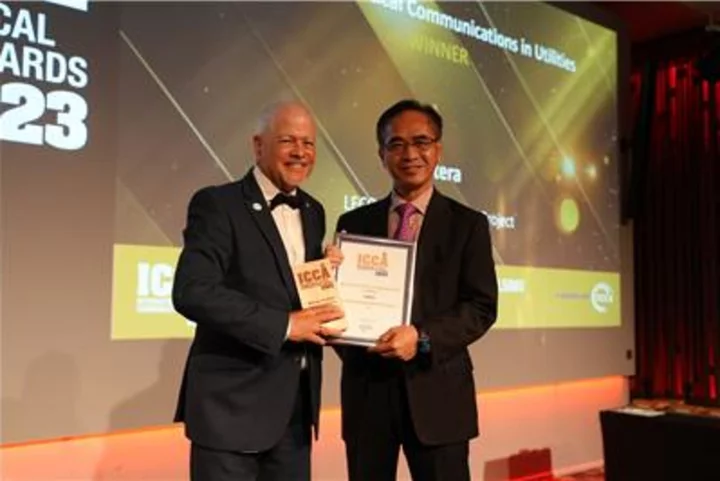

Hytera Mission-critical Push-to-talk Solution Wins Flagship Industry Award
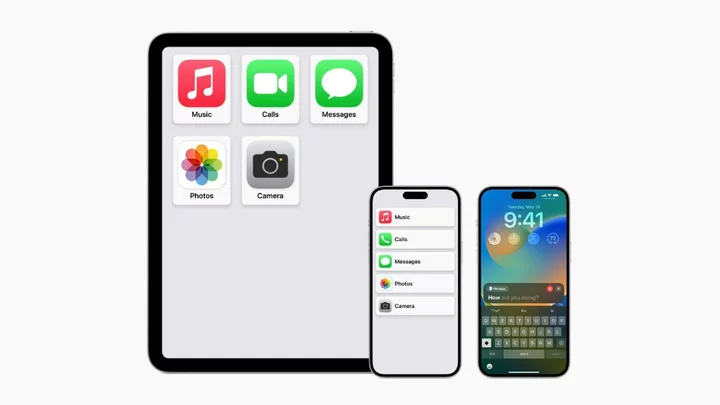
Apple previews new accessibility tools, including Live Speech and Assistive Access

Amazon, Shopify Strike Deal to Open Amazon Logistics to Sellers
