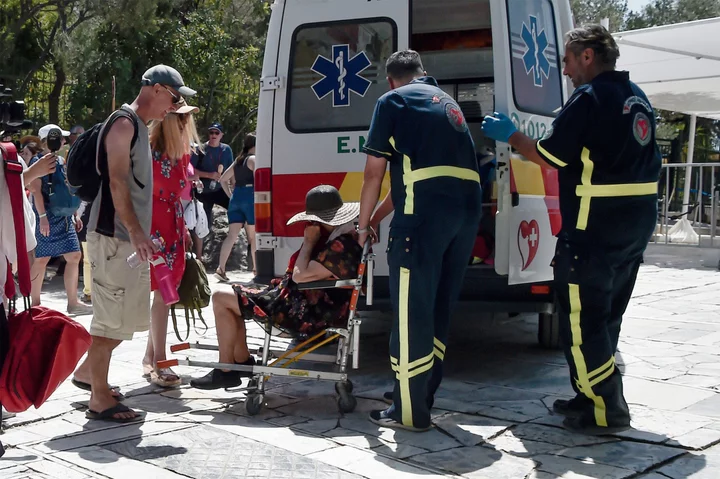

Extreme Heat, Weather Conditions Attributed to Stagnant Jet Stream
It’s no coincidence that extreme heat is engulfing huge swaths of Asia, Europe and North America all at
2023-07-21 07:23
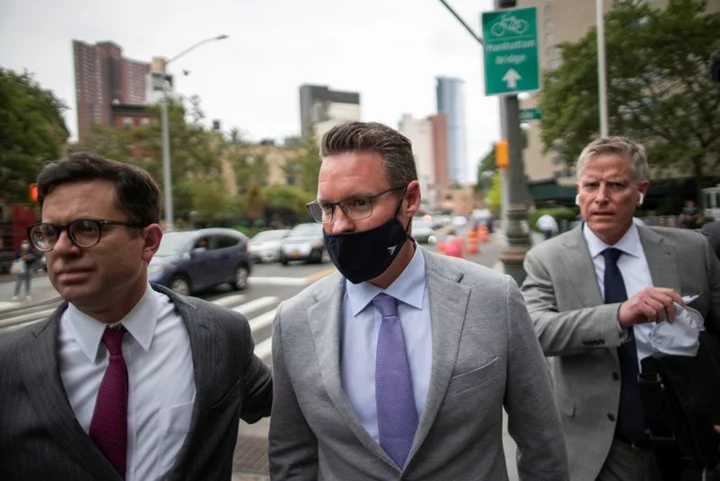

US judge rejects Nikola founder's juror bias claim
By Jody Godoy Nikola founder Trevor Milton lost his bid for a new trial on charges of defrauding
2023-08-31 02:27
Study finds ‘deepfakes’ from Ukraine war undermining trust in conflict footage
A first ever study of wartime “deepfake” videos has found the fake content undermined viewers’ trust in conflict footage to the point they became critical of all footage coming from warzones. The study, from researchers at University College Cork (UCC), is also the first of its kind to find evidence of online conspiracy theories which incorporate deepfakes. Deepfakes are artificially manipulated audio-visual material. Most deepfake videos involve the production of a fake “face” constructed by Artificial Intelligence, that is merged with an authentic video, in order to create a video of an event that never really took place. Although fake, they can look convincing and are often produced to imitate or mimic an individual. The study, titled A new type of weapon in the propaganda war, analysed close to 5,000 tweets on X (formerly Twitter) in the first seven months of 2022 to explore how people react to deepfake content online. The Russia-Ukraine war presented as the first real-life example of deepfakes being used in warfare. The researchers highlight examples of deepfake videos during this war including the use of video game footage as evidence of the urban myth fighter pilot “The Ghost of Kyiv”, and a deepfake of Russian president Vladimir Putin, showing the Russian president announcing peace with Ukraine. The study found deepfakes often undermined users’ trust in the footage they were receiving from the conflict to the point where they lost trust in any footage viewed. As well as the threat coming from the fake content itself, researchers found genuine media contact was being labelled as deepfakes. The study showed that the lack of social media literacy led to significant misunderstandings of what constitutes a deepfake, however, the study also demonstrated that efforts to raise awareness around deepfakes may undermine trust in legitimate videos. Therefore, the study asserts, news media and governmental agencies need to weigh the benefits of educational deepfakes and pre-bunking against the risks of undermining truth. John Twomey, UCC researcher, said much of the misinformation analysed in the study “surprisingly came from the labelling of real media as deepfakes”. “Novel findings about deepfake scepticism also emerged, including a connection between deepfakes fuelling conspiratorial beliefs and unhealthy scepticism,” he said. “The evidence in this study shows that efforts to raise awareness around deepfakes may undermine our trust in legitimate videos. “With the prevalence of deepfakes online, this will cause increasing challenges for news media companies who should be careful in how they label suspected deepfakes in case they cause suspicion around real media.” Mr Twomey added: “News coverage of deepfakes needs to focus on educating people on what deepfakes are, what their potential is, and both what their current capabilities are and how they will evolve in the coming years”. Dr Conor Linehan, from UCC’s School of Applied Psychology, said researchers “have long feared that deepfakes have the potential to undermine truth”. “Deepfake videos could undermine what we know to be true when fake videos are believed to be authentic and vice versa,” he said. This study is part of broader work by UCC’s School of Applied Psychology examining the psychological impact of deepfakes. Read More More than 500 potential cyber attacks logged every second, BT says AI being used to create child abuse imagery, watchdog warns ChatGPT and other chatbots ‘can be tricked into making code for cyber attacks’ Tinder adds Matchmaker feature to let friends recommend potential dates Google and Meta withdraw from upcoming Web Summit ‘Game-changing’ facial recognition technology catches prolific shoplifters
2023-10-26 02:52

Make your home the game day hub with Sling TV
We all have different versions of game day, whether it's cheering your team on to
2023-09-20 05:58

Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 3 Logo Leaked
The Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 3 logo has been leaked on social media confirming what's long been rumored about Call of Duty 2023.
2023-07-25 01:49

Consumption soft even amid deep discounts during major China shopping festival, analysts say
Chinese consumers have been snapping up billions worth of items in China’s first major online shopping festival after emerging from the pandemic as merchants slash prices, but analysts say that consumer confidence still remains weak as China re-emerges from the pandemic
2023-06-19 02:53
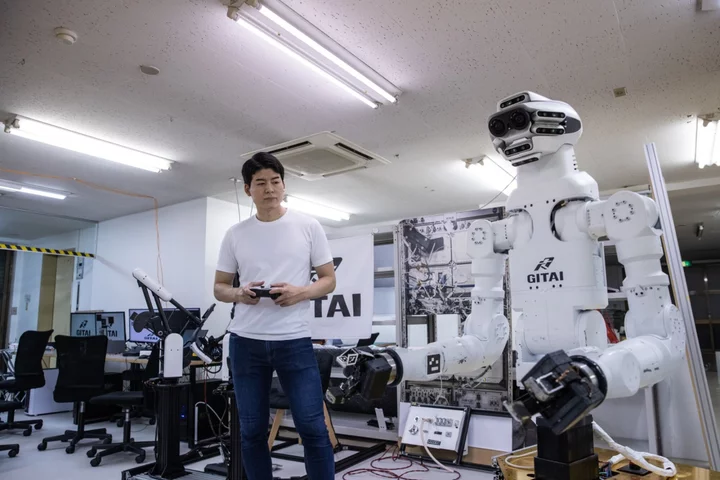

Japan Startup Raises $30 Million to Build Space Robot Workforce
The Japanese startup Gitai, fresh off raising a new round of funding, is expanding in the US as
2023-05-29 10:27

In transition from HBO Max to Max, writer and director credits got lost
The streaming service Max may only be hours into its rollout, but it’s already under fire by Hollywood’s top guilds for the way it credits writers and directors
2023-05-25 01:57
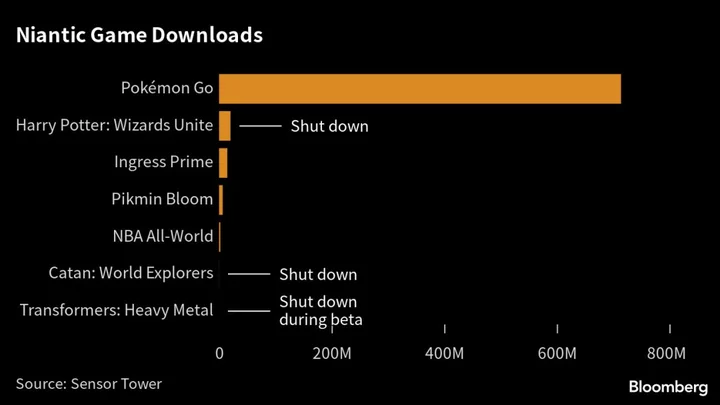
Pokemon Go Creator Niantic Suffers Metaverse Woes
Just a few years ago, tech evangelists were hailing Niantic Inc., the maker of the hit game Pokémon
2023-05-19 20:16

Job Cuts Are Mounting This Earnings Season. It’s a Warning for the Economy.
Oil’s run may be over amid three-month lows, consumer agency wants to supervise big fintech payment companies, and other news to start your day.
2023-11-08 19:58
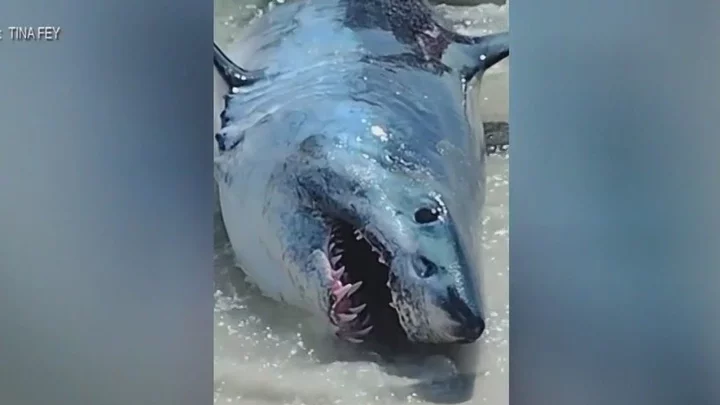

Great white sharks keep entering the twilight zone and experts are mystified
Great white sharks are displaying unprecedented behaviours, and experts can’t explain why. One of the ocean’s greatest apex predators has been entering the twilight zone way beneath the surface of the ocean, and far beneath the areas they normally feed in. The twilight zone, also referred to as the mesopelagic zone, is the area 200 to 1,000 metres down below the surface which is at least partly permeated by sunlight. The midnight zone, meanwhile, is found 1,000 to 3,000 metres down and is impenetrable to sunlight. Now, a new study published in the journal PNAS offered insight into the behaviours of 344 tagged predatory fish including great white sharks. Scientists would usually expect the creatures studied to dive to the deep scattering layer (DSL), which is full of small fish and other ocean life forms and therefore attracts more predators than other levels. However, there was also evidence that suggested predators dove down far deeper than the DSL, and scientists don’t know why. According to the research, great white sharks dive down to as deep as 1,128 metres. Camrin Braun is assistant scientist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and study lead. Braun told Live Science: "How, when, where they access the deep ocean certainly varies, but the clear anecdotal answer is that the deep ocean seems like an important habitat regardless of the predator species. It's clear there are good reasons for these animals to dive deep, otherwise why would they all do it? "There's good evidence for some species/situations in which diving deep is clearly for foraging," Braun added. "So that supported our expectation. However, we also find several cases where we can pretty definitively say the use of the deep ocean is not for feeding – or if it is it represents a totally different kind of predator-prey interaction or mysterious prey resource." The study could suggest that the twilight zone could be far more important to great white sharks and other predatory fish than previously thought. "If it turns out that there is indeed more biomass in the twilight zone than in all current marine capture fisheries combined then it's possible to imagine a kind of mesopelagic 'gold rush' to catch and use this biomass," Braun said. "There are many 'ifs' in this chain and many issues in making mesopelagic fishing feasible but it seems that biomass may be important for predators. Therefore, we really need to better quantify those links between predators and mesopelagic biomass before we can sustainably harvest/use those resources.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-11-22 23:26

SEC enforcement chief rejects criticism of crypto crackdown
By Chris Prentice NEW YORK A top U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) official on Friday rejected criticism
2023-06-17 04:26
You Might Like...

YouTube to prohibit false claims about cancer treatments under its medical misinformation policy

ChatGPT now has direct access to the internet

What Time Does Madden 24 Early Access Start?

Do Andrew Tate and Tristan Tate own 21M Bitcoin? Truth about Tate brothers' cryptocurrency worth $400M revealed

Micron Says Half of Sales Tied to China-HQ Clients at Risk
Japan eyes tax break for domestic EV battery, chip production - Nikkei

Indonesia Warns $20 Billion Climate Deal Looks Too Expensive

India Is Moving Forward With 28% Tax Levy on Online Gaming, Casinos
