
How to unblock Disney+ Hotstar for free
SAVE 49%: ExpressVPN is the best service for unblocking streaming sites. A one-year subscription to
2023-09-01 12:57

Leapsome Unveils New Startup Program to Empower Early-Stage Businesses with Intelligent People Enablement Tools
NEW YORK & BERLIN--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 20, 2023--
2023-07-20 20:15

Major breakthrough could soon allow us to actually use quantum computers, scientists say
Quantum computers might soon actually be useful, researchers have said after a new breakthrough. A new study showed that a quantum computer could be used for calculations that are beyond the capabilities of our current best classical – or non-quantum – computers. It means that the technology could soon be useful in practical applications, the researchers suggest. For years, quantum computing experts have been hopeful that the technology could allow for entirely new kinds of calculations, which might be useful across battery research, medicines and more. But the current versions are given to a host of problems, including the fact that they are prone to errors. Quantum computers need to be able to fix those errors more quickly than they accumulate. But even the best quantum computers have struggled to do so, meaning that practical use of the technology has remained beyond our grasp. New research from IBM showed that those errors could be mitigated, however, and a quantum computer could be used in ways that a classical computer could not. As such, the results “herald further opportunities for quantum processors to emulate physical systems that are far beyond the reach of conventional computers”, scientists away from the research say. Unlike many other similar breakthroughs – which focus on the extra speed that a quantum computer can provide – this new research focuses on the scale of the computer. Researchers used more 127 qubits, the equivalent of bits on a classical computer, to do research that classical computers do not have enough memory for. The breakthrough is described in a new paper, ‘Evidence for the use of quantum computing before fault tolerance’, published in Nature today. Read More Major finding boosts hope for finding alien life in our solar system Mother tells Congress about fearing her daughter was kidnapped after AI voice scam Battery breakthrough ‘offers 1,500 kilometre range from just 10 minutes of charging’
2023-06-14 23:57

SoftBank Group invests $65 million in UK AI firm - Nikkei
TOKYO SoftBank Group has resumed investment in new AI companies, investing $65 million in British firm Tractable, an
2023-07-18 18:19

How to unblock porn sites for free
TL;DR: Unblock porn sites with ProtonVPN. This popular VPN offers a free version with access
2023-06-01 12:28

Glastonbury festival-goers use data equivalent to 400 HD film downloads an hour
Glastonbury festival-goers used data equivalent to downloading the Rocket Man film in HD 400 times an hour for the entire five-day event, Vodafone has revealed. The festival’s “official connectivity partner” said 169 terabytes of data were consumed during the festival. The firm placed nine masts around the Worthy Farm site to cope with demand. Figures show 450 gigabytes of data were uploaded during Sir Elton John’s Sunday headline performance on the main Pyramid Stage. Over the course of the five-day event, some 20 terabytes of data were consumed at the biggest stage as the audience uploaded videos and pictures to social media. The Glastonbury app was downloaded 208,000 times, with more than 130,729 people using the “My Line-Up” feature, giving attendees reminders to get to pre-selected performances on time. Some 10,500 charging packs were sold through the event’s battery exchange scheme. Max Taylor, Vodafone’s UK chief commercial officer, said: “We are incredibly proud of our network team who boosted the network to its highest ever capacity in our first year as Official Connectivity Partner to Glastonbury. “We wanted to make sure that as many fans as possible could benefit from our reliable, award-winning network on site and we over-delivered on this promise. We can’t wait to bring even bigger and better things to Glastonbury next year.”
2023-06-29 22:48

Record-breaking sugar battery could supercharge transition to renewable energy
Scientists have used sugar to create a record-breaking battery capable of storing grid-scale energy for more than a year. The breakthrough could help speed up the transition to renewable energy sources, which require vast amounts of battery storage in order to avoid relying on fossil fuels to meet demand when solar or wind output is low. A team from the US Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) made the latest discovery while researching flow batteries, which use two liquid-filled chambers to produce an electrochemical reaction to store and release energy. Flow batteries have the potential to be scaled up to the size of football fields, capable of storing vast amounts of energy, however current methods for creating them rely on mined minerals that are difficult and costly to obtain. “This is a brand new approach to developing flow battery electrolyte,” said Wei Wang, a battery researcher who led the investigation into the new method. “We showed that you can use a totally different type of catalyst designed to accelerate energy conversion.” The researchers used a dissolved simple sugar called β-cyclodextrin, which is a derivative of starch, in order to boost their flow battery’s longevity and capacity. The system achieved 60 per cent more peak power than current methods, while also being capable of storing and releasing energy for more than a year continuously. The latest advance makes the next-generation battery design “a candidate for scale up”, according to the researchers. “We cannot always dig the Earth for new materials,” said Imre Gyuk, director of energy storage research at DOE’s Office of Electricity. “We need to develop a sustainable approach with chemicals that we can sythesize in large amounts – just like the pharmaceutical and the food industries.” A study detailing the research, titled ‘Proton-regulated alcohol oxidation for high-capacity ketone-based flow battery anolyte’, was published in the scientific journal Joule. Read More How tech could turn our homes into renewable energy power stations ‘Miracle material’ smashes solar panel efficiency threshold Mineral discovery could meet global battery and solar panel demand for next 100 years Why the Battle of the Boyne has made its way into your iPhone Twitter gets strange endorsement from Taliban over rival Threads
2023-07-11 18:53

Fresh Apple AirPods Deals Including AirPods Pro For $200
It took only two years from its announcement for the AirPods to become the most
2023-08-16 04:53

Kai Cenat reacts to BruceDropEmOff joining Kick after multiple Twitch bans: 'Fire announcement'
Kai Cenat is amazed after BruceDropEmOff's announcement, keep reading to know more
2023-06-02 19:21

What happened to Andrew Tate? Top G's training video shows disturbing whip scars on his back, fans say ‘true warrior mindset’
Andrew Tate believes that he has 'lived a life of pain to achieve the impossible' and that he struggles every day
2023-07-04 15:55

Nvidia sales hit record high as AI chip demand soars
Artificial intelligence chip giant Nvidia has seen its revenue double in the last quarter due to surging demands for AI technology. The company’s stock surged by nearly 10 per cent in after-hours trading on Wednesday after it posted a sales growth of 101 per cent year-over-year to $13.5bn for the three months ending in July. The company has been a pioneer in accelerated computing, popular among gamers for its GPU inventions that redefined computer graphics and sparked the growth of the PC gaming market. In recent years, the company ignited the era of modern AI and fuelled industrial digitalisation across markets. The American chipmaking giant makes processors behind generative AI, which form the backbone of chatbots like ChatGPT. “A new computing era has begun. Companies worldwide are transitioning from general-purpose to accelerated computing and generative AI,” said Jensen Huang, founder and chief of Nvidia in a statement. “The race is on to adopt generative AI,” he said. Since OpenAI’s ChatGPT came to prominence, many tech companies such as Google, Facebook and Snapchat have attempted to develop their own versions of the generative AI technology to better interact with users and offer human-like responses to queries. The revenue earned by the company over the last quarter is much stronger than the $11.2bn that Wall Street analysts expected. This surge in revenue was driven by the chipmaker’s data centre business that includes the production of AI chips. “During the quarter, major cloud service providers announced massive Nvidia H100 AI infrastructures. Leading enterprise IT system and software providers announced partnerships to bring Nvidia AI to every industry,” Mr Haung said. The company hopes for its earnings in the current quarter to be even greater, predicting a revenue of about $16bn. “Demand for our data center platform for AI is tremendous and broad-based across industries and customers.” Nvidia’s chief financial officer Colette Kress said on the company’s earnings call. “We believe global demand has returned to growth after last year’s slowdown,” Mr Kress said. Read More Google may soon roll out AI ‘personal life coach’ WhatsApp update gives users access to generative AI to create custom sticker art AI poses a profound threat – but could also help us in a variety of important ways, experts agree Jury finds teenager responsible for computer hacking spree Hackers ’emptied’ victims’ accounts and tried to blackmail GTA maker, court told Why India’s moon landing is about a lot more than exploring the lunar surface
2023-08-24 17:46

Power Apple products with this 3-in-1 cable
TL;DR: As of September 12, you can get a 3-in-1 USB-C Charging Cable for Apple
2023-09-12 17:18
You Might Like...

Woman captures herself sleep talking about work meetings

Ripple’s XRP Bucks Crypto Gloom After Latest Court Twist Sparks 8% Jump
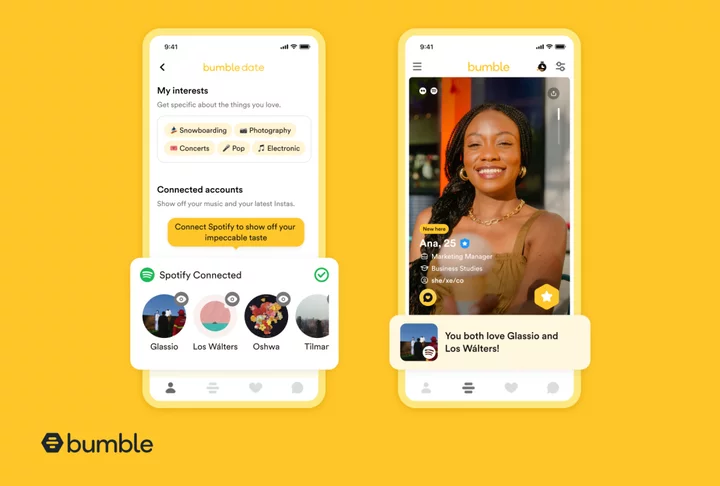
Bumble updates Spotify feature to encourage musical compatibility
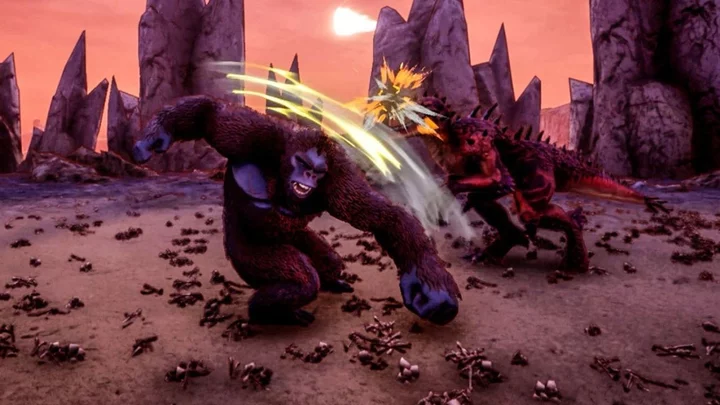

New King Kong game is being torn apart by the internet

LinkedIn lays off 668 employees in second cut this year

Logitech G Introduces the Newest Audio Innovation in Esports - The Logitech G PRO X 2 LIGHTSPEED Gaming Headset with PRO-G GRAPHENE Audio Drivers

This ice-free cooler can last up to 42 hours on one charge

xQc raises alarm over homophobic and misogynistic remarks by Sneako's young fanbase: 'What the f**k'
