Twitter adds video calling – and lets strangers ring you
Twitter has added video calling – and left it turned on by default. The feature is now being officially rolled out, Elon Musk confirmed. He said it was an “early version” of a tool he has been hinting at for a year. Video calls are part of Elon Musk’s plans to make Twitter, which he has renamed X, into the “everything app”, offering a wide array of different functionality. For now, video calls are limited to the iOS app, and appear to be rolling out slowly. But they are also switched on by default. The system means that all accounts are liable to receive calls from accounts you follow, or those run by people whose number you have in your address book. To be able to call someone, they must have sent at least one direct message to your account. Users have the option to change that setting, however, either to switch it off or to change who has the ability to make calls. From the direct message settings, users can either disable it entirely or change it so that they can receive calls from people in your address book, from people you follow, or from all “verified” users. Making phone calls is limited to premium subscribers, who pay the monthly subscription for what was once called Twitter Blue. It can be done by opening up the DM menu to start a conversation with someone. If the feature is enabled, then a phone icon should show within the direct message conversation, and tapping audio or video will start the relevant kind of call. Users will receive a notification that they are being called, and will get another telling them they missed the call if they do not pick up. Read More The Twitter app just went very, very strange TikTok prankster Mizzy arrested ‘on suspicion of perverting course of justice’ Study finds ‘deepfakes’ from Ukraine war undermining trust in conflict footage
2023-10-26 23:59
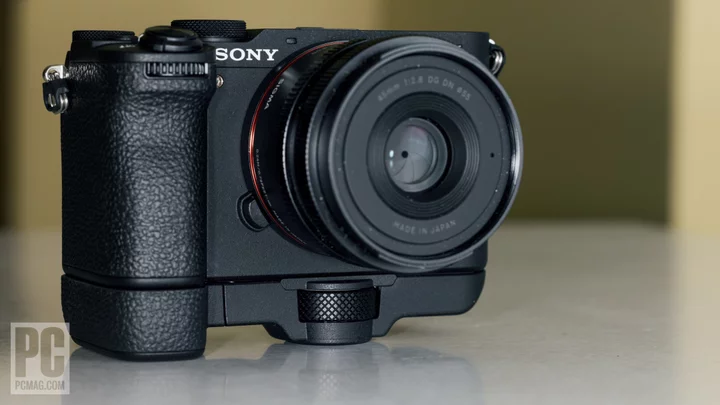

Sony a7CR Review
The full-frame Sony a7CR ($2,999.99, body only) squeezes the 60MP sensor and AI-assisted autofocus system
2023-08-29 22:54

IOC to explore Olympic eSports Games
The International Olympic Committee is looking at creating an Olympic eSports Games, IOC president Thomas Bach...
2023-10-15 00:47
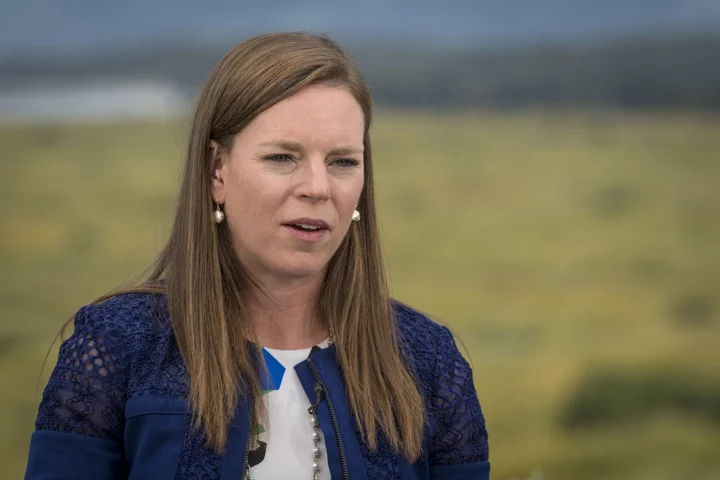

BOE’s Greene Sees Risk of 1970s-Style Crisis From Climate Change
Bank of England rate-setter Megan Greene said the economic impact of climate change could be on the scale
2023-09-29 01:20

US SEC asks judge to deny Coinbase motion to dismiss its lawsuit
By Hannah Lang and Chris Prentice The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) on Tuesday asked a federal
2023-10-04 07:53

From MrBeast to MKBHD: 5 YouTube content creators who spent money wisely by serving enormous audience
YouTube is great for content creators to show their creativity, and some who have made it big on the platform know how to spend their money wisely
2023-05-28 13:53

Eagle Eye Networks and Brivo Announce $192M Investment – One of the Largest Ever in Cloud Physical Security
AUSTIN, Texas & BETHESDA, Maryland--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 17, 2023--
2023-05-17 18:21

US layoffs halve in June as tech job cuts ease - report
Layoffs in the United States nearly halved in June from a month earlier as job cuts in the
2023-07-06 20:56
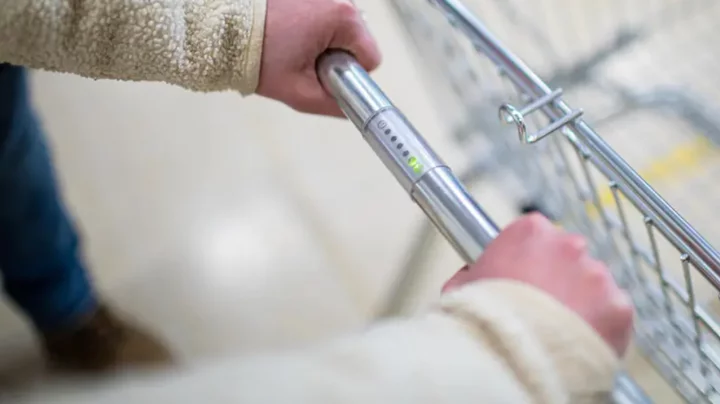

Heartbeat sensors on shopping trolleys 'could save lives', new study suggests
New findings have suggested that adding sensors to supermarket trolleys could save people’s lives. Scientists investigated whether installing electrocardiogram (ECG) sensors – designed to check the heart’s rhythm – on the handles of supermarket, trolleys could identify shoppers with atrial fibrillation, which causes an irregular and often abnormally fast heart rate. The sensors would detect heart conditions that put them at increased risk of stroke. The researchers said that over the course of two months, they identified 39 people who were unaware that they had the condition. Ian Jones, professor of cardiovascular nursing at Liverpool John Moores University, who led the study, said: “That’s 39 people at greater risk of stroke who received a cardiologist appointment.” He added: “This study shows the potential of taking health checks to the masses without disrupting daily routines.” It is estimated that around 1.5 million people in the UK have atrial fibrillation, contributing to one in five strokes. The condition is treatable, but at least another 270,000 people in the UK remain undiagnosed and unaware, according to the British Heart Foundation. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter There are wearable devices that can also spot irregular heartbeat but this would also require people to take responsibility and wear the device. Professor Jones said: “Nearly two-thirds of the shoppers we approached were happy to use a trolley, and the vast majority of those who declined were in a rush rather than wary of being monitored. “This shows that the concept is acceptable to most people and worth testing in a larger study.” He added: “Checking for atrial fibrillation while people do their regular shopping holds promise for preventing strokes and saving lives. “A crucial aspect is providing immediate access to a health professional who can explain the findings and refer patients on for confirmatory tests and medication if needed.” The findings were presented at ACNAP 2023 conference organised by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-25 16:59

KIOXIA Introduces New PCIe 5.0 SSDs for Enterprise and Data Center Infrastructures
SAN JOSE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 7, 2023--
2023-08-07 21:15
Anza Completes Separation from Borrego and Receives New Investment from Energy Capital Partners Led Consortium to Transform Solar and Storage Procurement
OAKLAND, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 17, 2023--
2023-05-17 18:28

How to Turn on Your Computer From Across the House With Wake-on-LAN
Ever wish you could wake your computer out of sleep mode without trudging over to
2023-08-17 05:24
You Might Like...

There’s a ‘lost continent’ which holiday makers have been visiting without knowing

Why is Adin Ross mad at Drake? What happened between them?

Getty asks London court to stop UK sales of Stability AI system

Matera Brings AI to Instant Payments, Acquires Brazilian AI Leader Cinnecta

As Temperatures Climb, Millions More People Face Food Insecurity

UFO hunter claims a giant spacecraft is being hidden under a major landmark
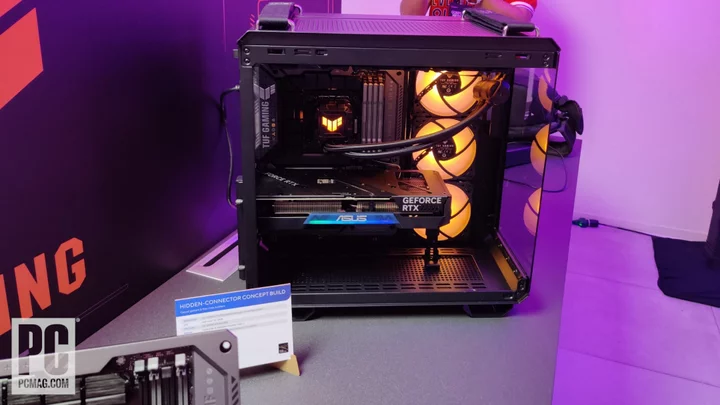

First Peek: Asus Demos a TUF Gaming Concept PC That Hides All the Cables

Kenya to Regulate Carbon Trade as Nations Seek More Benefits
