
California Issues Emergency Watch for Power Grid Amid Heat Wave
California’s main power grid operator issued an emergency watch notice for Tuesday evening as residents cranked up air
2023-07-26 12:15

China steps up response to US chip moves but economic reality limits how far
Beijing's restrictions on American chipmaker Micron in retaliation to sweeping US chip curbs marks a major step up in its response to Washington's pressure and could open the door for further...
2023-05-25 11:53

Paige Spiranac takes fans on trip down memory lane of her golf influencer career: 'It's been all worth it'
Paige Spiranac shared how she transformed her humble start as a collegiate golfer into the career of a golf influencer
2023-08-27 13:55
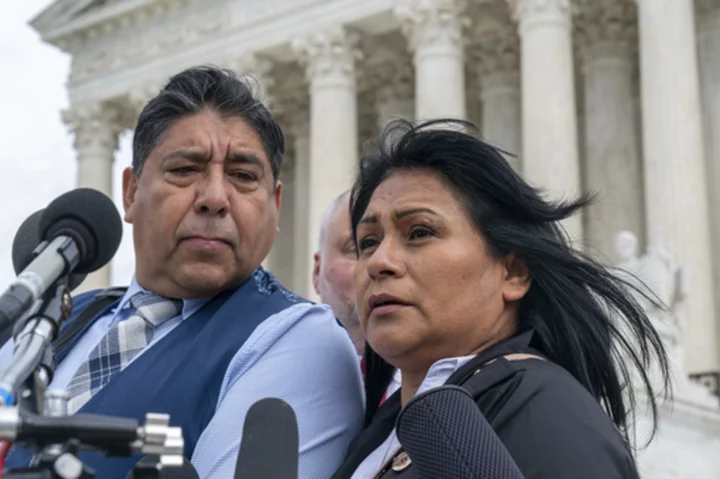

Supreme Court sidesteps challenge to internet companies’ broad protections from lawsuits
The Supreme Court has sidestepped a case against Google that might have allowed more lawsuits against social media companies
2023-05-18 23:17

Google earned $10 million by allowing misleading anti-abortion ads from 'fake clinics,' report says
Google has earned more than $10 million over the past two years by allowing misleading advertisements for "fake" abortion clinics that aim to stop women from having the procedure, according to an estimate from a report released Thursday from the non-profit Center for Countering Digital Hate.
2023-06-16 01:47
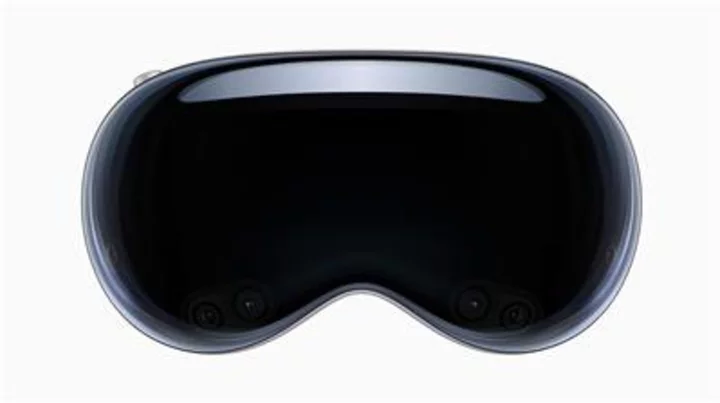

Introducing Apple Vision Pro: Apple’s first spatial computer
CUPERTINO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 5, 2023--
2023-06-06 03:18

Samsara Officially Named As A 2023 UK’s Best Workplace for Women™
LONDON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 20, 2023--
2023-07-20 21:28
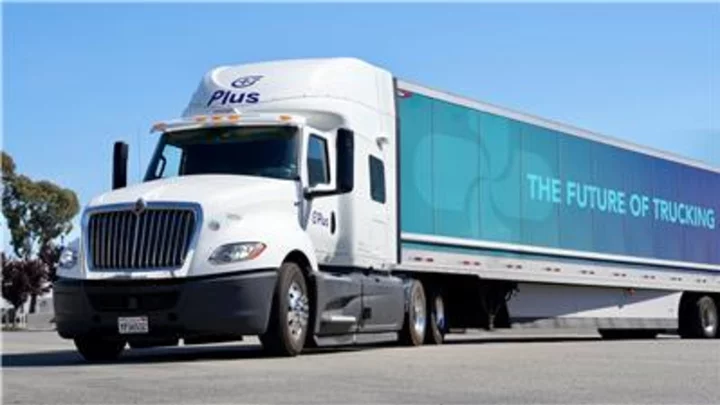

Luminar and Plus Partner for LiDAR and AI-Based Assisted Driving Software for Trucking
ORLANDO, Fla. & SANTA CLARA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 20:23

Fortnite Crew Pack December 2023 Offers This OG Remix Skin
The Fortnite Crew Pack December 2023 offers the Skull Scout skin, an OG remix of the Recon Expert and Skull Trooper, available on Nov. 30, 2023, at 8 p.m. ET.
2023-11-28 03:56

How to unblock YouTube Premium
SAVE 49%: Unblock YouTube Premium from anywhere in the world with a streaming-friendly VPN. A
2023-09-11 12:15

Eaton Invests More Than $500 Million in North American Manufacturing to Support Electrification, Energy Transition and Digitalization Across Industries
CLEVELAND--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 28, 2023--
2023-08-28 19:24

TurboTax is sending checks to 4.4 million customers as part of a $141 million settlement
Roughly 4.4 million people will soon receive checks from TurboTax, following a 50-state settlement accusing parent company Intuit for allegedly steering millions of low-income Americans away from free tax-filing services.
2023-05-09 22:54
You Might Like...

Here's All the Fortnite OG Bundles Coming to the Item Shop in November

Vanta Names Enterprise SaaS Leader Jeremy Epling as Chief Product Officer
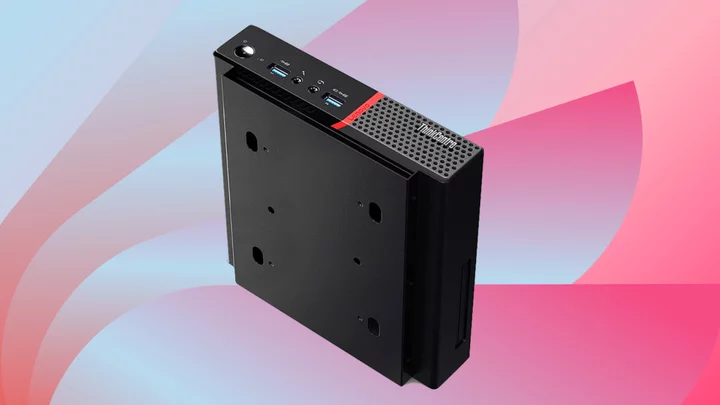

Get a refurbished Lenovo ThinkCentre Tiny for just $190
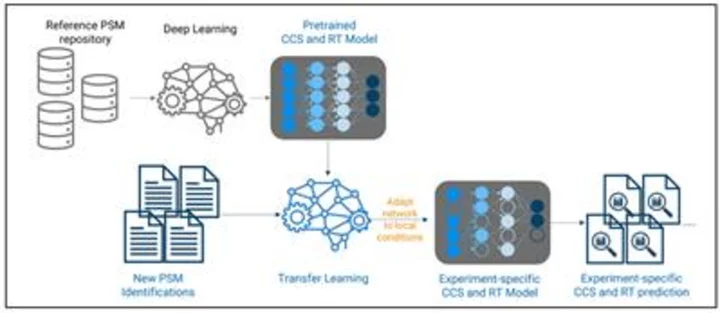
Bruker Introduces Novel 4D-Proteomics™ timsTOF® Capabilities

MrBeast leaves bizarre reply to Elon Musk's post about 'mind-blowing' reach of X, puzzled fans ask 'said what'

SOUTHTEC 2023 Programming Features Tooling U-SME Workforce Day, CESMII SMART Manufacturing Experience and Manufacturing USA’s Modern Makers

Claim Free FIFA 23 90+ Brazilian TOTS, TOTS Moments, Shapeshifters or Premium Shapeshifters Player

Air Force Starts Multibillion-Dollar Contest for New Fighter Jet
