
US takes on Google in landmark antitrust trial
Google faces its biggest ever legal challenge in a Washington court on Tuesday, as it fends off accusations from the US government that it acted unlawfully to build...
2023-09-10 10:51

X sues hate speech tracker over Twitter reports
X is suing a nonprofit group in US federal court over reports that hate speech has flourished at the platform...
2023-08-02 01:59

Bungie: Destiny 2 Hit by DDoS Attack Amid Weapons Glitch
Bungie had a wild start to the week and not in a good way. The
2023-09-22 07:24
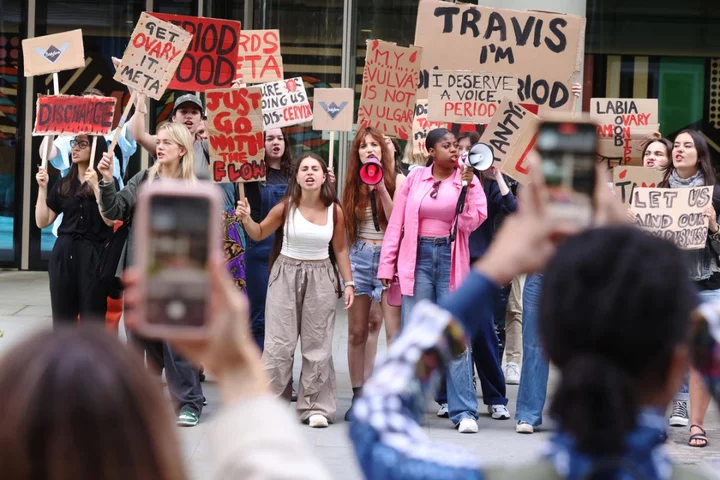

Meta rejects accusation of censorship of language around female body
Technology giant Meta has rejected an accusation of online censorship as protesters called for language around women’s bodies to be normalised. Demonstrators gathered outside the company’s London office in King’s Cross on Friday morning. She Oath, described as a female empowerment charity, joined representatives from period product firm Bodyform, which is running a campaign aimed at normalising use of words such as vagina, clitoris and vulva online. These are our bodies and we shouldn’t be shamed or cast into the shadows for what we naturally have to experience Brookmorgan Henry-Rennie, She Oath Bodyform said that since launching its campaign it has been “slapped with multiple violations of Meta’s ad policy – deeming their content as too sexual and labelling it with an 18+ warning”. It says menstrual health “shouldn’t be censored” and doing so makes “important subjects, that are already taboo, almost impossible to talk about”, affecting lives and health. But Meta said some adverts had been removed by mistake and had since been reinstated, and apologised for any confusion. The company said it has no blanket ban on words like menopause or vagina, adding that adverts are governed by a stricter set of policies “because they receive paid distribution to appear in people’s feeds”. She Oath’s founder Brookmorgan Henry-Rennie said: “We use our platform to educate, entertain and inform around subject matters like authentic confidence, women’s health and well-being. “So this shadow-banning is not just depriving trauma-experienced girls and women from gaining access to our resources, it’s putting them in further danger. These are our bodies and we shouldn’t be shamed or cast into the shadows for what we naturally have to experience. “If it wasn’t for Bodyform’s ads being banned, we wouldn’t have even realised that our posts were being deprioritised. “Meta really does need to do better.” The adverts were removed by mistake by our automated review systems and have since been reinstated. We apologise for any confusion caused Meta spokesperson Ruth Gresty, spokesperson for Bodyform, said: “It’s unfortunate but not surprising that our latest campaign, which calls out the unnecessary censorship of words commonly used to talk about, describe and define women’s bodies and their experiences, has been censored by some social media companies. “In doing so, these companies have simply underlined the need for campaigns of this nature that seek to break down the barriers that prevent women from being able to speak openly and confidently about their bodies. “We at Bodyform will not be deterred from our mission to make talking about the female body normal.” A spokesperson for Meta, which owns Facebook, said: “We want Facebook to be a place where people can express themselves and we are proud of the way our community uses the platform to have important and open conversations about women’s health. “The adverts were removed by mistake by our automated review systems and have since been reinstated. We apologise for any confusion caused.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live AI developing faster than laws aiming to regulate it, academic warns Facebook Marketplace is most complained-about online retail platforms UKRI announces £50 million to develop trustworthy and secure AI
2023-06-23 18:46

TikTok Signs Payments Pact With Advance Intelligence in Malaysia
TikTok’s e-commerce arm struck a partnership with Advance Intelligence Group, a financial technology startup, to expand its online
2023-07-21 08:48

Cloud Security is the Greatest Area of Concern for Cybersecurity Leaders According to EC-Council’s Certified CISO Hall of Fame Report 2023
TAMPA, Florida--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 1, 2023--
2023-06-01 21:59
“i-PRO” a Global Leader of Advanced Sensing Company Joins NICE Alliance
TOKYO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 18, 2023--
2023-07-19 08:26

How to get the AirPods Max for nearly $200 less than their usual price
Save 33%: As of July 17, you can grab a factory reconditioned (aka basically new)
2023-07-18 00:50

How to restart your iPhone
Restarting your iPhone is as simple as powering it off and turning it back on
2023-07-15 17:52
RingCentral Unveils RingCX – A Native, Intelligent Contact Center Solution
BELMONT, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 7, 2023--
2023-08-08 04:57

National Bank to buy SVB's Canada loan book to boost tech sector lending
By Nivedita Balu and Jaiveer Shekhawat (Reuters) -National Bank of Canada said on Tuesday it has agreed to buy collapsed
2023-08-02 04:54

Elon Musk’s X ordered to pay over $1m in legal fees for laid off Twitter execs
Elon Musk’s X has been ordered by a judge to pay $1.1m in legal fees to its laid off former executives. Since Mr Musk’s takeover of X, the company formerly known as Twitter, the multibillionaire and X have faced a number of lawsuits. These include suits over the firm’s failure to pay its vendors and delays in paying rent for its office premises, as well as former employees suing Twitter alleging they were laid off without adequate notice. On Tuesday, Delaware Chancery Court judge Kathaleen St J McCormick ruled in favour of the company’s ex-chief Parag Agrawal and said X must pay $1.1m in legal fees linked with probes of the platform during Mr Musk’s 2022 takeover, Bloomberg first reported. After buying out the microblogging platform in November last year, the Tesla titan fired Mr Agrawal and Twitter’s then-lead policy officer Vijaya Gadde as well as a number of other executives. Mr Agrawal and Ms Gadde then sued Twitter/X for failing to pay for their legal bills, including for the latter’s appearance before the House Committee on Oversight and Reform. The lawsuit filing alleged the company paid only about $600,000 of what it owes, withholding $1.1m in fees for its lawyers’ work representing the former executives in an inquiry on the role played by social media on US elections. The filing alleged Twitter/X “breached the agreements and contravened the bylaws” by not paying the former staff. The latest ruling by the Delaware court judge observed that X “violated its duties to cover legal expenses generated by their work for the company”. While acknowledging that $1.1m is a lot of money, the judge still ruled in favour of the former Twitter executives. “I have reviewed the amount in question, and although it is high and probably higher than most humans would like to pay, it’s not unreasonable,” judge McCormick was quoted as saying by Bloomberg. X did not immediately respond to The Independent’s request for comment. The company is also being sued over its rebrand to X by an ad agency also named X, alleging the social media platform’s new name violates Florida common law because of “unfair competition and trademark and service mark infringement”. Read More Elon Musk’s mockery of Ukraine president Volodymyr Zelensky ‘unhelpful’ Elon Musk’s X Corp sued by another social network company named X ‘Reckless’ Elon Musk hit with $1m lawsuit for accusing student of being in Proud Boys ‘false flag’ attack Elon Musk’s X Corp sued by another social network company named X Elon Musk to live stream himself gaming on X in ‘everything app’ bid Musk confirms he is cutting election integrity staff from X/Twitter ahead of 2024
2023-10-04 12:47
You Might Like...
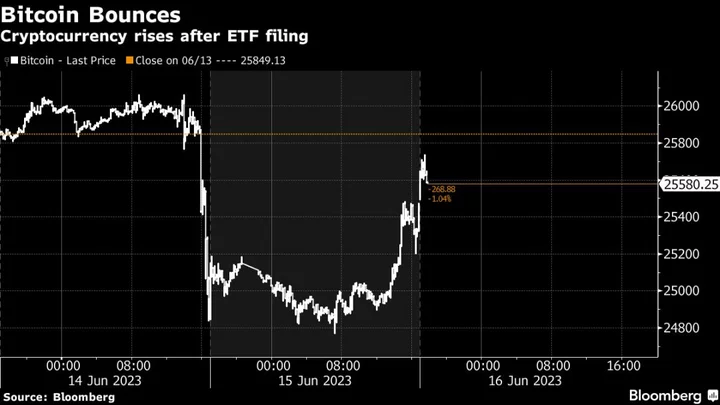
BlackRock Tries for Spot-Bitcoin ETF With Fresh Filing

US podcast misinformation goes largely unchecked

Pokimane: Does Twitch star wear fake teeth? Here's what we know

Save $50 on the noise-canceling Bose Quiet Comfort II earbuds at Amazon

The best Apple rumours confirmed in 2023 so far – and 4 we'd still love to see happen

Clarify Health Appoints Doug Klinger and Mary Lantin to Board of Directors

Quizlet Review

Get a 3-month stackable subscription to the entire Adobe Creative Cloud Suite for under $30
