Top TikTok exec and public face of company in US is stepping down
TikTok's chief operating officer Vanessa Pappas is leaving the company, according to an internal memo obtained by CNN, after spending several tumultuous years as its top public advocate and a champion of TikTok creators in the face of accusations the platform poses a national security risk.
2023-06-23 01:51

Amazon Basics Low-Profile Wired USB Keyboard Review
The best productivity keyboard PCMag has tested is the Razer Pro Type Ultra, closely followed
2023-06-28 07:20

Debunking the Newest Titanfall 3 Rumor Trailer
The newest Titanfall 3 rumor trailer is likely not backed by Respawn Entertainment and EA, debunking the global reveal date of Oct. 27.
2023-10-12 03:46

Score fitness equipment on sale thanks to early Prime Day deals and Fourth of July sales
UPDATE: Jun. 30, 2023, 3:45 p.m. EDT This list has been updated with the latest
2023-07-01 04:23

Microsoft Posts Tepid Sales Growth as Cloud Business Slows
Microsoft Corp. reported tepid fourth-quarter sales growth, held back by decelerating demand for cloud-computing services while the software
2023-07-26 04:56

Singapore-based Deeptech Startup Zero-Error Systems (ZES) Raises USD $7.5M in Oversubscribed Series A
SINGAPORE--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 12, 2023--
2023-06-13 07:24

Doctor reveals most dangerous sex position which ‘cause penis fractures’
An NHS doctor and TikTok star has revealed the most dangerous sex position – which he says is the cause of 50% of penis fractures. Dr Karan Rajan, a surgical doctor, shares his experience and knowledge with his 5.1 million followers on TikTok. In a video which has recently gone viral, Dr Karan told his followers about the sex position he thinks is most likely to lead to a hospital visit. He gives the title to the reverse cowgirl, as if there is any erratic thrusting during intercourse or if the two parties are not in sync, the penis can slip out and be crushed by their partner's pubic bone, causing a fracture. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Although the penis is boneless, the word 'fracture' is used to describe a tear in the tunica albuginea - a piece of fibrous tissue that connects the framework of the testis and allows the penis to enlarge during an erection. Patients who suffer from a ‘penile fracture’ and don’t have treatment, are usually left with erectile dysfunction, scarring and a permanent curvature of the penis for the rest of their lives. Dr Karan finished his educational video with a warning that over-enthusiastic sex, can lead to your penis really looking like an aubergine. @dr.karanr Reply to @budsfn the one with the broken ? #schoolwithdrkaran #learnontiktok #doctor #storytime The popular clip was posted back in 2021 but has recently gone viral, garnering millions of views and racking up 411,000 likes. Many of Dr Karan’s followers were saddened by the educational video, with one saying: “This is my favourite position,” followed by a sad face emoji. Someone else commented: “They can just break, did I hear...well now I can finally take revenge." Another viewer said: “My husband is now scared to come near me because of that.” A fourth added: “But that’s the best position." Dr Karan answered people who wanted evidence for these claims and said: “Men coming to the emergency room with this issue.” Some people were rather concerned, and one asked: “Just to clarify, by breaking it, will it look swollen and bigger? How long will this swelling last? Asking for a friend.” Another person wrote: “I heard mine crack from this position once." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-25 19:15

Hurricane Otis Lashes Mexico After Landfall Near Acapulco
Hurricane Otis’s top winds are weakening with its move across southern Mexico, drenching the region with flooding rains
2023-10-25 21:21
Chinese artists boycott big social media platform over AI-generated images
Artists across China are boycotting one of the country's biggest social media platforms over complaints about its AI image generation tool.
2023-09-29 06:24
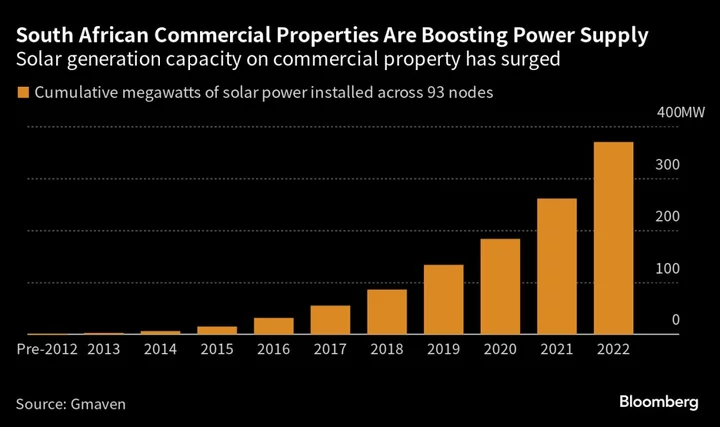
Offices, Shops Could Hold Answers to South Africa’s Power Woes
South Africa’s commercial property industry has the potential to ease the country’s power crisis, with enough roof space
2023-06-20 18:47

'Is Amouranth still getting forced by her husband?': Concerned fans seek clarity about ASMR Queen's relationship status
Amouranth once broke down during a live stream and claimed that her husband had threatened to kill her dogs and steal all their money
2023-06-25 20:25

Sao Tome and Principe media guide
An overview of the media in Sao Tome and Principe, including links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-07-20 00:47
You Might Like...

Broadcom's $61 billion deal to buy VMware gets cleared by European Union regulators
Elon Musk's 'purge' announcement sparks backlash from bereaved families including Andrew Tate

Big Tech Earnings Are Being Punished. Will the Bad Mood Spread to Amazon?

The tech that could make the iPhone 15 last hours longer – and change phones forever

Minnesota lawmakers bolster quota protections for warehouse workers

Cherre Recognized As “Overall Data Management Platform Of The Year” By PropTech Breakthrough

For captioning, humans are still the key to accessible, AI-driven tech
'Black Lives Matter' coffee T-shirt sparks outrage on TikTok
