
'Diablo IV' is almost here. What to know about the video game's coming release
The release of “Diablo IV” is right around the corner
2023-06-02 02:26

Germany Must Be Able to Run Budget Deficits, Ifo’s Fuest Says
The German government can’t manage without deficits if it wants to fulfill its investment and climate ambitions, according
2023-11-24 18:59
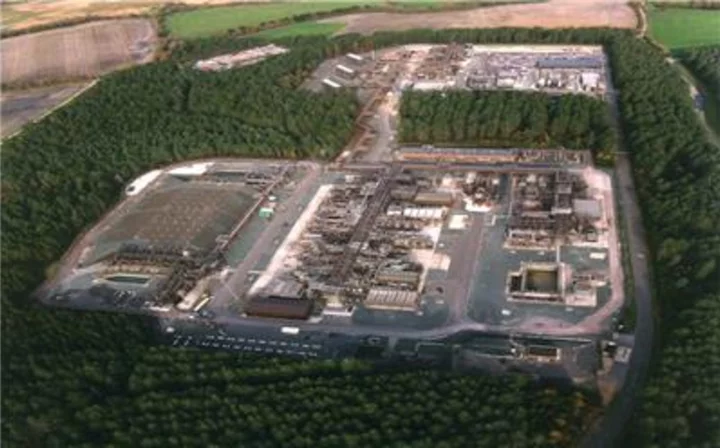

Bloom Energy, Perenco to Deploy Solid Oxide Fuel Cells in the United Kingdom
SAN JOSE, Calif. & LONDON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 7, 2023--
2023-06-07 19:20

Why are fans calling Paige Spiranac 'Golf Mommy'? TikTok star's Q&A session takes a fun turn
Paige Spiranac had a fun Q&A session with her fans recently during which they bestowed the nickname on her
2023-07-21 15:46

Apple Mac Studio (M2 Ultra, 2023) Review
With its new, more-powerful-than-ever M2 Ultra processor, Apple has not one but two flagship examples
2023-06-13 01:51

Amazon just revealed the exact dates for Prime Day 2023
Amazon's flagship Prime Day sale may not be as singular as it once was, but
2023-06-21 20:54
Sierra Space and BioServe Space Technologies to Demonstrate In-Space Stem Cell Production to Better Treat Cancer Patients on Earth
LOUISVILLE, Colo.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 2, 2023--
2023-08-02 20:29

Twitter challenger Threads struggles for traction
After a wildly successful first few days, Threads popularity has waned in the weeks since Meta launched its challenge to Twitter, which...
2023-07-23 12:28
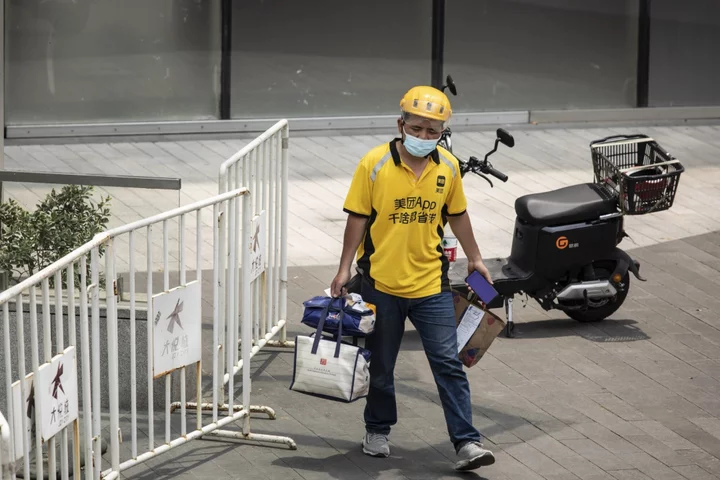

Meituan Planning Hong Kong Debut as Soon as Monday, Sources Say
Meituan is set to launch a sister app in Hong Kong as soon as Monday, taking the world’s
2023-05-18 18:55
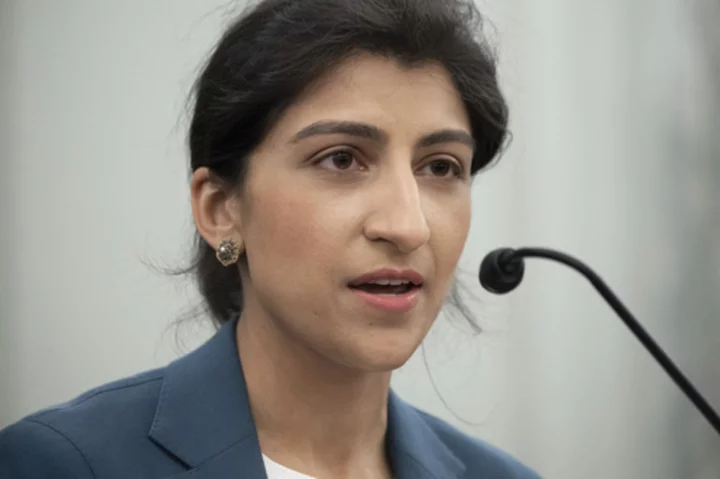

House Republicans interrogate FTC's Khan over ethics, antitrust issues
House Republicans who say the Federal Trade Commission has been overzealous and politicized under President Joe Biden are interrogating agency head Lina Khan
2023-07-13 22:51

Three Top Rated Awards from TrustRadius Confirms Kofax Power PDF as the Industry Leading PDF Editor
IRVINE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 23, 2023--
2023-05-23 20:17

Briton Admits to Twitter Hack That Hijacked Celebrity Accounts
A British man has admitted to his involvement in one of the most high-profile social media hacks, a
2023-05-10 09:48
You Might Like...
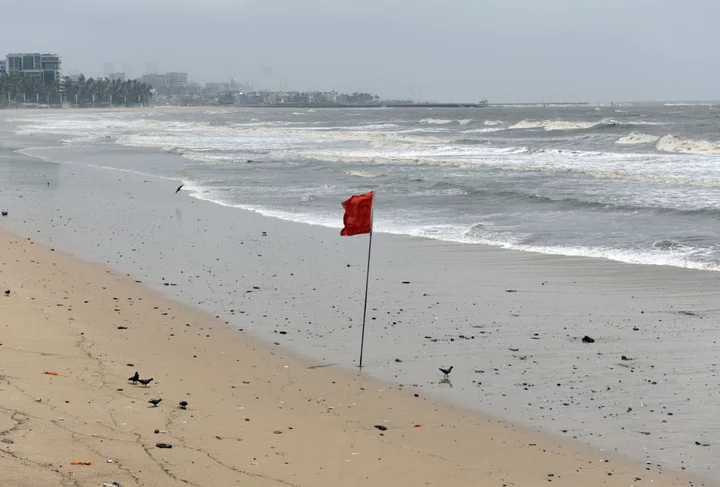

Texas Bakes in Heat, Cyclone Heads for Pakistan: Weather Watch

Get extended 30-day free trials of selected Prime Video channels this Prime Day

Bild Expo Is Live: Join Us at Gear Expo for New Product Announcements and Educational Presentation

ICO seeks permission to appeal against Clearview AI tribunal ruling
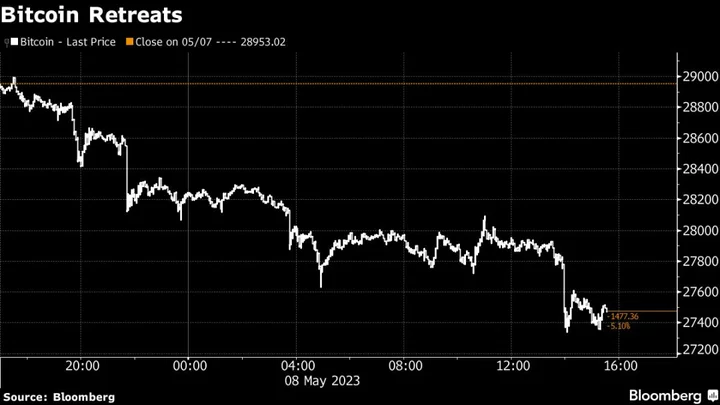
Memecoin Lead Crypto Declines After Weighing on Bitcoin Fees
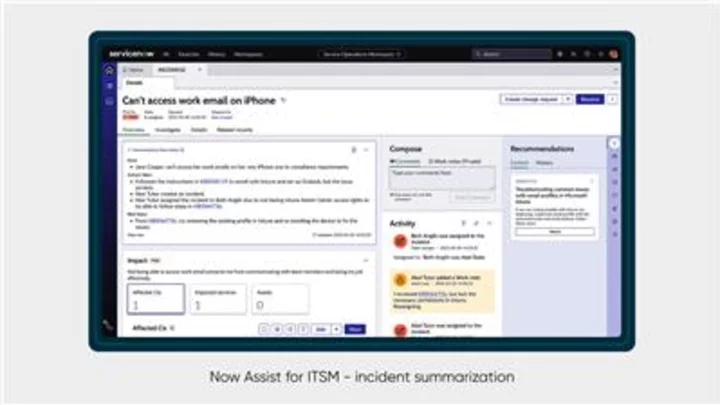
ServiceNow Launches Now Assist for ITSM, CSM, HRSD, and Creator to Embed Generative AI Across All Workflows on the Now Platform

It's Real! Lenovo Legion Go Gaming Handheld Images Leak

Microsoft Teams down: Office chat app not working in the middle of the working day
