
Legendary Sequel to Award-Winning Indie Game, Do Not Feed The Monkeys 2099, Now Available on Steam, coming to Nintendo Switch In Q3 2023
MADRID--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 25, 2023--
2023-05-25 22:24

Exclusive: 42% of CEOs say AI could destroy humanity in five to ten years
Many top business leaders are seriously worried that artificial intelligence could pose an existential threat to humanity in the not-too-distant future.
2023-06-15 01:53

Police chief calls for parents to be made accountable over social media crazes
Parents should be held accountable for the actions of children taking part in criminal social media crazes, the chairwoman of the Association of Police and Crime Commissioners (APCC) has said. Donna Jones said she believes parents could be fined over the behaviour of youngsters who take part in incidents such as the mass looting seen in London’s Oxford Street last week. She said it is a sign of “societal breakdown” and parents should be disciplining their children and teaching them that such acts are “morally abhorrent” to prevent further incidents. The Hampshire Police and Crime Commissioner also highlighted a craze in Southampton in which a “handful” of 15 to 17-year-olds took paracetamol to see who could stay in hospital the longest. The former magistrate told the PA news agency: “This is a real indication of societal breakdown. “This has not just suddenly appeared from nowhere. We’ve seen the warning signs of this coming for a really long time. We know these type of incidents are happening in America, and what happens in America very often gets here within a 12-month period. “Hundreds of young people rampaging through London shops, which are putting their security shutters down… You know, this is Britain in 2023. “This is incredibly worrying, and somebody needs to call it out. The draw on police resources is wholly unacceptable APCC chairwoman Donna Jones “The Home Secretary has said this has got to stop, it’s not good enough. I support her in that but I’m going one step further to say the draw on police resources is wholly unacceptable. “This is mindless vandalism, and it’s also criminal activity in terms of shoplifting and theft, looting, mass looting. “This is taking away police hours from operational policing that they should be doing to keep genuine people that need protecting safe. “We need to send a clear message – this is not acceptable and the parents need to be held accountable.” Ms Jones said parents could be forced to pay the fines for the criminal behaviour of their children under the age of 16, or under 18 if in full-time education. It's criminal, and morally it's also an abhorrent thing to do APCC chairwoman Donna Jones She added: “There have to be formal sanctions taken. We also have to call out the lack of discipline – parents need to be parenting their children and teaching them right from wrong. “Any parent or guardian of a young person who believes that they were in central London last week and could have been involved with that should be sitting down with that young person, having a really strong conversation with them about exactly what they have done, how it’s completely unacceptable. “It’s criminal, and morally it’s also an abhorrent thing to do. That’s certainly what I would be doing if it was my children. “And I’d like to think that’s what all decent good parents and guardians of young people should be doing, otherwise this is never going to stop.” Ms Jones also called on social media companies such as TikTok to investigate and crack down on posts orchestrating flashmobs which encourage criminal behaviour or explain publicly what action they are already taking. TikTok has been approached for comment. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Hackers ’emptied’ victims’ accounts and tried to blackmail GTA maker, court told AI can predict Parkinson’s subtype with up to 95% accuracy, study suggests Oxford scientists find no evidence to suggest Facebook not good for wellbeing
2023-08-15 17:17

Amazon Settles FTC Claims Ring Doorbell Spied on Users
Amazon.com Inc.’s Ring unit agreed to pay $5.8 million to settle Federal Trade Commission allegations Wednesday its doorbell
2023-06-01 02:48

AVG AntiVirus for Mac Review
Longtime Mac aficionados may miss the old days when “everyone knew” that Macs didn’t need
2023-05-26 23:54

Ripple Token Is Security in Institutional Sales, Judge Says
A federal judge ruled that the Ripple Labs Inc. token is a security when sold to institutional investors
2023-07-14 00:22
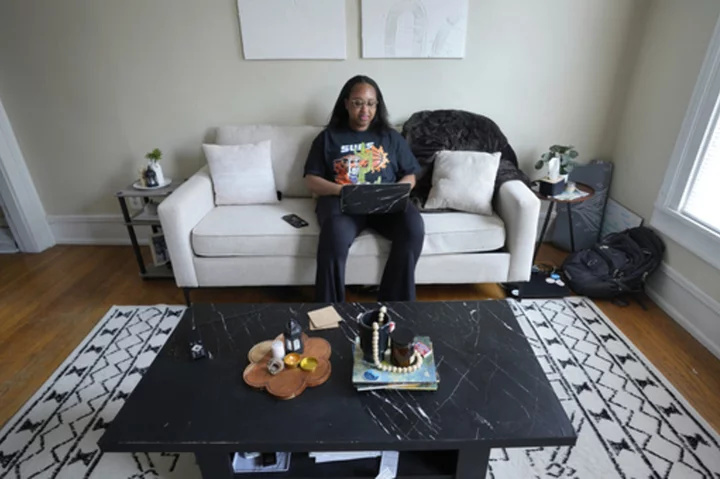

Supreme Court's affirmative action ruling leaves colleges looking for new ways to promote diversity
The Supreme Court has sent shockwaves through higher education with a landmark decision that struck down affirmative action and left colleges across the nation searching for new ways to promote student diversity
2023-06-30 12:46
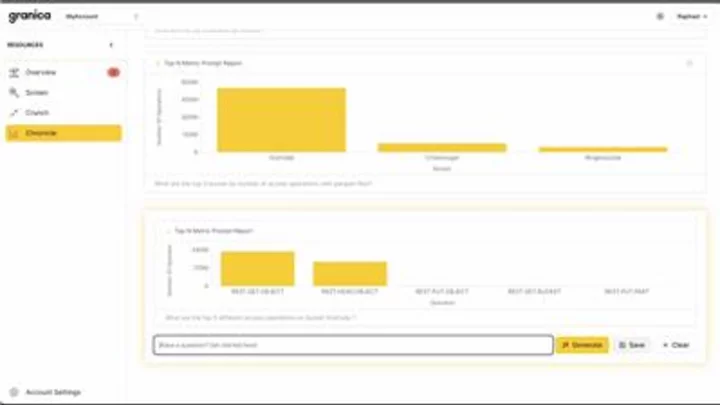
Granica Introduces Chronicle AI for Deep Data Visibility for Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage Customers
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 14, 2023--
2023-09-14 21:20

Enhance your car's interior with this wireless car display for $105
TL;DR: As of September 12, you can get a 9" wireless heads-up car display with
2023-09-12 17:22

How to Get Mew in Pokémon Scarlet and Violet
A new event in Pokémon Scarlet and Violet lets you have your very own Mew. Here's how to get him.
2023-08-10 05:21

Using banana skins as an ingredient has unexpected benefits
A study last year found that every time you throw away a banana peel, you're missing out on a great snack. The study, published in ACS Food Science & Technology, found that if banana peels are blanched, dried, and ground into a flour, they can be turned into baked goods that taste just as good as wheat-based products. And it turns out it's actually really food for you. Consuming products made from banana peel means you consume minerals and cancer-fighting minerals. Sugar cookies that were enriched with banana peels not only tasted the same as peel-free sugar cookies, but contained much more fibre, magnesium, potassium, and antioxidant compounds. In 2021, a study on banana peel cake found the yellow skin of the fruit provided a natural food colour as well as a nutritional boost. Whilst a 2016 study found that substituting up to 10 per cent of wheat flower with banana peel flour can enrich baked bread with higher protein, carbohydrate, and fat contents. Not only is it a healthy food option, it also helps reduce food waste! And the same goes for other fruits too, such a mango skin, what was found to boost a cake's antioxidant properties and improve its flavour. Just make sure to add the right amount of banana peel to your bakes and makes. Adding too much banana peel flour did result in the study's cookies going somewhat brown and hard, possibly from all the extra fibre. 7.5 percent of banana peel flour seems to be the sweet spot, with the texture and taste hitting an appealing balance. So maybe reconsider next time you go to thrown a banana skin away. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel
2023-12-01 00:55

Brenmiller to Unveil Next-Generation Thermal Energy Storage System—the bGen™ ZERO for Heat Electrification and Industrial Sector Decarbonization: Register for Live Presentation to be held August 9, 2023
ROSH HA’AYIN, Israel--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 4, 2023--
2023-08-04 20:21
You Might Like...
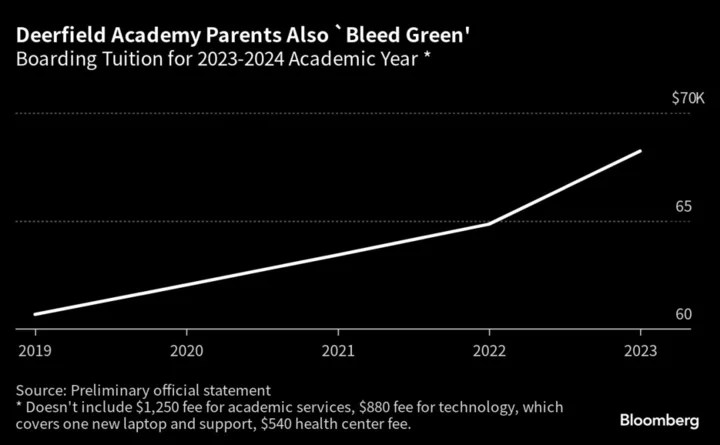
Deerfield Academy Is Raising $89 Million to Build a Dining Hall
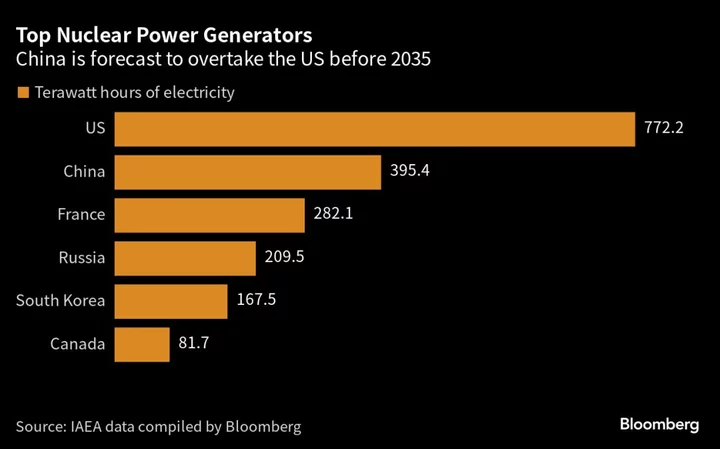
Nuclear Industry Needs More State Money, Officials Warn
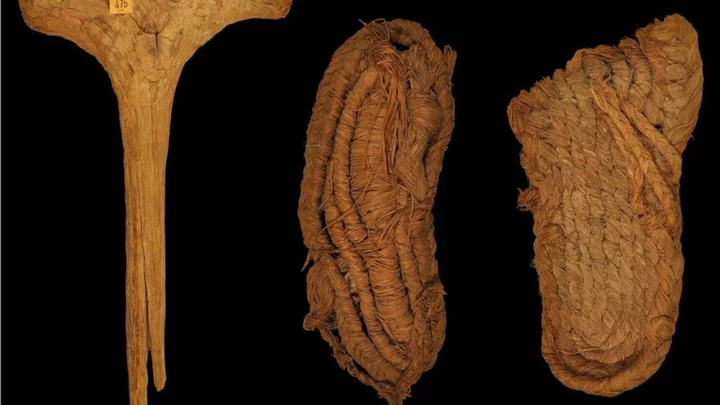

Prehistoric footwear dating back 6,200 years discovered in a Spanish cave
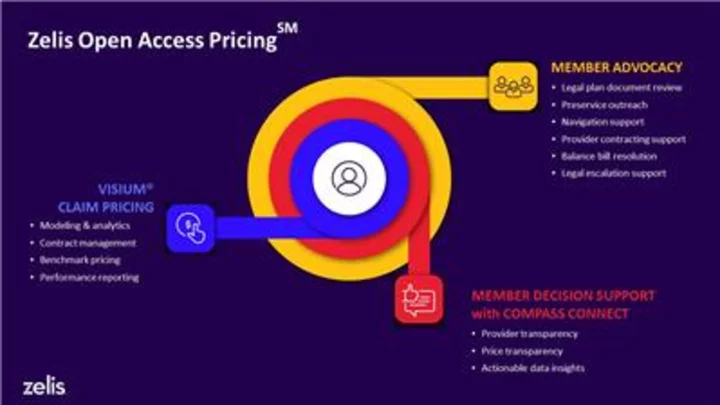
Zelis® Launches Reference-Based Pricing Solution that Prioritizes Members, Aligns Member Experience and Cost Containment

China's regulator says finds serious security issues in US Micron Technology's products

Ripped From the Headlines: Where to Stream the Best Tech Dramas

Microsoft to take non-voting, observer position on OpenAI's board

Australia sees wheat, barley output dropping by a third next year
